Data / Module Relationships
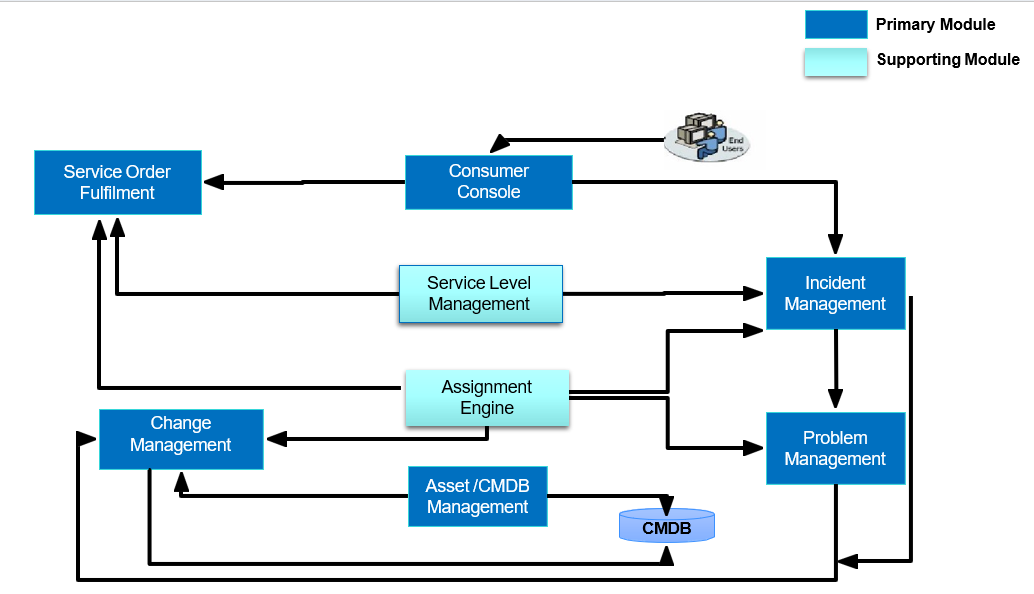
This diagram illustrates the interaction between primary modules and supporting modules within the IT Service Management (ITSM) ecosystem. Together, they ensure smooth service delivery, incident handling, problem resolution, and change management.
- End Users and Consumer Console
- End Users interact with the ITSM system through the Consumer Console.
- This is the entry point for raising incidents, requesting services, or tracking progress.
- From here, requests are routed to the appropriate ITSM modules for action.
- Service Order Fulfilment
- Service requests raised by users are passed from the Consumer Console to the Service Order Fulfilment module.
- This module ensures that requests are processed and delivered to the user.
- It works closely with other modules like Change Management and Asset/CMDB to complete requests.
- Incident Management
- The Incident Management module handles tickets when something is broken or not working.
- It receives requests directly from the Consumer Console and interacts with Service Level Management and Assignment Engine to ensure proper prioritization and resolution.
- If recurring issues are detected, they can be escalated to Problem Management.
- Problem Management
- Problem Management investigates the root cause of incidents.
- It works hand-in-hand with Incident Management to prevent repeated issues.
- Identified problems may trigger Change Management if fixes require modifications to services, systems, or configurations.
- Change Management
- Change Management governs changes to IT systems, ensuring they are properly assessed, approved, and implemented.
- It receives input from Problem Management (for root cause fixes) and Service Order Fulfilment (for new service requests).
- Changes often require updates to the Asset/CMDB Management system.
- Asset/CMDB Management
- The Asset and Configuration Management Database (CMDB) serves as the central repository of all configuration items (CIs).
- It supports modules like Change Management, Incident Management, and Problem Management by providing accurate information about assets, dependencies, and relationships.
- Supporting Modules
- Service Level Management (SLM): Ensures that incidents, problems, and service requests meet defined service level agreements (SLAs). It monitors compliance and escalates breaches.
- Assignment Engine: Automatically assigns work items (incidents, problems, service requests) to the appropriate teams based on rules, workload, and expertise.
Summary of Flow
- End users raise requests through the Consumer Console.
- Requests flow to Service Order Fulfilment, Incident Management, or directly into Problem/Change Management depending on the type.
- Supporting modules like Service Level Management and Assignment Engine ensure requests are routed correctly and resolved within agreed timelines.
- The CMDB underpins all modules by providing accurate configuration and asset data.
Together, these modules create an integrated ITSM ecosystem that ensures efficient service delivery, quick issue resolution, and proactive management of IT infrastructure.