Branches in marketing activities
Here is an example of aweb activity that contains a branch element that creates three paths; in this case, each path displays a different ad:
Activities can have multiple branch elements, and each branch element can have two or more paths. Additionally, branch elements can be nested within other branch elements, up to a maximum of four consecutive branch elements. You can add branch elements to both web and dialog activities.
When you set up the branch element in your activity, you must choose one of the following three branch types, depending on how you want the server to assign paths to customers:
- First path for which the customer qualifies
- All paths for which the customer qualifies
- Random path
First path for which the customer qualifies
Choose this branch type if you want to target different customer groups with personalized marketing actions within the same activity. When the activity is triggered, each customer will experience the first path for which he or she qualifies, and no other paths.
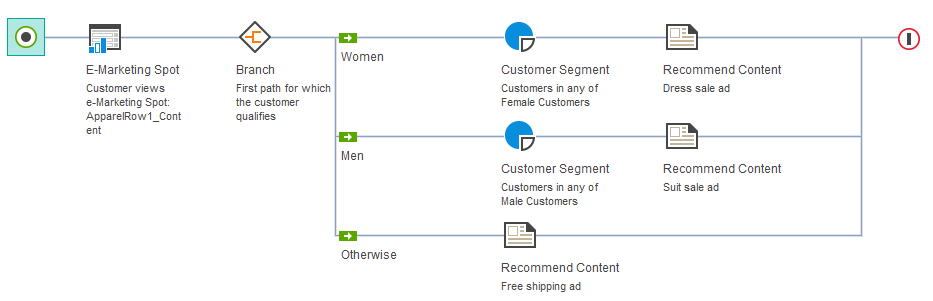
The web activity example at the beginning of this topic uses this type of branch element to display one of three possible ads in the e-Marketing Spot on the Apparel category page, depending upon who is looking at the page:
- Customers in the Female customer segment will see an ad for dresses.
- Customers in the Male customer segment will see an ad for suits.
- Customers who are not part of either customer segment will see a generic ad for free shipping.
When the activity is triggered, the server evaluates the customer against the targets at the beginning of each path, starting with the first path and working down to the last path. As soon as the customer qualifies for the targets in a path, he or she proceeds down the path and experiences the action. If there are multiple targets on a path, the customer must qualify for all targets on that path.
- Typically, all paths following the branch element should begin
with one or more targets, followed by one or more actions, except
for the last path (the
otherwise
path). - The last path should include one or more actions, but placing a target before the action is optional. In many cases, you might want to use the last path as a catch-all for customers who do not qualify for any of the previous paths; excluding a target achieves this result. In the previous example, the path labeled Otherwise does not have a target; this ensures that any customers who do not qualify for the first two paths will automatically qualify for the Otherwise path.
- A customer experiences only one path, that is, the first one for which he or she qualifies. This is an important distinction between this branch type and the following type, All paths for which the customer qualifies.
All paths for which the customer qualifies
Choose this branch type if you want customers experiencing the activity to be evaluated for each path independently of the other paths. In this scenario, a customer can potentially experience all the paths in the activity as long as he or she meets the requirements of the targets at the beginning of each path.
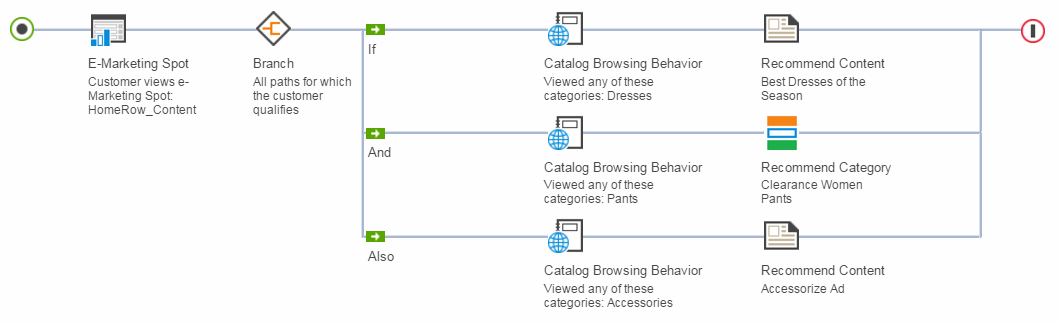
- Customers who have browsed the Dresses category will see content with a link to the "Best Dresses of the Season".
- Customers who have browsed the Women Pants category will see a recommendation for the Clearance Women Pants category.
- Customers who have browsed the Accessories category will see the content advertising "Accessorize Ad".
- Customers who have browsed all three of the target categories will see all three types of content in the e-Marketing Spot at the same time.
- Customers who have not browsed any of the target categories will see nothing in the e-Marketing Spot (unless there is default content or another Web activity scheduled for this spot).
- Typically, all paths following the branch element should begin with one or more targets, followed by one or more actions.
- Using this branch type makes sense if:
- You have an e-Marketing Spot that can display multiple categories, catalog entries or content at the same time.
- You want to use customer targets that are not mutually exclusive. In the previous example, all three paths use the Catalog Browsing Behavior target; one customer could potentially browse all three categories.
If neither of the above is true, consider using the First path for which the customer qualifies branch type instead. Or, if your e-Marketing Spot can display only one piece of data at a time, consider using the Random path branch type.
Random path
Choose this branch type if you want the server to randomly assign a path in the activity to a customer based on a percentage you assign to each path. When the activity is triggered, each customer will experience one of the paths.
Here is an example of a Web activity that includes a Random path branch type; in this case, each path displays a different advertisement.
When a customer views the e-Marketing Spot on the category display page, display Advertisement A to 50% of customers and display Advertisement B to the other 50%.
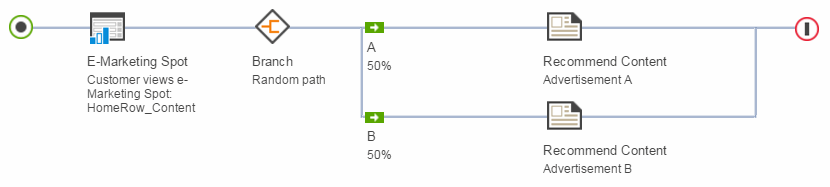
The server randomly displays one of the two advertisements on the page according to the percentages you assign. If 200 customers viewed this page, roughly 100 customers would see Advertisement A and the other 100 would see Advertisement B.
- Each path following the branch element should contain an action element, for example, the Recommend Content action.
- Optionally, you can include target elements at the start of a path, for example, the Customer Segment target. Keep in mind, however, that the server randomly selects only one path for each customer. Therefore, if the customer does not qualify for the target on the selected path, he or she will not move down any paths.
- Each time a customer triggers the activity, the server randomly assigns that customer a path. This means that if the same customer views the e-Marketing Spot multiple times, they could see either one of the two advertisements on each viewing, but you cannot control which one.
- You can assign any percentage value to each path as long as the total percentage for all paths is 100 percent.