Deploying an IAST agent on Azure App Service
Use the IAST agent to monitor applications that run on Azure App Service.
Deploying a .NET Core IAST agent using the HCL AppScan IAST .NET Core site extension
About this task
Note: The HCL AppScan IAST .NET Core site extension is applicable to .NET
Core applications running on Windows.
Procedure
-
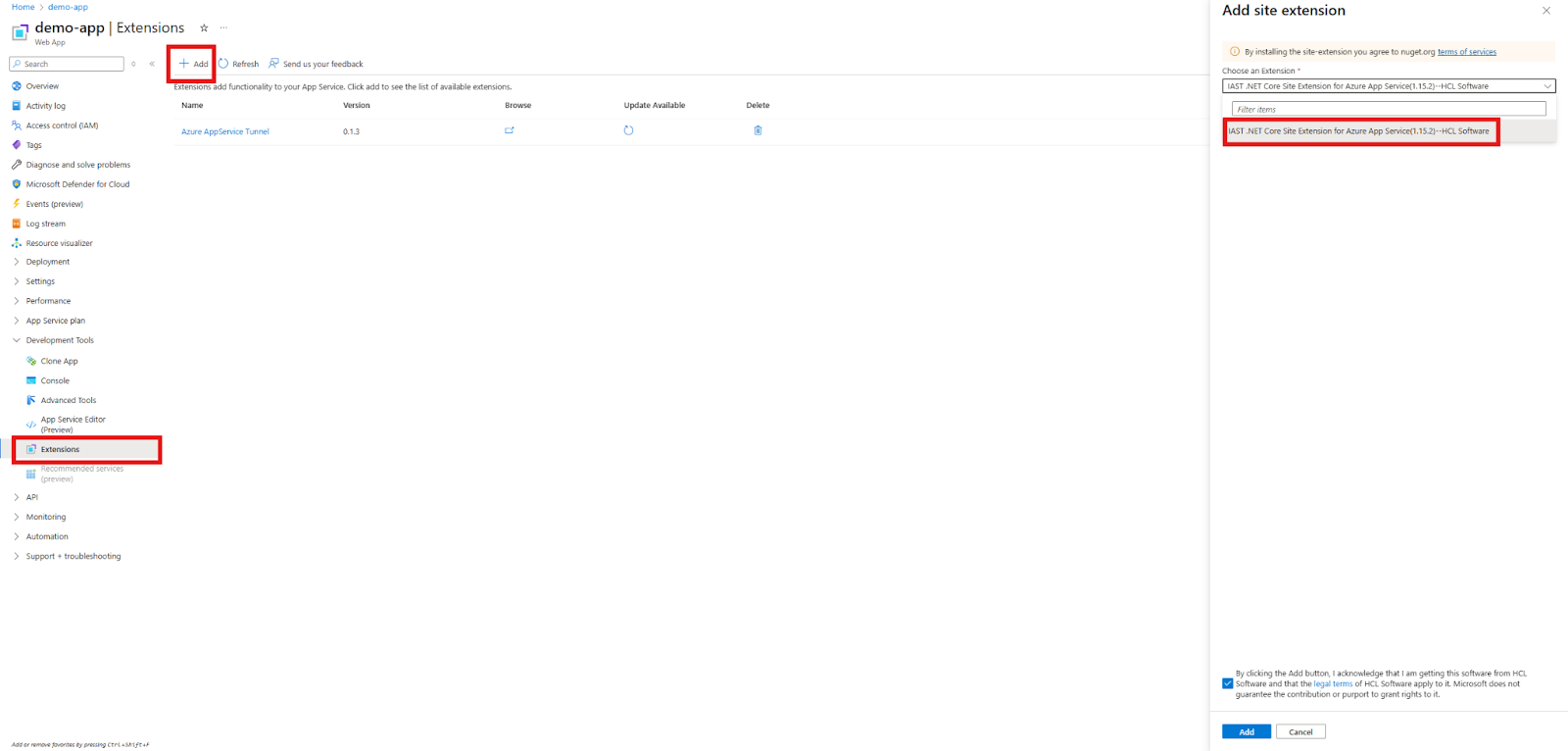
Adding the HCL AppScan IAST .NET Core Site Extension:
-
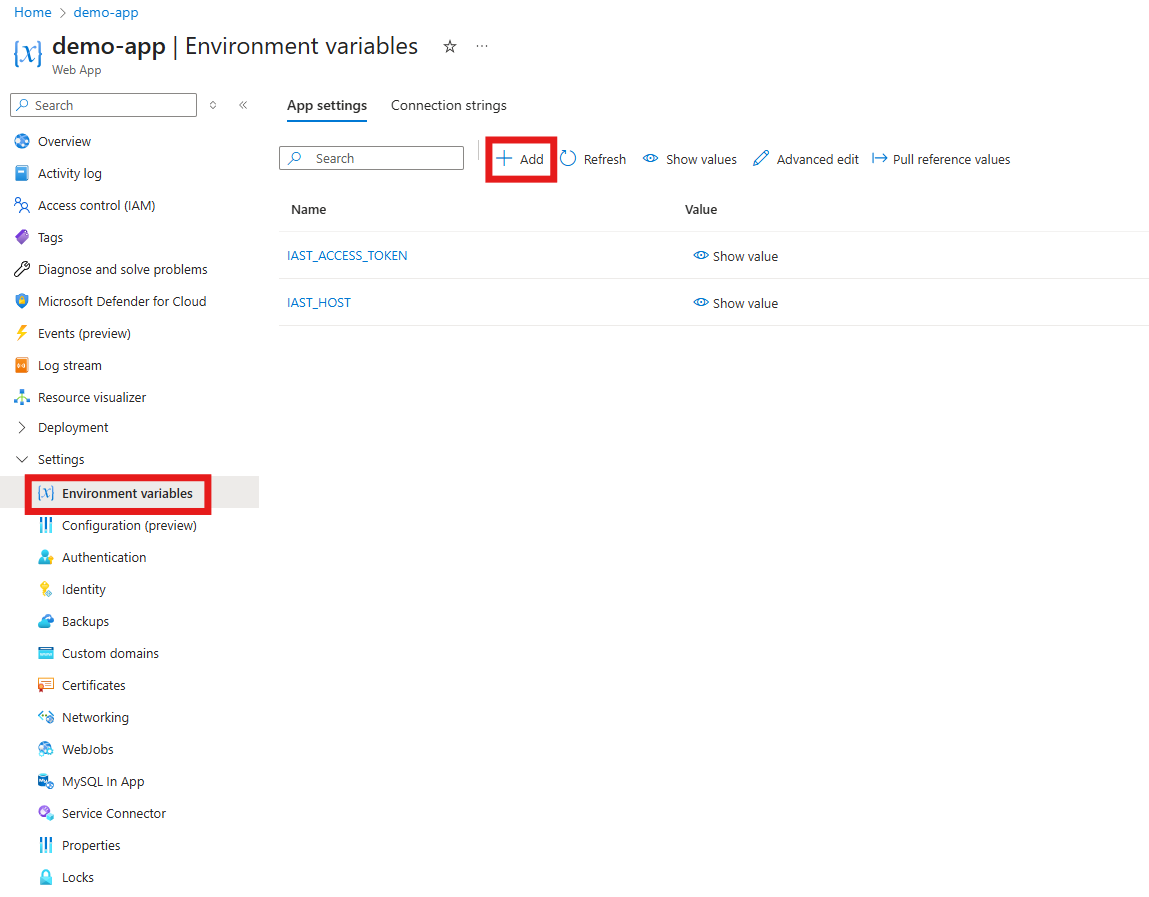
Configuring the site extension:
-
Verification: After the restart, the agent starts automatically.
Deploying a .NET IAST agent on Azure
About this task
Note: This method is applicable to .NET Framework and .NET Core
applications.
Procedure
- Start a .NET IAST session and download the agent NuGet as described here.
- Open Visual Studio and select Menu > Tools > Options > NuGet Package Manager > Package Source.
- Select the folder containing the IAST agent NuGet.
- Click the + sign to add a new NuGet source, and then give it a name.
- In the Solution Explorer, right-click the project that you want IAST to monitor and select Manage NuGet Packages.
- In the Search field, type com.HCL.AppScan.IAST.agent and select the first package listed in the results.
- Click Install.
-
.NET Core only: Configuration in the Azure environment.
Set the environment variable with these steps:
- In the Azure portal, go to Settings > Environment variables.
- Add the following environment variable:
Name Value ASPNETCORE_HOSTINGSTARTUPASSEMBLIESSecagentCore - Click Save to apply the changes.
- Restart the App Service to enable the agent.
- Deploy your application to Azure App Services.
-
Verification: The agent is now installed.
In ASoC: Open your application and confirm an active IAST connection.
In Azure: Check the log stream for IAST agent startup and connection messages.
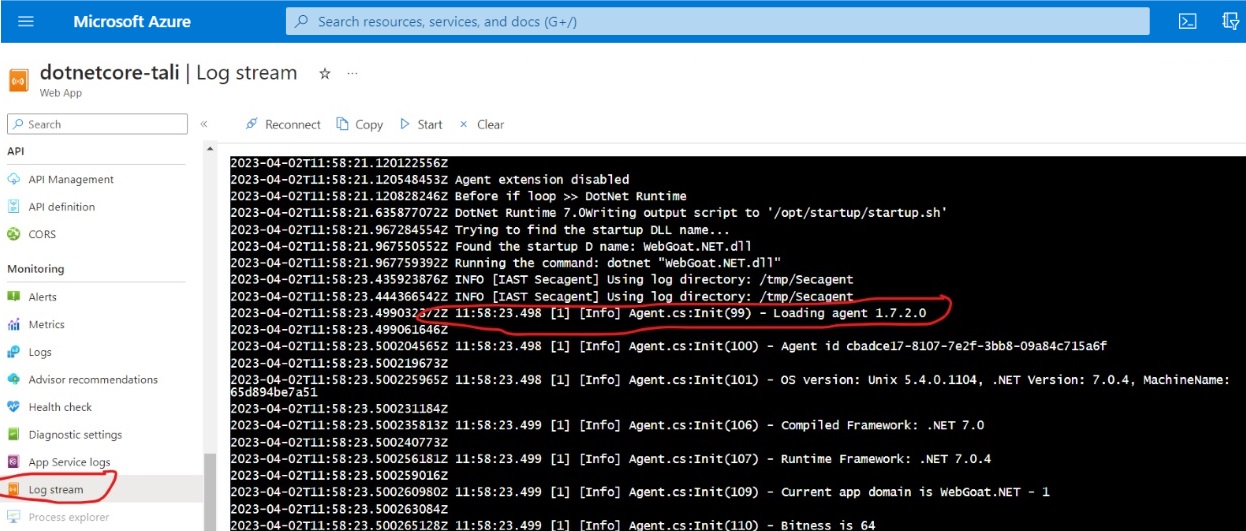
As you use or test your application (run functional tests, run a DAST scan, or explore the application manually), the IAST agent monitors requests as they are sent, and reports on security issues it finds.
Deploying a Node.js IAST agent on Azure
Procedure
- If you have not yet done so, create an application for your scans.
- In the Application view, click Create Scan to open the wizard, then select Interactive (IAST).
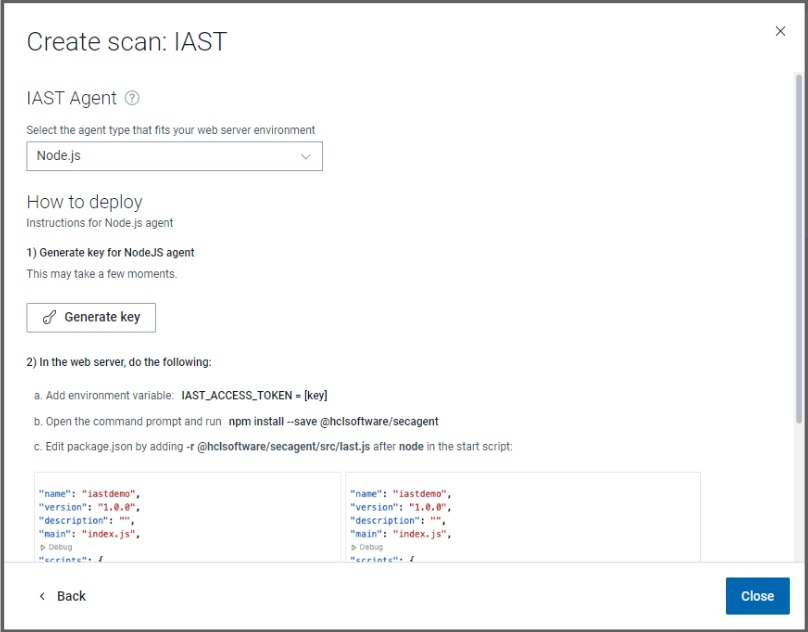
-
Select Node.js and click Generate key. This generates a unique key that
connects your application with the IAST session in ASoC. Save
this key for later.
-
In your workspace, install the IAST agent from npm with the command:
This addsnpm install --save @hclsoftware/secagent@hclsoftware/secagentto the dependencies in thepackage.jsonfile of your application: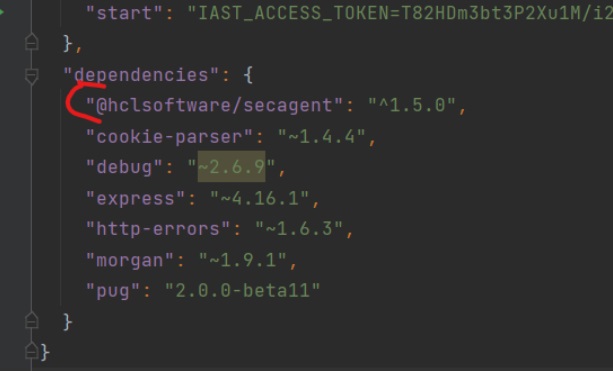
-
By default, Azure App Services use the start script in your
package.jsonas the run command. Edit the start script to set the agent key from step three above as an environment variable and to run the IAST agent from step four as a required package.For example, if the original command was: Edit it to
this:
Edit it to
this:
- Configuring the site extension: Select Settings > Environment variables.
-
Add the following environment variables, using the value saved in step #3:
Name Example Description IAST_ACCESS_TOKEN(your access token) Authenticates the agent with ASoC. IAST_HOSThttps://cloud.appscan.com/IAST The ASoC host URL that the agent connects to. 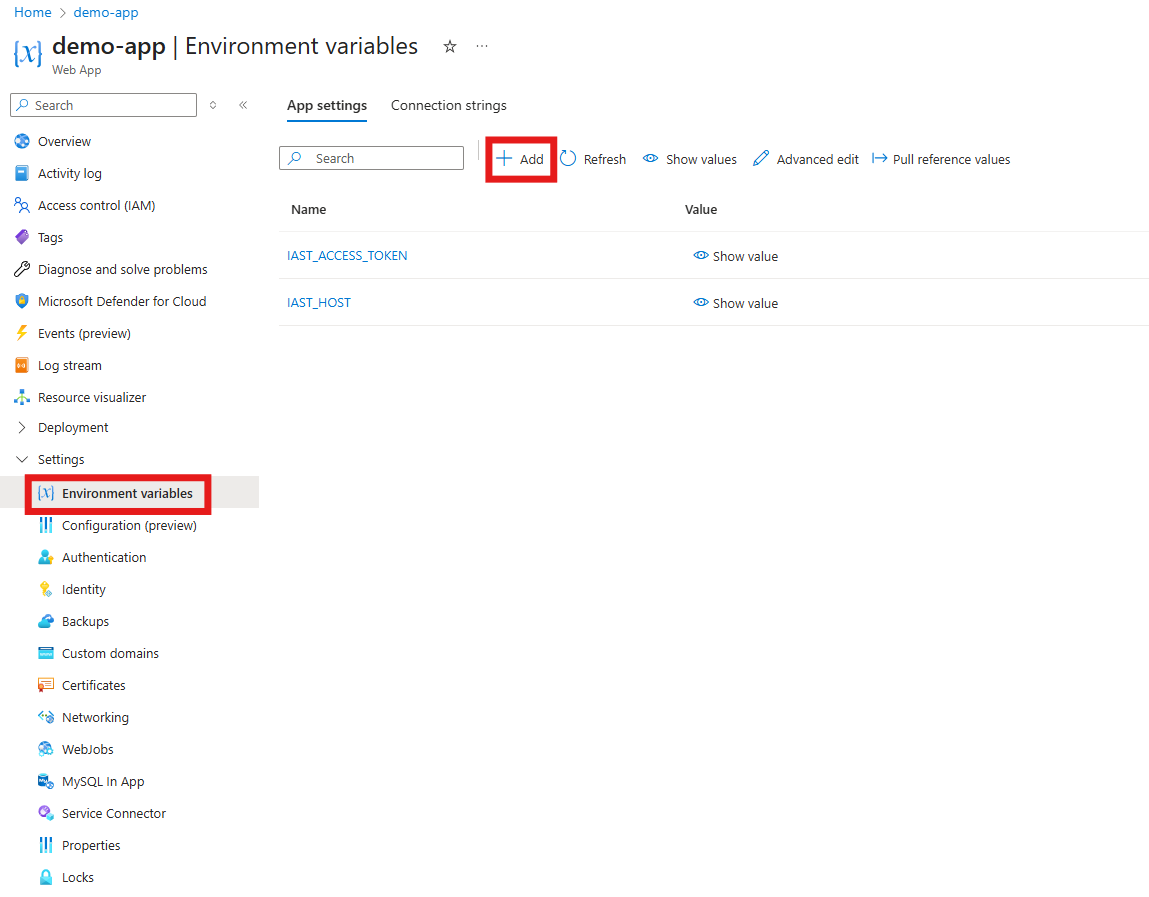
- Click Save to apply the changes.
- Restart the App Service to enable the agent.
- Deploy your application to Azure App Services.
-
Verification: After the restart, the agent starts automatically.
- In ASoC: Open your application and confirm an active IAST connection.
- In Azure: Check Log stream for IAST agent startup and connection messages.
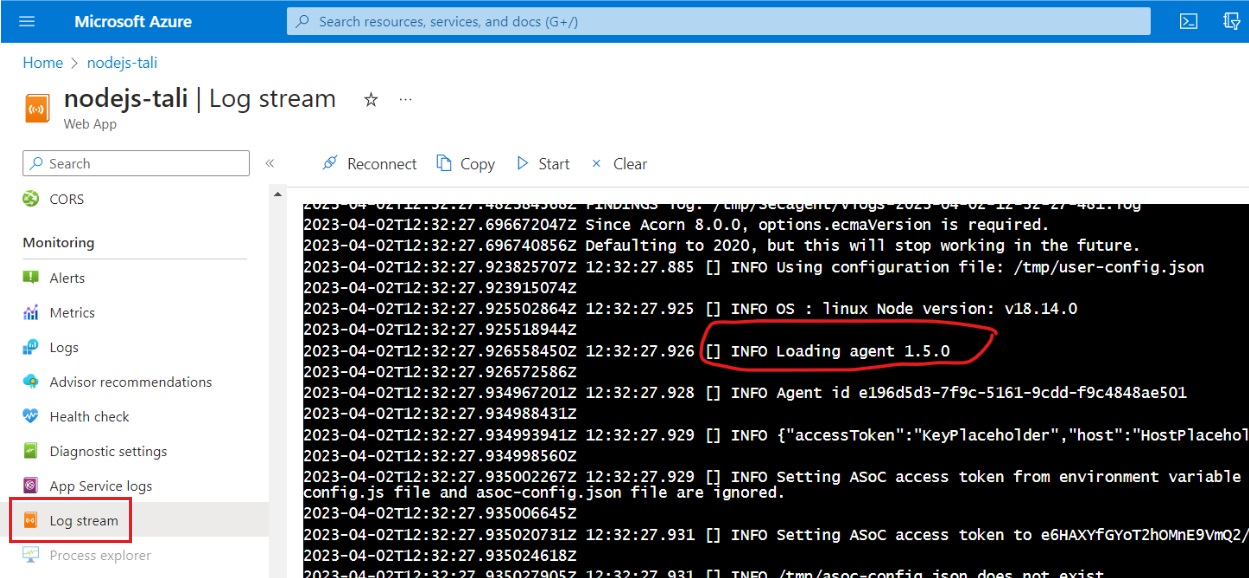
As you use or test your application (run functional tests, run a DAST scan, or explore the application manually), the IAST agent monitors requests as they are sent, and reports on security issues it finds.