Incident Management
To create data sources for Incident Management, perform the following steps.
- On the left menu bar, click Configuration 🡪 Manage Data Sources.
- The Create Data Source page appears with the following tabs:
- Organization
- Fetch Data
- Release Rules
- Close Rules
- InProgress Rules
- Assignation
Figure 1. Create Data Source 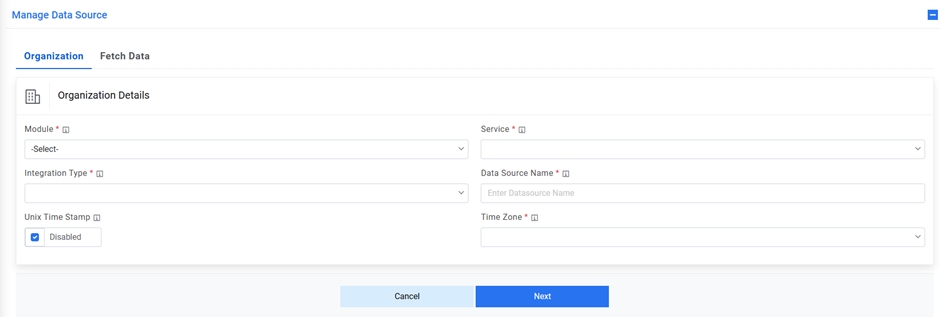 Note:Release Rules are only applicable for the following Module types- Incident Management, Change Request Task and Service Request Task. This tab will not be activated for other module types.
Note:Release Rules are only applicable for the following Module types- Incident Management, Change Request Task and Service Request Task. This tab will not be activated for other module types. - On the Organization tab,
- Select the Module as Incident Management, since we are configuring this data source for pulling the incident tickets.
- Select the Service as SX Tool as we are configuring the data source for Cherwell
- Select the Integration Type as REST, since we will be integrating through REST APIs.
- Select the Timezone to specify the time zone of the selected data source.
- Select Timestamp to view the present data with date and time.
- Click Next.
Figure 2. Create Data Source (Cont.) 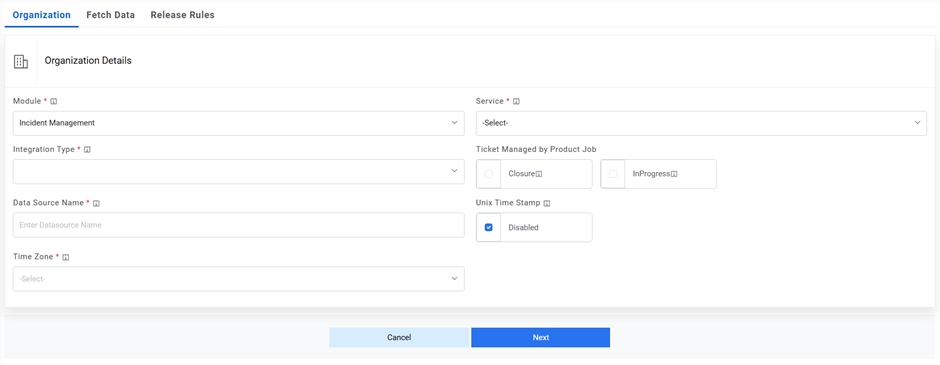
Figure 3. Create Data Source (Cont.) 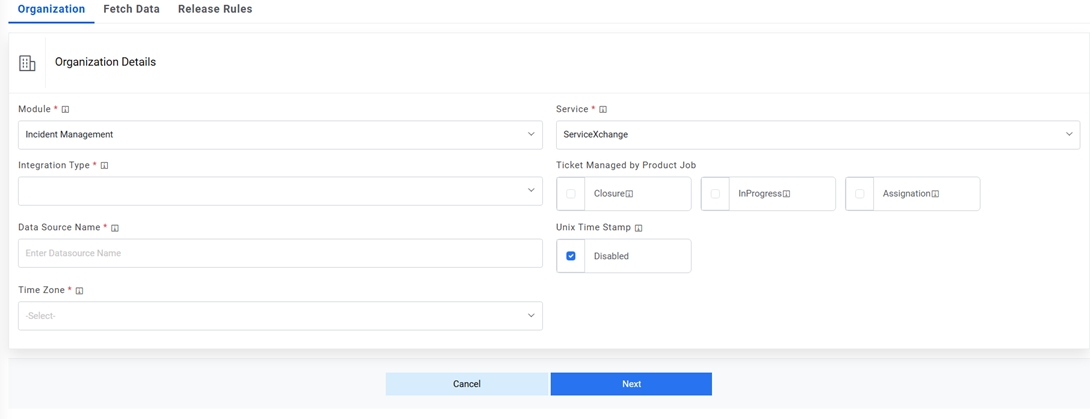
- On the Fetch Data tab, type in the details as per the environment.
- In the Connection Details section, enter the following details:
-
URL – Type the URL which contains the
placeholders that display the parameters based on
the applied clause such as the number of records to be fetched, query type, date on
which the data is fetched, and the order by and so on. It depends on the URL or API
provided by the tool.
Sample URL – http://<Product_API_URL>/iAutomateAPI/Request/ GetIncidentTicketData/<Org_ID>?ModuleId=1&start_date>=#Start_Date#&end_date<=#End_Date#&
Here, <Product_API_URL > is the API URL of iAutomate where Push APIs are present and <Org_ID> is the OrgID for the organization for which you are creating the data source. It is available in Organization Master in Database.
-
Authentication Type – Select one of the Authentication Types from Basic /
Windows, OAuth 2.0Note:The user details that are entered here should be an API User
- Selection of Basic / Windows requires you to enter -
- User Id
- Password.
- Selection of OAuth 2.0 requires you to enter -
- User Id
- Password
- Authentication URL
- Selection of Basic / Windows requires you to enter -
- Proxy Required – Check Proxy Required, if the environment needs access to content from data sources outside the firewall.
- Click on Test Connection to check accessibility of URL from service. Testing
the connection is not mandatory, you can still create Data source.
Figure 4. Create Data Source (Connection Details) 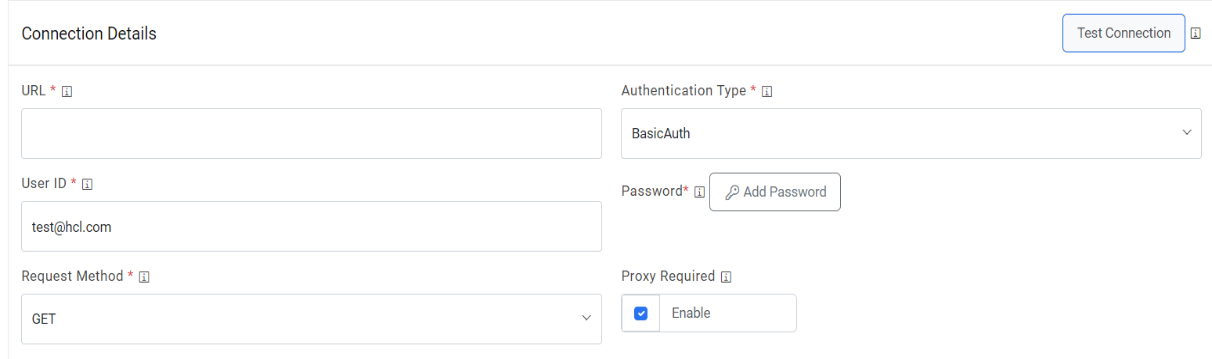
-
URL – Type the URL which contains the
placeholders that display the parameters based on
the applied clause such as the number of records to be fetched, query type, date on
which the data is fetched, and the order by and so on. It depends on the URL or API
provided by the tool.
-
Password - For password, click on icon next to it. If the password is available in
plaintext, then select Input type as Input Text and enter the password in Value field. Else
if it is available in Azure Key Vault then select Input Type as Azure Key Vault and then
select any of the configured details from the value field. Else if it is available in any
Key Vault such as CyberArk or Secret Manager then select Input Type as CyberArk or Secret
Manager respectively and then select any of the configured details from the value field.
Figure 5. Password in plaintext 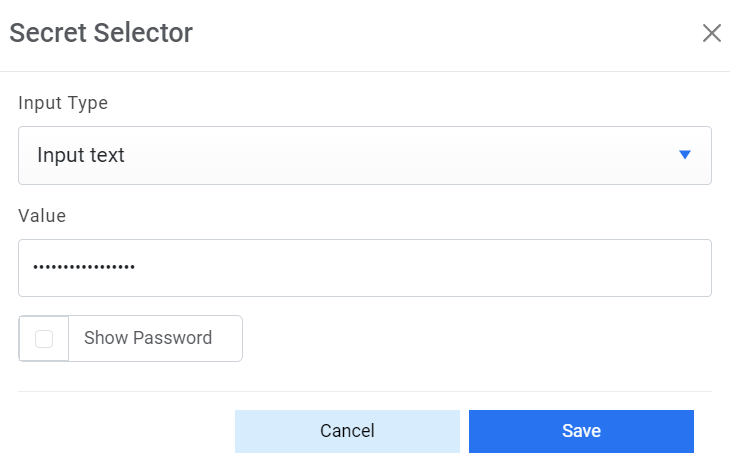
Figure 6. Password from Key Vault (CyberArk) 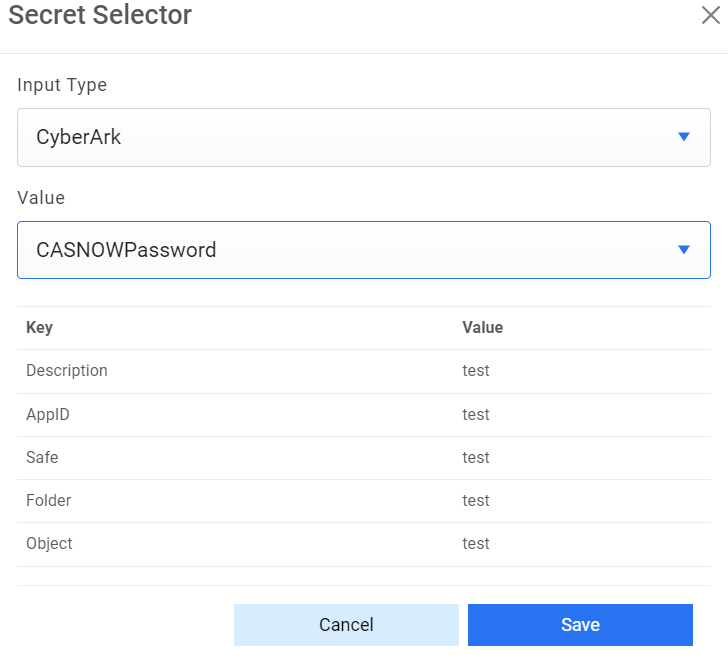
Figure 7. Password from Secret Manager 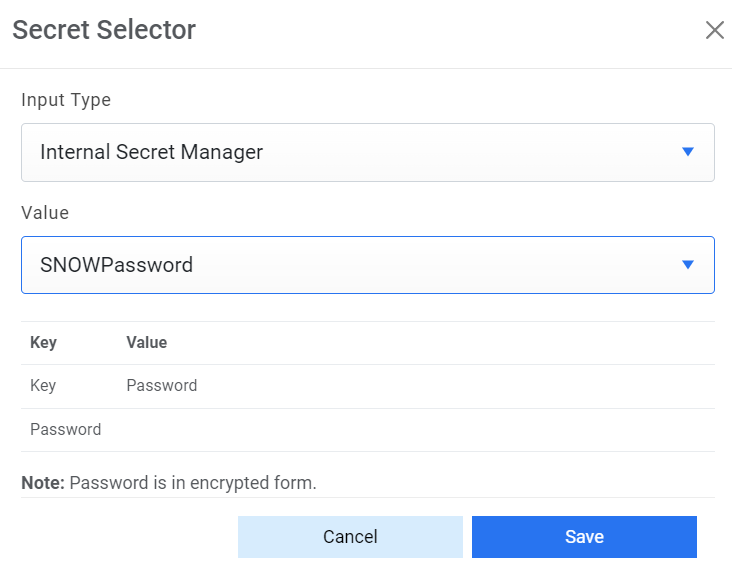
Figure 8. Password from Azure Key Vault 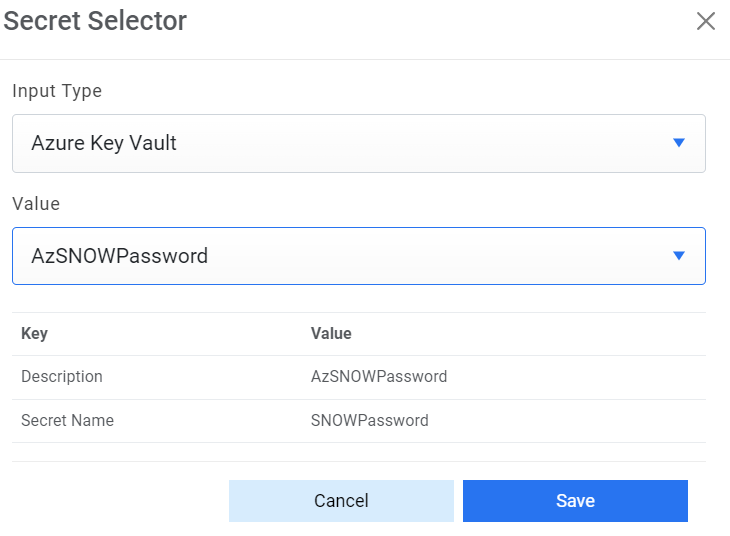
-
Request Authentication Parameters – If the user has additional parameters, click Add
Authentication Parameters under the Request Authentication Parameters Tab. Based on the
Authentication Type, add the parameters mentioned in the below table.
Sample Authentication Parameters
Authentication Type Key Value Is Encrypted? Is Key? OAuth2.0 username <username> NO YES OAuth2.0 password <password> YES YES OAuth2.0 AuthMethod POST NO NO OAuth2.0 AuthPrefix Bearer NO NO OAuth2.0 client_id <clientID> YES YES OAuth2.0 client_secret <clientsecret> YES YES OAuth2.0 TokenKey access_token NO NO OAuth2.0 ResponseType JSON NO NO OAuth2.0 grant_type Password NO YES Figure 9. Create Data Source (Request Authentication Parameters for OAuth2.0) .png)
-
URL Path Parameters – Based on the URL entered earlier, please map the values to the
URL Path Parameters. E.g., for the URL entered earlier, please populate the below
inputs:
URL Path Parameters
Key Value Type Value #start_date# SQL UDF @@GetFromDateTimeUsingIncidentModifiedDate_ServiceXchange #end_date# SQL UDF @@GetToolCurrentDateTime_ServiceXchange Figure 10. URL Path Parameters 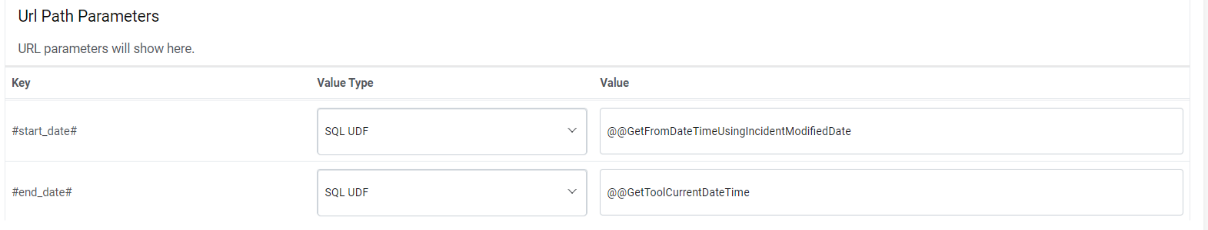
- Request Header Parameters – Please enter the request header parameters as required.
-
Response Body – In this section, please enter the output of URL query for one of the
incidents in JSON format. A sample response is mentioned
below:
{ "statusCode": 200, "status": "Success", "message": null, "result": [ { "TicketNumber": "INC0303869", "Summary": "testing", "Description": "testing data", "AssignedGroup": "xxxxxxxx", "StatusCode": "1", "CreationDate": "2022-09-23 09:26:52.000", "LastModifiedDate": "2022-09-23 09:26:52.000", "ClosedDate": "2022-09-22 06:24:52.000", "sys_id": "xxxxxxxx", "Col1": "", "Col2": "", "Col3": "", "Col4": "", "Col5": "", "Col6": "", "Col7": "", "Col8": "", "Col9": "", "Col10": "", "iAutomate_CreatedDateInGMT":"2022-09-23 09:27:22.773", "iAutomate_UpdatedDateInGMT": "2022-09-23 09:27:22.773" } ] } - After entering the response, click Extract Keys to add the parameters in the Mandatory Parameter Mapping section.
-
Mandatory Parameter Mapping – Please map the mandatory parameters to the respective
values as mentioned in the screenshot below:
Sample Mandatory Parameter Mapping
Key Value Type Value TicketNumber JSON.Keys result.0.TicketNumber Summary JSON.Keys result.0.Summary Description JSON.Keys result.0.Description CreationDate JSON.Keys result.0.CreationDate StatusCode JSON.Keys result.0.StatusCode ResolvedDate JSON.Keys result.0.ClosedDate LastModifiedDate JSON.Keys result.0. LastModifiedDate Figure 11. Mandatory Parameter Mapping 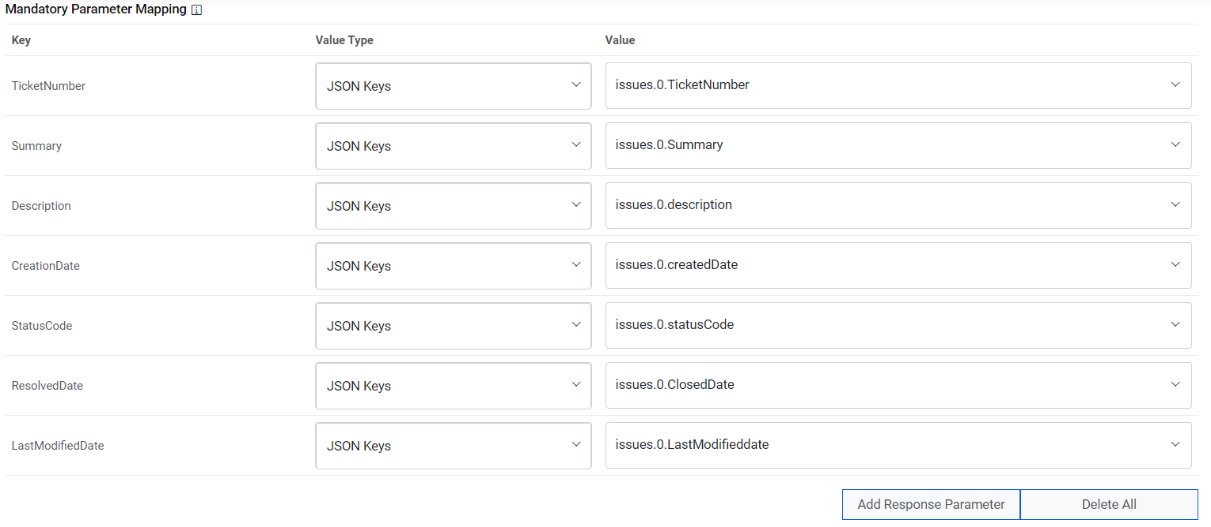
- If you need to add Optional parameters, click Add Response Parameter to add
more parameters. For our purpose, we will be adding a couple of extra parameters, as
mentioned below, as we need them in the later section.
Sample Optional Parameters
Key Value Type Value AssignedGroup JSON.Keys result.0. AssignedGroup Figure 12. Optional Parameter Mapping 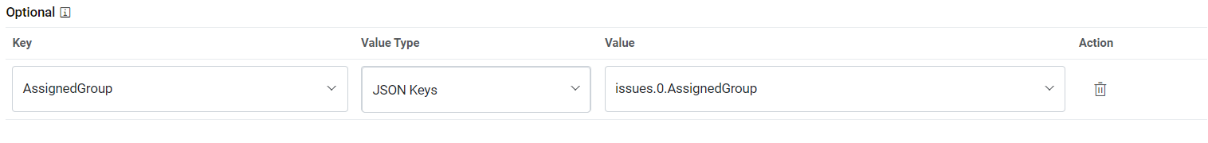
- Click Next to proceed to Release Rules.
- On the Release Rules tab, type in the details as per the requirement.
- In the Connection Details section, enter the following details:
-
URL – Type the URL of the selected service type to release the ticket. It
contains the placeholders that display the parameters
based on the applied clause and is dependent on the URL or API provided by the
tool.
Sample URL: https://inboundBoomiDevCHN1.mycompany.com/ws/simple/updateIncidentInSX
- Authentication Type – Please enter the information in line with the Authentication type configured for fetching data configuration previously. For e.g., Basic.
- Request Method – Select Request Method as POST from the drop-down.
-
Proxy Required – Check Proxy Required, if the environment needs access to
content from data sources outside the firewall.
Figure 13. Release Rules (Connection Details) 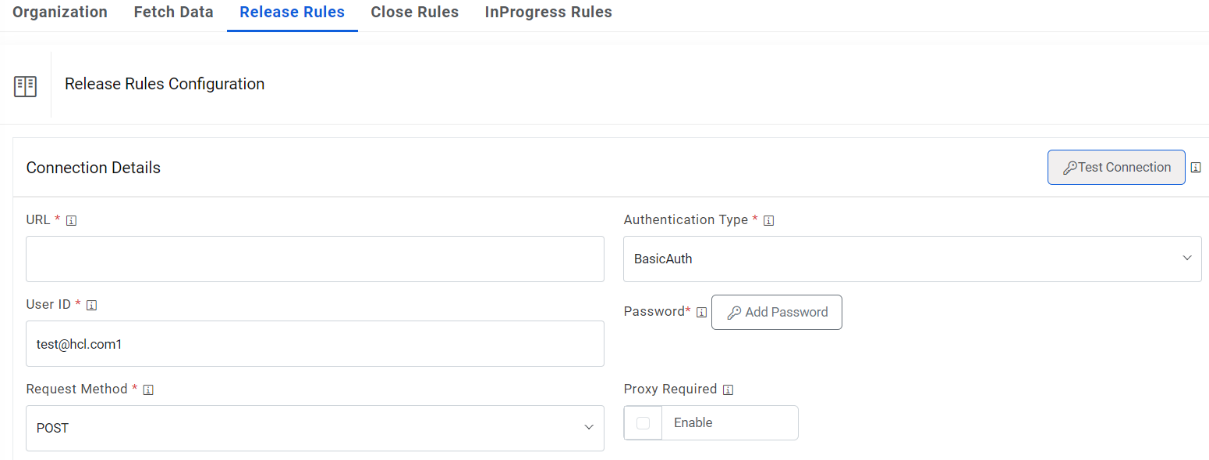
- Password - For password, click on icon next to it. If the password is available in plaintext, then select Input type as Input Text and enter the password in Value field. Else if it is available in Azure Key Vault then select Input Type as Azure Key Vault and then select any of the configured details from the value field. Else if it is available in any Key Vault such as CyberArk or Secret Manager then select Input Type as CyberArk or Secret Manager respectively and then select any of the configured details from the value field.
Figure 14. Password in Plaintext 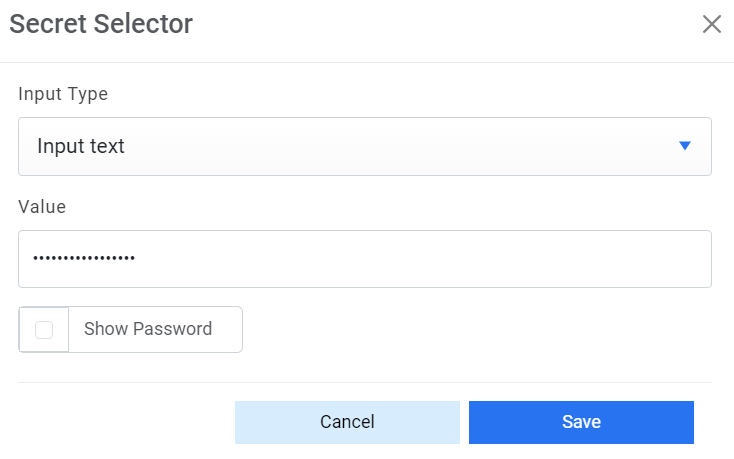
Figure 15. Password from Key Vault (CyberArk) 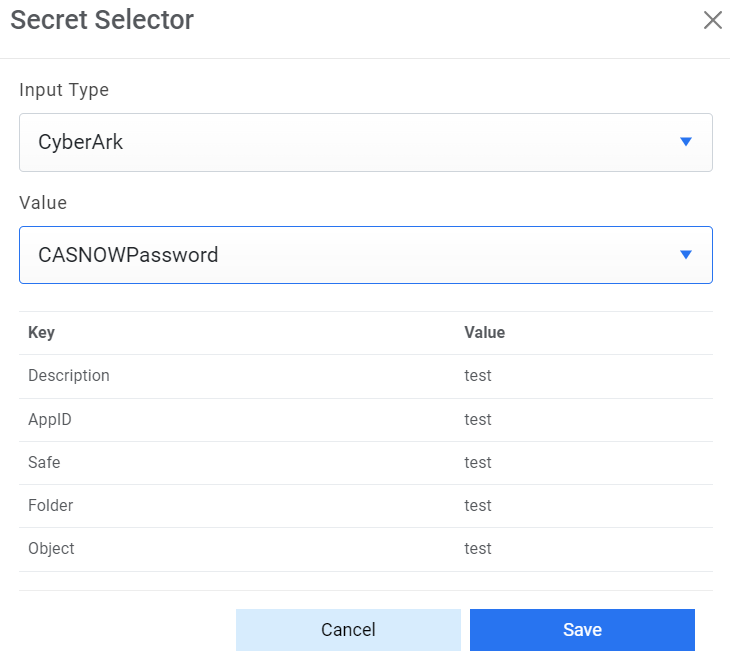
Figure 16. Password from Secret Manager 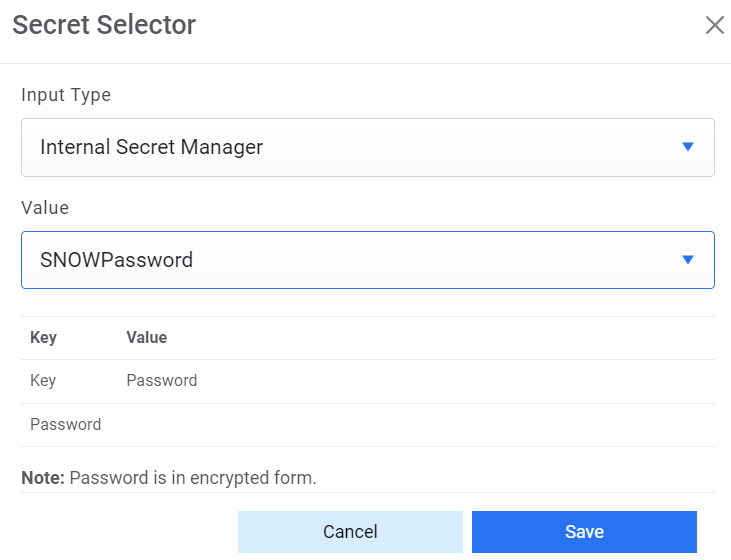
Figure 17. Password from Azure Key Vault 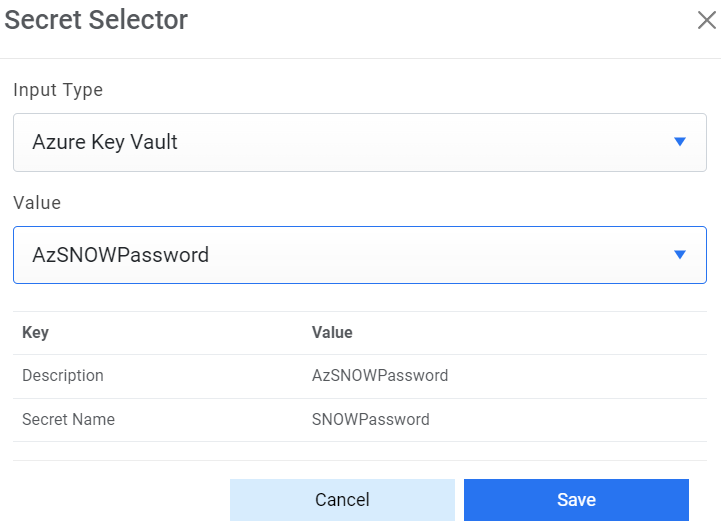
-
URL – Type the URL of the selected service type to release the ticket. It
contains the placeholders that display the parameters
based on the applied clause and is dependent on the URL or API provided by the
tool.
- Request Authentication Parameters - If the user has additional parameters, click Add Authentication Parameters under the Request Authentication Parameters tab.
- Based on the Authentication Type, add the parameters mentioned in the below table
Sample Authentication Parameters
Key Value Is Encrypted? Is Key? grant_type password N Y username <username> N Y Password <password> Y Y client_id <client_id> N Y AuthPrefix Bearer N N AuthMethod POST N N ResponseType JSON N N TokenKey access_token N N Figure 18. Create Data Source (Request Authentication Parameters) .png)
-
Request Body - In this section, please enter the request body in JSON format. A
sample request is mentioned below:
Request Body – { "ticketnumber": "#ticket#", "status": "#status#", "worknote": "#worknote#", "assignmentgroup":"#assignmentgroup#", "clientName": "#clientname#", "clientItemNumber": "#clientitenumber#" }Figure 19. Request Body 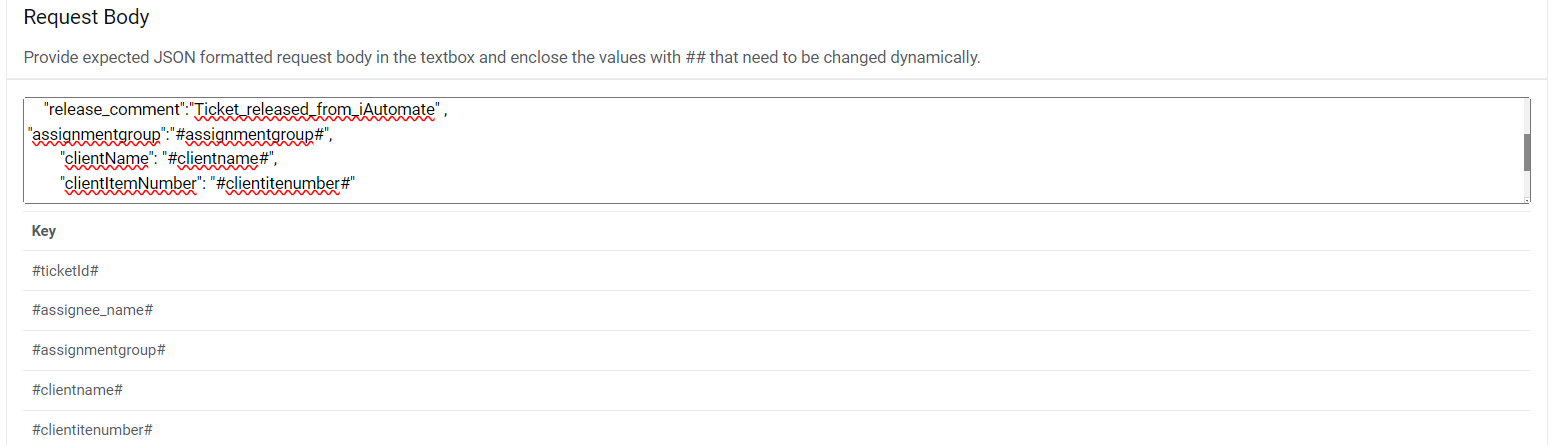
-
Response Body – In this section, please enter the response body in JSON format. A
sample request is mentioned below:
Response Body – { "result" : "#success#" }Figure 20. Release Rules (Response Body) 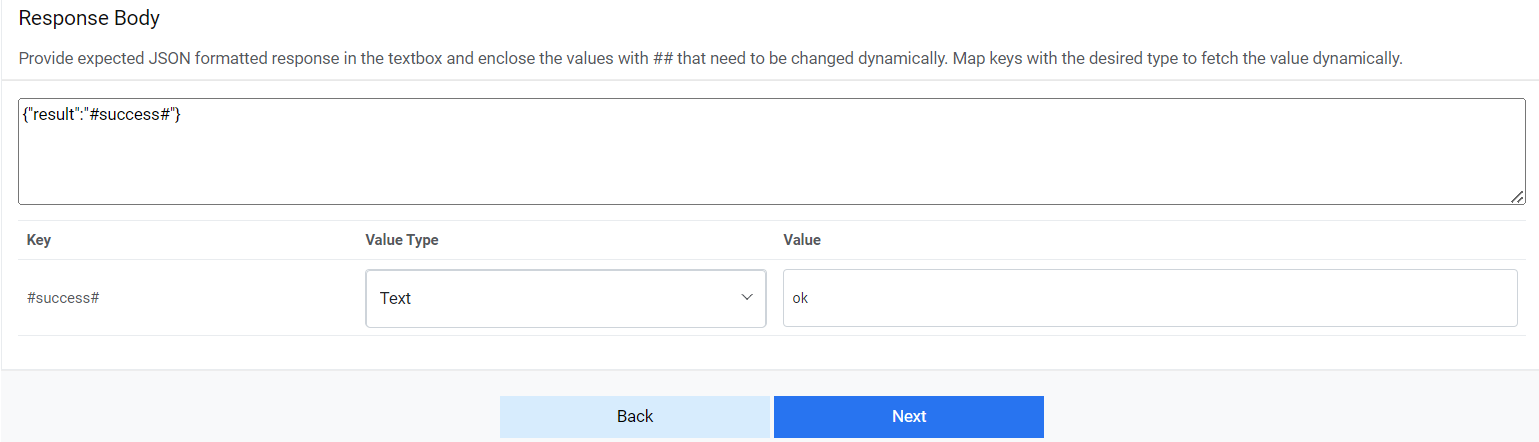
-
Response Key Value mapping can be done as per the below table.
Sample Response Key Value Mapping
#success# Text OK - Click Save to add the data source.
- On Close Rules tab, type in the details as per the requirement.
- In the Connection Details section, enter the following details:
- Type the URL of the selected service type to release the ticket. It contains the
placeholders that display the parameters based on
the applied clause and is dependent on the URL or API provided by the tool.
Sample URL - https://url.servicenow.com/api/now/v1/table/sc_request?sysparm_fields=#Columnshost>
- Authentication Type – Please enter the information in line with the Authentication type configured for fetching data configuration previously. For example, Basic.
- Request Method – Select Request Method as POST from the drop-down.
-
Proxy Required – Check Proxy Required, if the environment needs access to content
from data sources outside the firewall.
Figure 21. Close Rules (Connection Details) 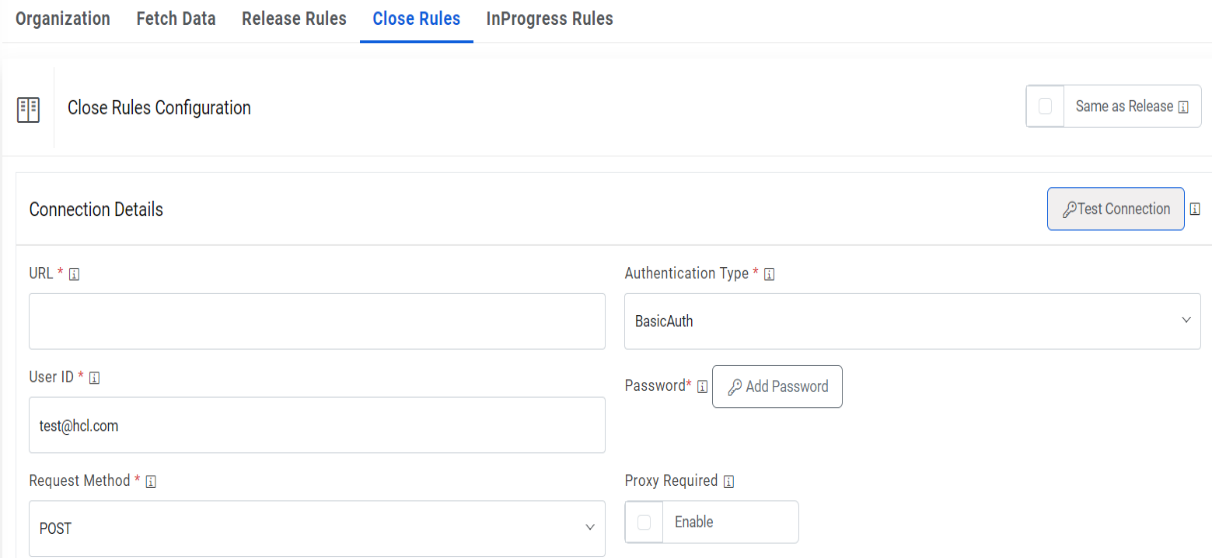
- Proxy Required – Check Proxy Required, if the environment needs access to content from data sources outside the firewall.
-
Password - For password, click on icon next to it. If the password is available
in plaintext, then select Input type as Input Text and enter the password in Value
field. Else if it is available in Azure Key Vault then select Input Type as Azure Key
Vault and then select any of the configured details from the value field. Else if it is
available in any Key Vault such as CyberArk or Secret Manager then select Input Type as
CyberArk or Secret Manager respectively and then select any of the configured details
from the value field.
Figure 22. Password in Plaintext 
Figure 23. Password from Key Vault (CyberArk) 
Figure 24. Password from Secret Manager 
Figure 25. Password from Azure Key Vault 
- Type the URL of the selected service type to release the ticket. It contains the
placeholders that display the parameters based on
the applied clause and is dependent on the URL or API provided by the tool.
- Request Authentication Parameters - If the user has additional parameters, click Add Authentication Parameters under the Request Authentication Parameters tab.
- Based on the Authentication Type, add the parameters mentioned in the table below
Sample Authentication Parameters
Key Value Is Encrypted? Is Key? grant_type password N Y username <username> N Y Password <password> Y Y client_id <client_id> N Y AuthPrefix Bearer N N AuthMethod POST N N ResponseType JSON N N TokenKey access_token N N Figure 26. Create Data Source (Request Authentication Parameters) .png)
-
Request Body - In this section, please enter the request body in JSON format. A
sample request is mentioned below:
Request Body – { "ticketnumber": "#ticket#", "status": "#status#", "worknote": "#worknote#", "clientName": "#clientname#", "clientItemNumber": "#clientitenumber#" }Figure 27. Close Rules (Request Body) 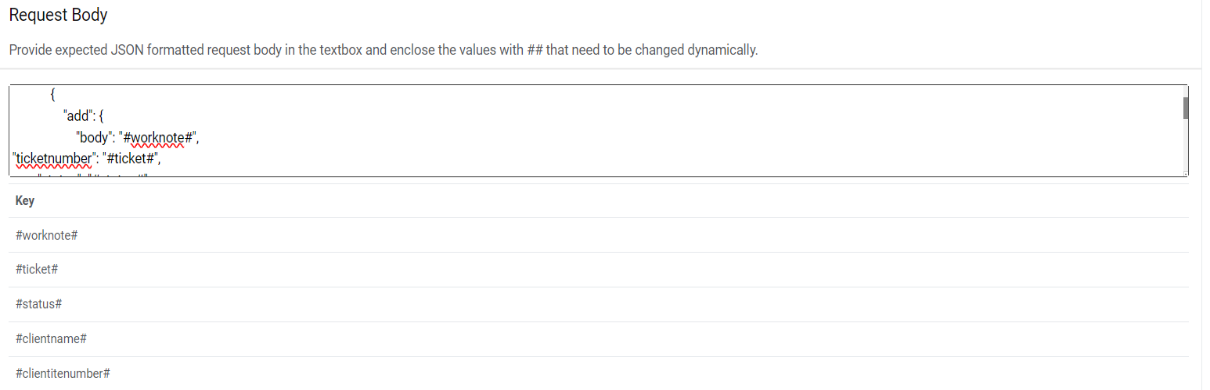
-
Response Body – In this section, please enter the response body in JSON format. A
sample request is mentioned below:
Response Body – { "result" : "#success#" }Figure 28. Close Rules (Response Body) 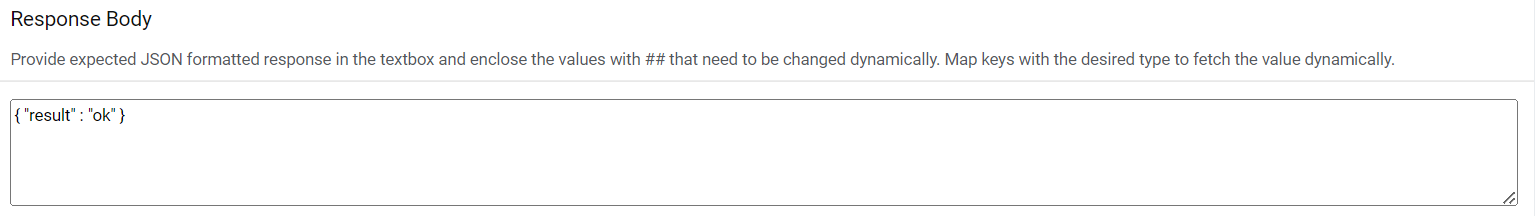
-
Response Key Value mapping can be done as per the table below.
Sample Response Key Value Mapping
#success# Text OK - Click Save to add the data source.
- On the InProgress Rules tab, type in the details as per the requirement.
- In the Connection Details section, enter the following details:
-
URL – Type the URL of the selected service type to release the ticket. It
contains the placeholders that display the parameters
based on the applied clause and is dependent on the URL or API provided by the tool.
Sample URL - https://<ipaddress>:<port>
- Authentication Type – Please enter the information in line with the Authentication type configured for fetching data configuration previously. For example, Basic.
- Request Method – Select Request Method as POST from the drop-down.
- Proxy Required – Check Proxy Required, if the environment needs access to content from data sources outside the firewall.
- Password - For password, click on icon next to it. If the password is available in plaintext, then select Input type as Input Text and enter the password in Value field. Else if it is available in Azure Key Vault then select Input Type as Azure Key Vault and then select any of the configured details from the value field. Else if it is available in any Key Vault such as CyberArk or Secret Manager then select Input Type as CyberArk or Secret Manager respectively and then select any of the configured details from the value field.
Figure 29. Password in Plaintext 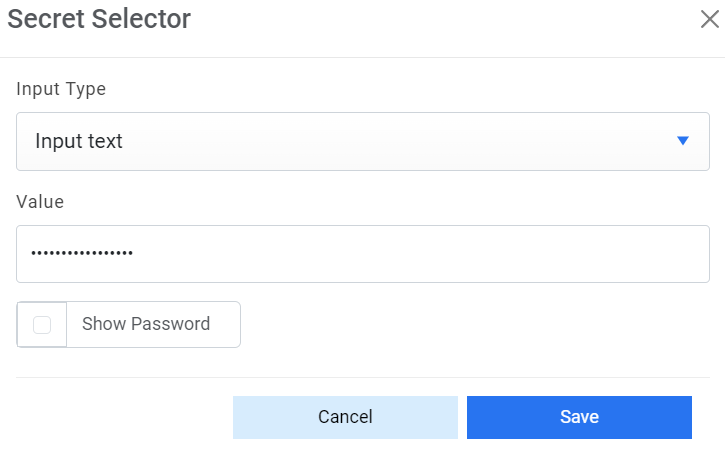
Figure 30. Password from Key Vault (CyberArk) 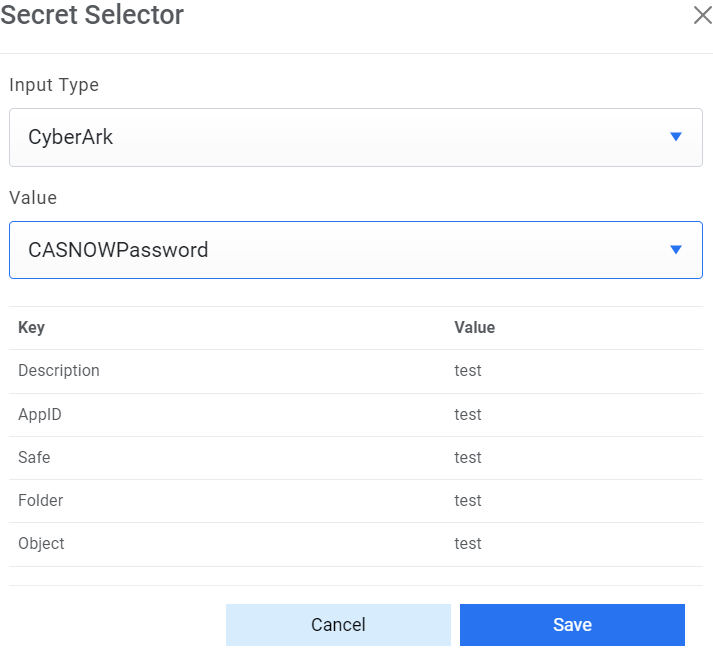
Figure 31. Password from Secret Manager 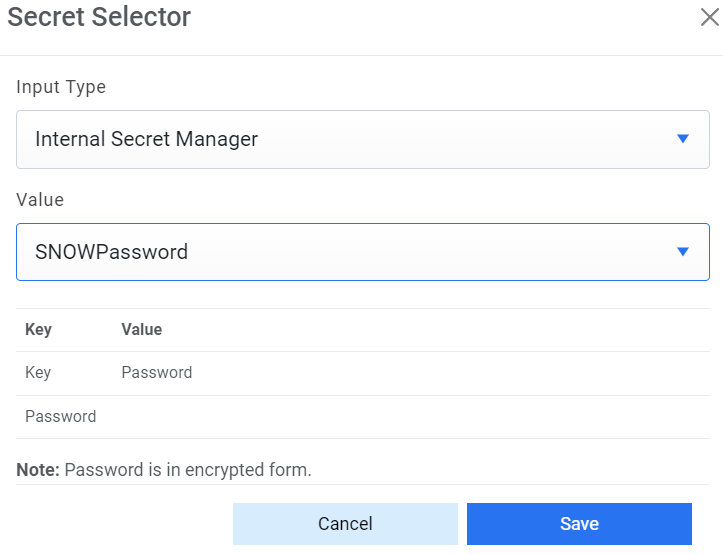
Figure 32. Password from Azure Key Vault 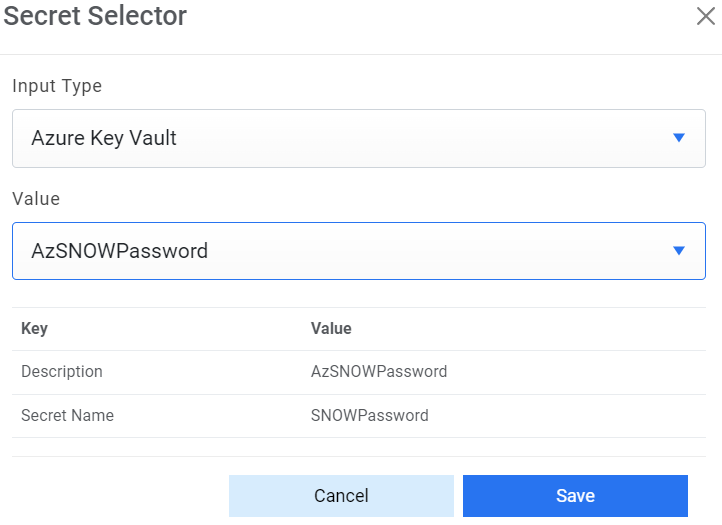
-
URL – Type the URL of the selected service type to release the ticket. It
contains the placeholders that display the parameters
based on the applied clause and is dependent on the URL or API provided by the tool.
- Request Authentication Parameters - If the user has additional parameters, click Add Authentication Parameters under the Request Authentication Parameters tab.
- Based on the Authentication Type, add the parameters mentioned in the table below
Sample Authentication Parameters
Key Value Is Encrypted? Is Key? grant_type password N Y username <username> N Y Password <password> Y Y client_id <client_id> N Y AuthPrefix Bearer N N AuthMethod POST N N ResponseType JSON N N TokenKey access_token N N Figure 33. Create Data Source (Request Authentication Parameters) .png)
-
Request Body - In this section, please enter the request body in JSON format. A
sample request is mentioned below:
Request Body – { "ticketnumber": "#ticket#", "status": "#status#", "worknote": "#worknote#", "clientName": "#clientname#", "clientItemNumber": "#clientitemnumber#" }Figure 34. Request Body 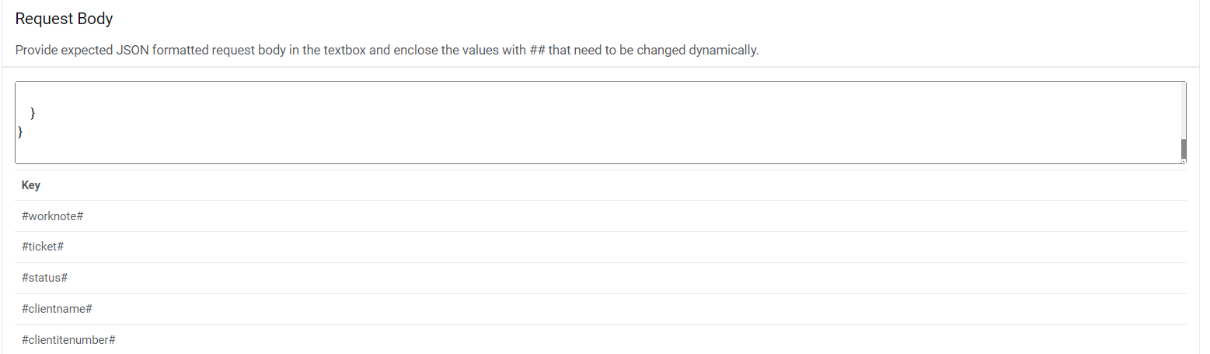
-
Response Body – In this section, please enter the response body in JSON format. A
sample request is mentioned below:
Response Body – { "result" : "#success#" }Figure 35. InProgress Rules Configuration (Response Body) 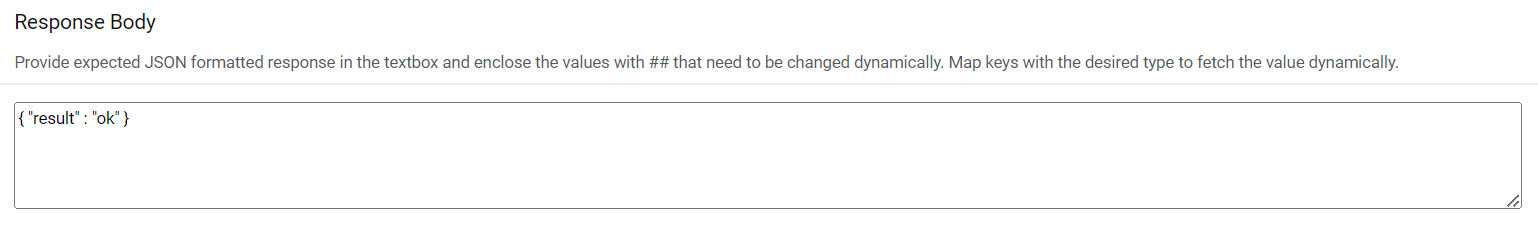
-
Response Key Value mapping can be done as per the table below.
Sample Response Key Value Mapping
#success# Text OK
- On the Assignation Rules tab, type in the details as per the requirement. Check Same as Release of similar configurations as mentioned in “Release Rules Configuration” are required, else proceed ahead.
- In the Connection Details section, enter the following details:
- URL – Type the URL of the selected service type to release the ticket. It contains the placeholders that display the parameters based on the applied clause and dependent on the URL or API provided by the tool.
- Sample URL - https://<url>.service-now.com/api/now/table/incident/#incident#
- Authentication Type – Please enter the information in line with the Authentication type configured for fetching data configuration previously.
- User Id - Enter the user id for the configured ITSM tool.
- Password - For password, click on the icon next to it. If the password is
available in plaintext, then select Input type as Input Text and enter the password in
Value field. Else if it is available in Azure Key Vault then select Input Type as
Azure Key Vault and then select any of the configured details from the value field.
Else if it is available in any Key Vault such as CyberArk or Secret Manager then
select Input Type as CyberArk or Secret Manager respectively and then select any of
the configured details from the value field.
Figure 36. Password in Plaintext .jpg)
Figure 37. Password from Key Vault (CyberArk) .jpg)
Figure 38. Password from Secret Manager .jpg)
Figure 39. Password from Azure Key Vault .jpg)
- Request Method – Select Request Method as PUT from the drop-down.
- Proxy Required – Check Proxy Required, if the environment needs access
to content from data sources outside the firewall. Click on Test Connection to check accessibility of URL from service. Testing the connection is not mandatory, you can still create a Data source.
Figure 40. Assignation Rules (Connection Details) 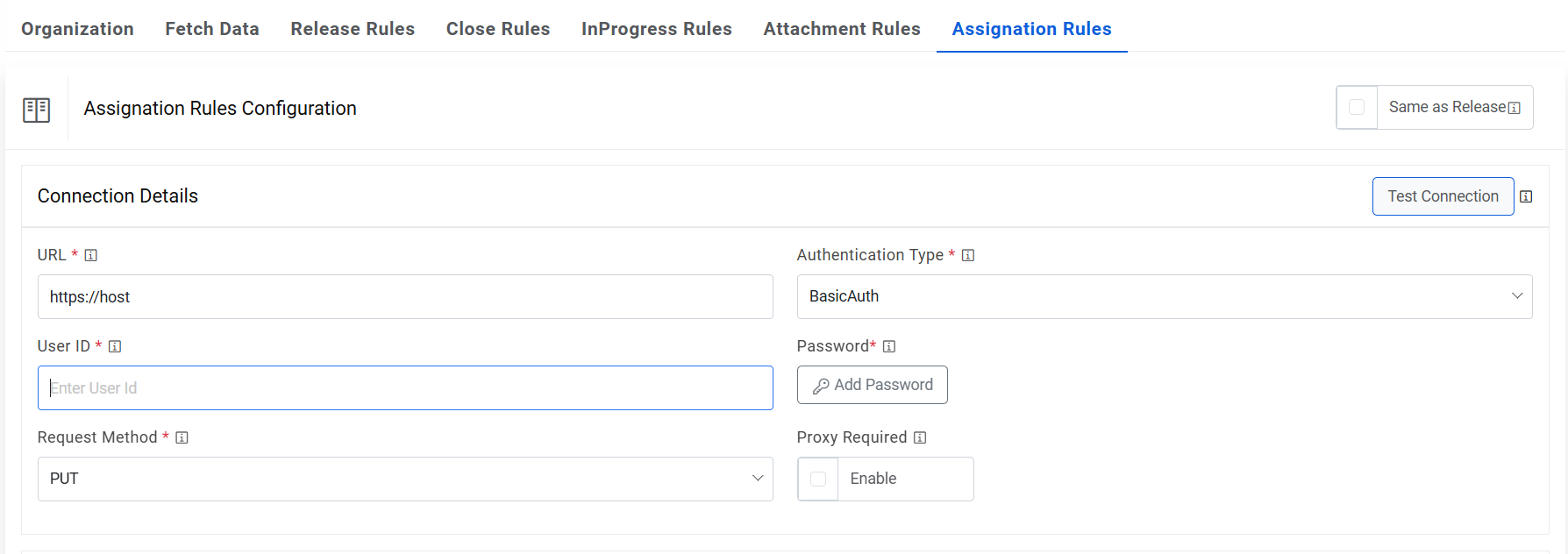
- URL Path Parameters – Based on the URL entered earlier, please map the values to the URL Path Parameters.
- Request Header Parameters – Please enter the request header parameters as required.
- Request Body – In this section, please enter the request body in JSON format.
A sample request is mentioned
below:
Request Body – {"assignment_group":"#Assignment_Group#","assigned_to":"#Assigned_To#","work_notes" : "#worknotes#"}Figure 41. Assignation Rules (Request Body) 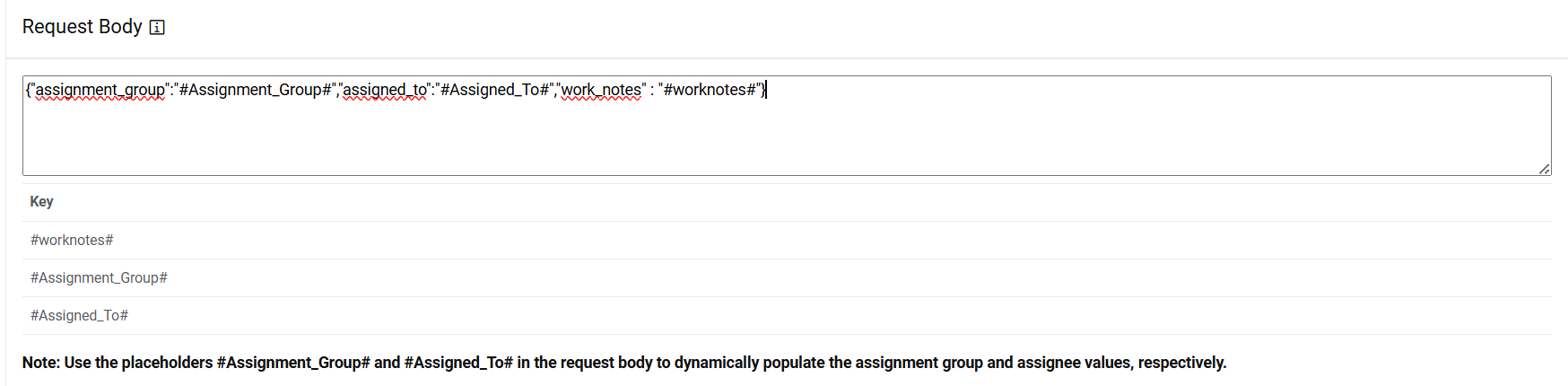
- Response Body – In this section, please enter the response body in JSON
format. A sample response is mentioned
below:
Response Body – { "result" : "#success#" }Figure 42. Assignation Rules (Response Body) .jpg)
- Response Key Value mapping can be done as per the below table:
Table 1. Sample Response Key Value Mapping #success# Text OK
- Click Save to add the data source.
- To bring the tickets within iAutomate scope, a specific queue needs to be configured in
the ITSM tool and same has to be configured in iAutomate. This is achieved through Manage
the Entry Criteria. Please follow the below steps:
- Go to Configuration and click Manage Data Sources.
- On the Data Sources tab, click
 next to the data source
user wants to manage. Manage Entry Criteria screen appears.
next to the data source
user wants to manage. Manage Entry Criteria screen appears.Figure 43. Manage Entry Criteria 
- Select ‘AssignedGroup’ for the Column field and ‘equals to’ for the Operator field.
- Enter the sys_id of the assignment group in SX in the Value field.
-
Clause and Sub-Clause fields can also be added based on requirement.
Figure 44. Manage Entry Criteria (Cont.) 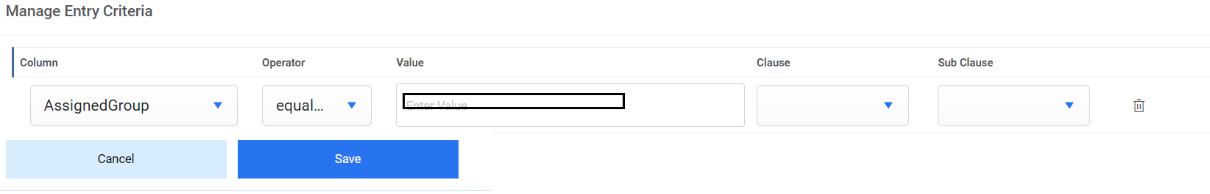
- Click Save.
- To configure the rules for the data source created earlier, perform the below steps:
- Go to Runbooks → click Manage Rules.
- Select the Organization and the data source created from Data Source
dropdown.
Figure 45. Manage Rules 
- Click on
 corresponding to
–No Rule—
corresponding to
–No Rule—
- Map the parameter #Assignmentgroup# with ElasticOps Rhythm ROW as value and value Type is Text.
- Map the parameter #ticket# with iIncident.TicketNumber as value and value type is Table Columns.
- Map the parameter #status# with Assigned as value and text as Value Type.
- Map the parameter #clientname# with DB Cheques as value and text as Value Type.
- Map the parameter #clientitemnumber# with iIncident.TicketNumber as value and table column as Value Type.
- Map the parameter #worknote# with @@GetReleaseWorkNoteForIncident as Value and SQL UDF as Value Type.
- Click OK.
Figure 46. Manage Rules (Cont.) 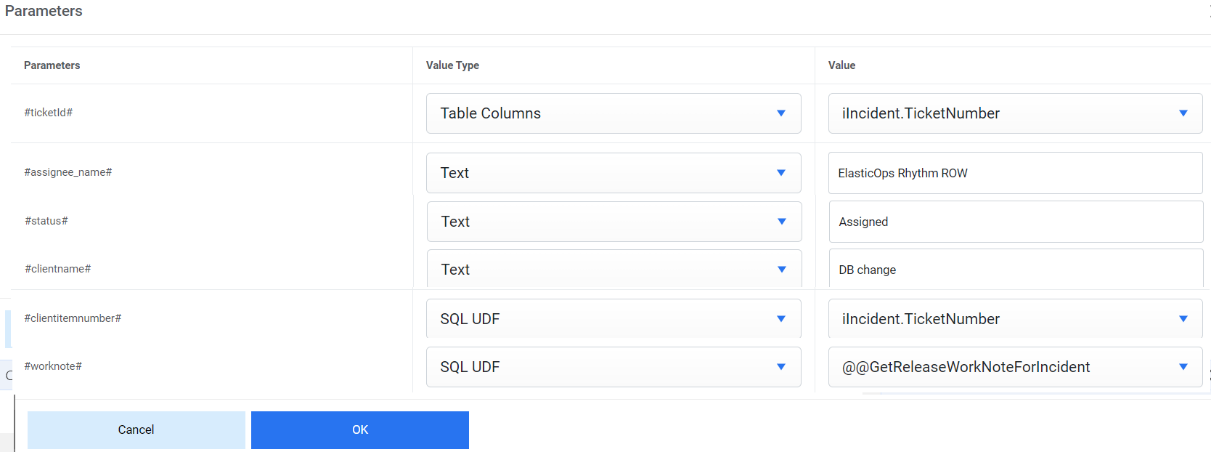
- Click the OK Rule.
- To configure the Close rules for the data source created earlier, perform the below
steps:
- Go to select Runbooks 🡪 click Manage Rules.
- Select the Organization and the data source created from Data Source
dropdown.
Figure 47. Manage Rules 
- Click on
 corresponding to
–No Rule—
corresponding to
–No Rule—
- Map the parameter #ticket# with iIncident.TicketNumber as value and value type is Table Columns.
- Map the parameter #status# with Fixed as value and text as Value Type.
- Map #worknote# again to the value type as SQL UDF in which #worknote# was mapped with function @GetToolWorkNoteForIncident.
- Map the parameter #clientname# with DB Cheques as value and text as Value Type.
- Map the parameter #clientitemnumber# with iIncident. TicketNumber as
value and table column as Value Type
Figure 48. Manage Rules (Cont.) 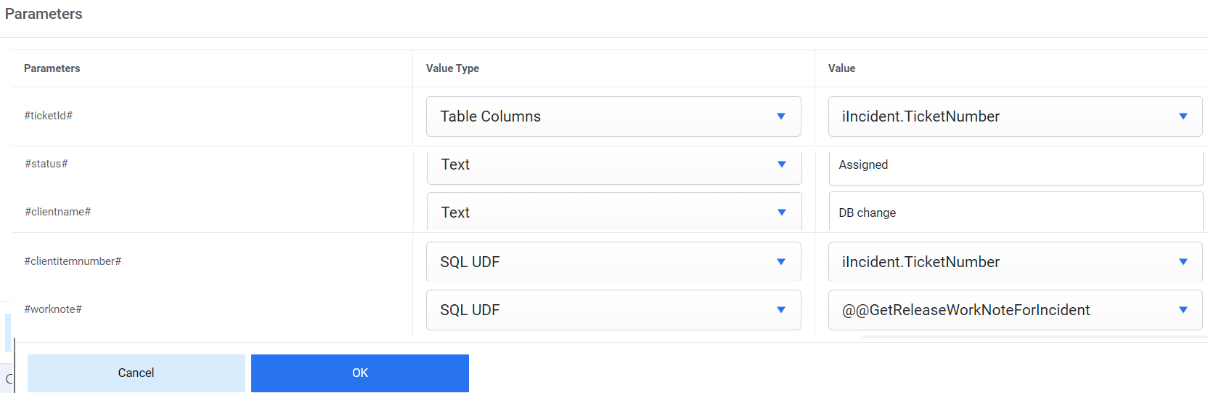
- Click OK.
- Click Save Rule.
- To configure the InProgress rules for the data source created earlier, perform the
following steps:
- Go to Runbooks 🡪 click Manage Rules.
- Select the data source created from Data Source dropdown.
Figure 49. Manage Release Rules 
- Click on
 corresponding to
–No Rule—
corresponding to
–No Rule—
- Map the parameter #ticket# with iIncident.TicketNumber as value and value type is Table Columns.
- Map the parameter #status# with InProgress as value and text as Value Type.
- Map the parameter #worknote# with iAutomate is working on the ticket as Value and text as Value Type.
- Map the parameter #clientname# with DB Cheques as value and text as Value Type.
- Map the parameter #clientitemnumber# with iIncident.TicketNumber as
value and table column as Value Type.
Figure 50. Manage Rules (Cont.) 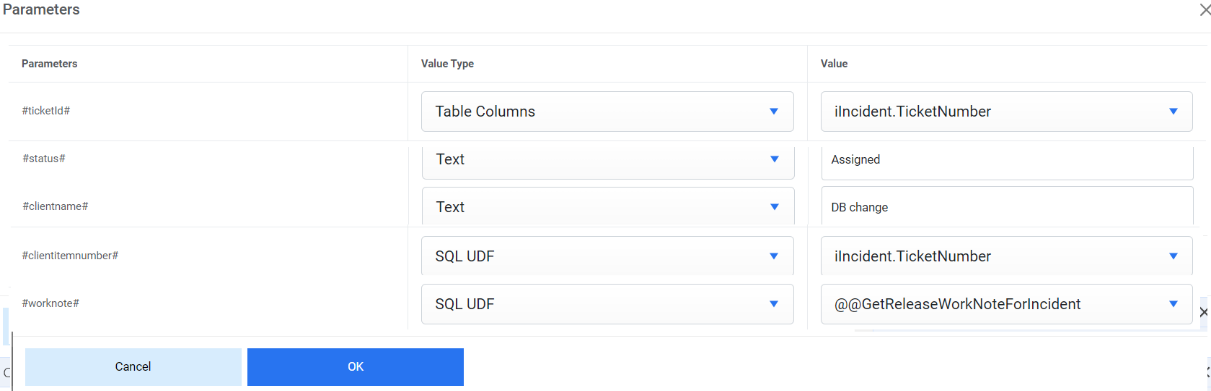
- Click OK.
- Click Save Rule.
Integration with Event Management Tools:
Any Event Management tool acts as a data source for iAutomate from where it pulls the event or Probable Root Cause data and then performs appropriate actions for resolution. Thus, to enable integration with Event Management, it requires a data source to be created as part of iAutomate configuration.
Before proceeding with the configuration related to Data Source creation, the user must ensure that an organization has been configured. If not done already, please refer to the Configuration Guide for the same and create the organization before proceeding ahead.
Please note that for integration with Event Management tool; while creating the organization, users need to select the Event Management tool from the dropdown.