
Ingest profiles
You can use Ingest profiles to define Java extensions for SQL database data extraction and to define data transformation logic. Ingest profiles are bound to connector pipes and executes as part of the pipe process.
- 1. Data Extraction
- You can assign default SQL to a flow file attribute
ingest.database.sqlso that optional downstream SQL providers implemented in Java can perform additional modifications to it. - 2. Data Transformation
- You can use a list of optional Java pre-processors to modify the database result set before sending it to the default transformation logic. You can also provide another list of optional Java post-processors. These can perform additional customization against the Elasticsearch document being generated by the default logic, before sending it to Elasticsearch for indexing.
You develop and build these custom Java extensions the same way as a typical NiFi Processor, inside the NiFi Toolkit in Eclipse.To activate your binaries, you package them and deploy them to the /lib folder inside the NiFi container.
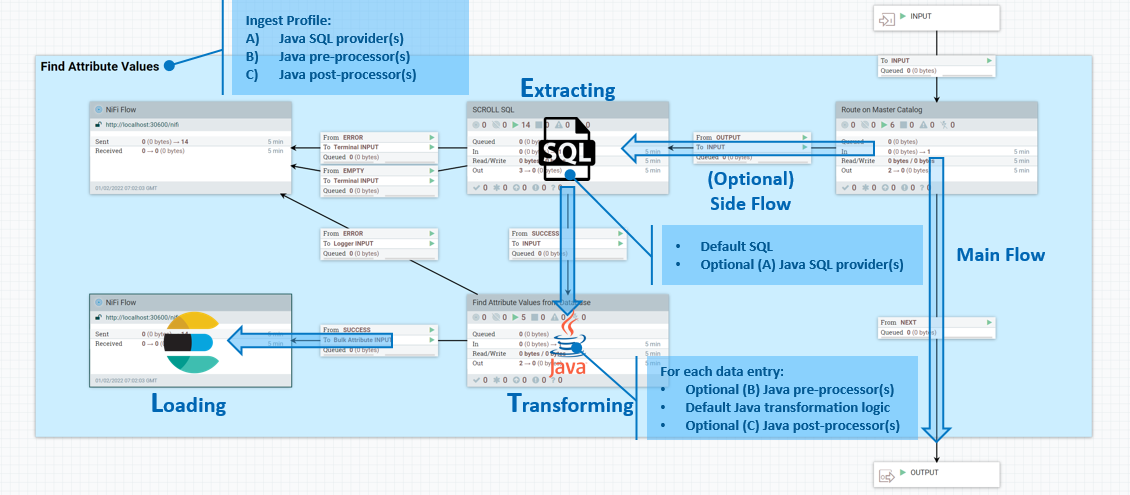
Managing Ingest profiles
profileType=Ingest
that has been added to the existing profiles API in the Query service application.
You can find the endpoint at
http://query_host:query_port/search/resources/api/v2/documents/profiles?profileType=Ingest Note that /profiles contains a directory,
custom, with three further subdirectories in it:
ingest, nlp, and
search. You can place custom profiles in the appropriate
subdirectory. Doing this allows your custom Data Query images to include their own
custom configurations. These can then be built using your own CI / CD pipeline. In
this way, your images can be reused in multiple environments, without requiring you
to use configurations from the environment-specific ZooKeeper.
Note that /profiles contains a directory,
custom, with three further subdirectories in it:
ingest, nlp, and
search. You can place custom profiles in the appropriate
subdirectory. Doing this allows your custom Data Query images to include their own
custom configurations. These can then be built using your own CI / CD pipeline. In
this way, your images can be reused in multiple environments, without requiring you
to use configurations from the environment-specific ZooKeeper.
For more information about the Query API, see Query service API specifications.