









 Single-instance
versus multi-instance environments
Single-instance
versus multi-instance environments
Prior to in Fix Pack 2, WebSphere Commerce already supported single instance Oracle environments. With Fix Pack 2, WebSphere Commerce adds support for multiple instance Oracle environments.
WebSphere Commerce and single instance Oracle environments
- The production system mainly provides the services to the internet users, or shoppers.
- The authoring system mainly provides the services to the intranet users, such as the administrators and business users.
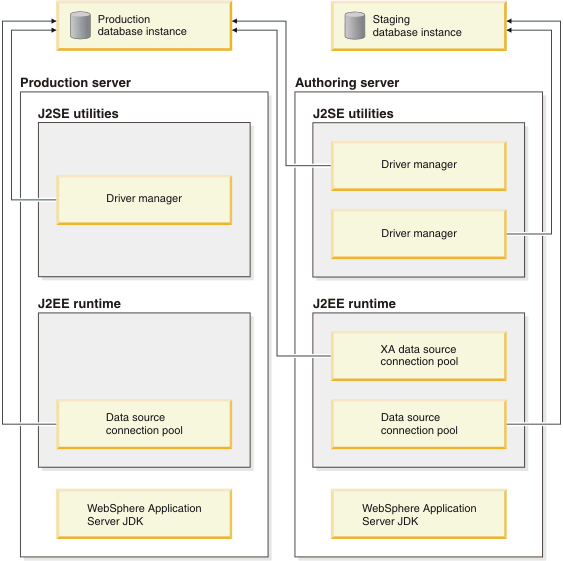
- runtime functions running as a J2EE application on top of WebSphere Application Server
- command line utilities, for example, dbclean, running as J2SE applications
The authoring system has a similar configuration to the production system. In addition, the authoring utilities, such as stagingprop and stagingcopy, need to connect to both production databases. These utilities are long running applications that use the JDBC driver manager to make database connections. They probably do not require much workload balancing and failover. Furthermore, the Workspace QuickPublish function in the authoring system uses both the distributed transaction and the XAdata source connect pool to connect to production database, and use the non-XA datasource to connect to authoring database. Special settings are needed in the XADatasource for QuickPublish if the QuickPublish and workspace is needed.
WebSphere Commerce and multi-instance Oracle environments
WebSphere Commerce, as a J2EE application, can be configured in different ways to work with Oracle RAC. For instance, you could choose to use Oracle implicit connection cache or WebSphere Application Server data source connection pooling. We recommend you use Oracle single client access name (SCAN) to connect to Oracle RAC.
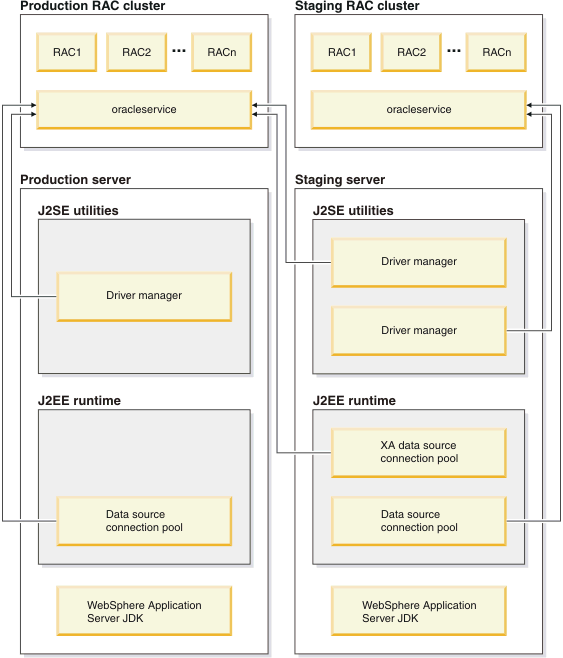
In
production RAC cluster server-side, multiple instances (RAC1, RAC2,…
RACn) can be created, and at least one Oracle service needs to be
created, for example, oracleservice.
In
authoring RAC cluster server-side, multiple instances (RAC1, RAC2,…
RACn) can be created, and at least one Oracle service needs to be
created, for example, oracleservice.