Customization and Extension Framework
The canonical model is intentionally designed to allow controlled customization without compromising the standardized architecture. Extensions are managed through a structured framework that maintains consistency across implementations and subject areas.
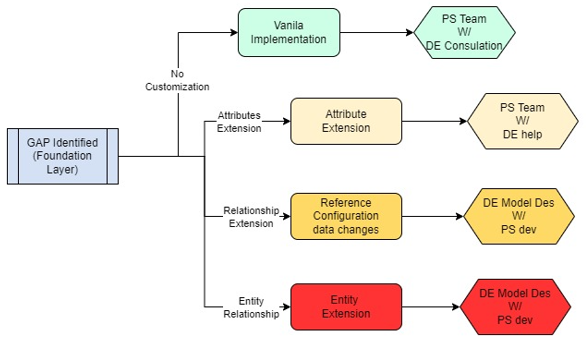
Levels of Customization
Level 0: No Customization (Strict Canonical)
Description: Use the canonical model exactly as defined. Apply only standard transformations.
When to Use: When subject areas perfectly match canonical definitions.
Scope: No structural changes; configuration only through metadata tables.
Example: Party subject area typically requires minimal customization.
Roles played: PS Teams leads vanilla implementation as per the redbook with consultation with DE for any support needed.
Level 1: Attribute Extension (Low Impact)
Description: Add new attributes to existing canonical entities using the flexible ATTRIB_* columns.
When to Use: When adding a few client-specific or domain-specific attributes.
Scope: Limited to 5 flexible attributes per entity (attrib_1 through attrib_5).
Example: Adding a "customer_segment_code" attribute to the Party entity.
Roles played:
- Tech BA - Gaps identified through foundation layer that represents difference in attributes to be added for an entity
- DE -
- Identifies the requirement of attributes being added for creating new or mapping to existing attributes
- Changes the Model accordingly
- Generates LDZ - RDV code through meta data model
- PS -Dev -
- Works with the Tech BA / DE team to finalize the addition of attributes.
- Develops ETL according to the data structures created through change in the model
Level 2: Relationship Extension (Medium Impact)
Description: Existing Reference values do not map with the Client specific values and GAP identified to make changes accordingly.
When to Use: Inherent reference data values (i.e. account type) has separate reference set from client side
Scope: Map the reference values with existing one and generate any snippet changes that refer to reference values.
Example: Event names are indifferent for clients and they need to club, map in standardized form to map into 360 calculations.
Roles played:
- Tech BA - Gaps identified through foundation layer that identifies Impact on existing Reference data
- DE -
- Analyzes overall impact and list out of plan of action with estimated changes required
- Provides change development requirement to PS
- Provides specific data changes to PS
- Provides changes in 360s if needed
- PS -Dev -
- Works with the Tech BA / DE team to understand the Development requirement.
- Develops ETL according to the data structures created through change in data entities and ETL
Level 3: Entity Extension (High Impact)
Description: Add entirely new entities (Hubs) not in the canonical model.
When to Use: When a completely new subject area or business entity is required.
Scope: Creates new Hub table with corresponding Link and Satellite tables.
Example: Adding a Partner/Vendor entity for B2B use cases.
Roles played:
- Tech BA - Gaps identified through foundation layer that represents list of additional entities and its relationships
- DE -
- Identifies model changes , works with Stakeholders and BA to finalize the changes
- Changes models under client specific version
- Generates LDZ - RDV code through meta data model by making meta data entries
- Changes 360s to absorb the required enhancements across feature lists.
- PS -Dev -
- Works with the Tech BA / DE team to to review and finalize the changes
- Prepares ETL bespoke additional development requirement
- Develops ETL according to the data structures created through change in the model till LDZ