Understanding LLM guard models
Starting with version 14.5.1, Domino IQ supports the use of guard models alongside large language models (LLMs).
An LLM guard model ensures ethical and secure interactions when accessing Domino IQ from your applications. The guard model acts as a protective layer, helping to prevent the generation of harmful or inappropriate content, data leaks, and other risks linked to LLMs.
Multiple LLM guard models are available for use, such as Meta’s Llama Guard 3, IBM’s Granite Guard 3, and Google’s ShieldGemma. These models are typically trained to ensure that LLM-based applications operate within acceptable boundaries and greatly reduce the chances of prompt injection or jailbreak attempts.
Domino IQ can use a guard model to automatically make decisions about the content in real time. The guard model usually classifies the content into one of two categories: risk or not a risk. The guard model also has a risk guideline to determine which risk categories apply to the content. Please refer to the reference information for each guard model for a detailed description of its risk categories. As examples, see information for ShieldGemma or information Llama Gurad 3.
How a guard model works with your Domino IQ
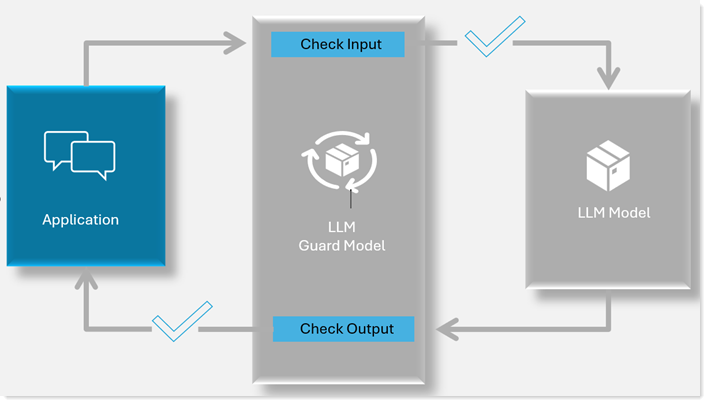
- The guard model gets enabled in your existing Domino configuration
- If Domino IQ is enabled for local mode, you need to either manually place the guard model file in the llm_models directory on the Domino server, or let the server download it automatically when you create the Guard Model document. Once you enable the guard model configuration, the local AI inference server will automatically load the guard model along with the large language model.
- What happens once your guard model is enabled
-
- Guard checks input
When an application submits a request to a large language model (LLM) through Domino IQ with the guard feature enabled, Domino IQ first evaluates the request content—including both the system prompt and user input—using the guard model. If the guard model classifies the content as "Safe," the request is forwarded to the LLM. If the content is deemed "unsafe," Domino IQ returns the following error to the application: DominoIQ Guard: The content of the request is inappropriate and cannot be processed. The application developer is responsible for implementing appropriate error handling. In cases where the input is “unsafe,” the end user will not receive a response from the LLM.
- Guard checks output
The output validation feature can be enabled or disabled by the administrator during Domino IQ guard model configuration. When enabled, any response generated by the LLM is evaluated by the guard model for safety. "Safe" responses are returned to the application, while "Unsafe" responses are blocked and an error is triggered: DominoIQ Guard: The content of the response is inappropriate and cannot be processed. Application developers must handle these errors and notify end users accordingly.
Note: For asynchronous LLM queries, responses are delivered in chunks. Each chunk is individually evaluated by the guard model. Chunks classified as "Safe" are returned to the application; if a chunk is deemed "Unsafe," an error is triggered, and the response stream is terminated. Developers must implement error handling to inform end users and determine how to process any previously received safe chunks.
- Guard checks input
For detailed steps on adding a guard model to your existing Domino setup, see Adding model documents. Then see either Adding a Domino IQ Configuration for Local mode or Adding a Domino IQ Configuration for Remote mode.