Adminstration features
Domino 14.5 provides the following new features and enhancements related to administering.
AdminCentral app enhancements
Enhanced Activity Log Page and Registration:
- If there are custom password policy settings assigned to the user's policy, AdminCentral will generate passwords as part of user registration.
- The look and feel of the Registration Profile page is improved by organizing
related fields under tabs in the form.
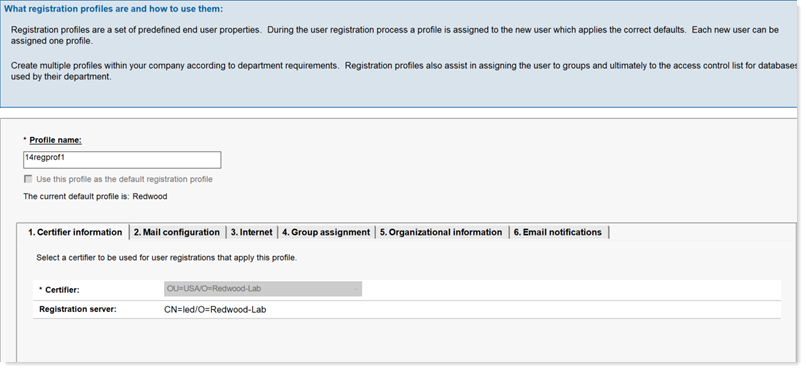
For more information, see Setting up a registration profile in AdminCentral.
- On the log page, in addition to filtering requests by their status (errors, pending, complete), administrators can now sort on these column heads: Admin (administrator name) and Status (date completed). Note that new sorting option does not apply to mobile devices.
Replication enhancements
New PIRC (Purge Interval Replication Control) column

For more information, see Limiting the contents of a replica.
Bulk approval of replica deletion requestsUnlike the previous release where administrators can approve only a single "Approve Replica Deletion" request, you can now select and approve multiple of these request types under the Pending Administration Approval view.
Introducing Domino License Administration (DLA)
The Domino License Administration (DLA) database (dominodla.nsf) automatically collects server and user information for a single Domino domain. It uses this data to classify users by license type, and features a license dashboard that displays the latest reports. For more information, see Administering Domino licenses with DLA
DAOS repair enhancements
The following repair options have been added:
- Repairing a single .nlo file
You can now check if an .nlo file is missing and repair if necessary. This command can be useful for scenarios like restoring a database from a backup.
-
Repairing all .nlo files for a database
This new variation checks each .nlo file attached to a specific database and repairs as necessary. This command is useful in cases where a database is restored from backup.
- Dynamic repair of .nlo files
If an attempt to read a .nlo fails because the file doesn't exist, then a repair will be attempted dynamically.
DAOSTune estimation tool
DAOSTune is a new application for estimating object size to help Domino administrators decide which minimum size to use for DAOS. For more information, see the article DAOSTune Estimation Tool for HCL Domino and how it is used on the HCLSoftware Support site.
Domino SNMP Agent for Linux updates
On the Linux platform, the former way of using SNMP under init-d is moved to systemd. New scripts are added to support SNMP under systemd. For more information, see Configuring the Domino SNMP Agent for Linux.
DBMT tool updates
- The following DBMT tool command line options are added:
- -regex (-re for short)
- -systemDbs (-sd for short)
- -validateDbs (-vd for short)
For more information, see Running the database maintenance tool from a Program document.
- Regular expressions allow the administrator to use a template that takes advantage of special characters to select which databases the DBMT tool will work on. For more information, see Regular expressions for the DBMT tool.
New options for Design task
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -sd | Refresh design of System Databases. |
| -sdm | Refresh design only if current server is Administration server of database. |
| -mt name | Mail design update log to the Internet Address name. |
For more information, including a list of System Databases, see Synchronizing databases with master templates.
SNMP update
Domino's SNMP support now include stats for CertMgr, HTTP, DAOS, and Security in the Domino.mib file.
Administrator Client Files panel updates
- now includes options for to display columns for Large Summary property and DAOS Tier 2 full-text indexing on the Files panel.
- On the Files panel, in the Tools pane, options when creating one or more full-text indexes for a database now include the Index DAOS Tier 2 attachments option. See Creating and updating full-text indexes for single databases.
Documentation update: Disaster recovery
A new section augments the backup and restore documentation for the Domino server, specifically for disaster recovery of Domino databases, which include NTF and NSF files. This addition helps ensure that critical data can be recovered in the event of a disaster, thereby maintaining the integrity and availability of essential information. To learn more, see Disaster recovery.