The RFC_READ_TABLE is a very widely used RFC in ECC. Special
functionality has been added to make working with this call as easy as possible. Normally,
the data returned by RFC_READ_TABLE comes in the table DATA, which has one column of text
512 bytes wide. It is normally your job to parse this field and reconvert the text values to
the proper data types that exist in the SAP table's "was is" being read.
About this task
Optional functionality has been implemented that passes a structure (the table that you
want to read) back to you. This means that you do not need to work with the table DATA
or worry about parsing and converting the data in it. The SAP Connector will do this for
you.
In the following description of how to activate this functionality, assume that you are
reading from the ECC table KNA1.
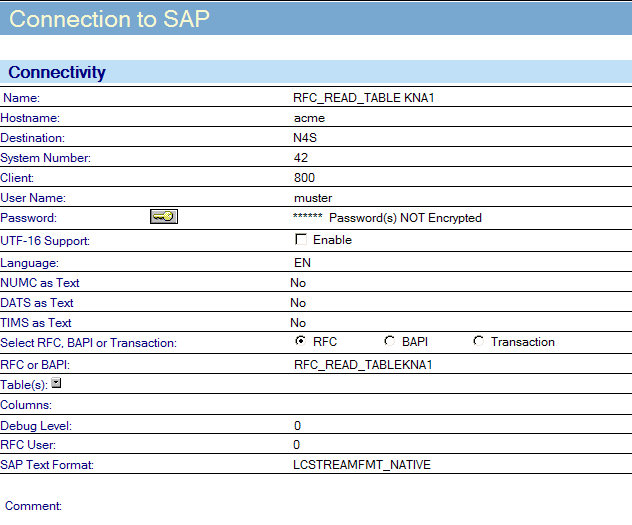
To enable this functionality, you need a properly configured SAP connection document.
Complete the connection document fields as you would for any other RFC/BAPI, with one
exception. In the field Function Module, instead of entering RFC_READ_TABLE, enter
RFC_READ_TABLE with the name of the table you want concatenated to the end of it. For
example, to read table KNA1 enter RFC_READ_TABLEKNA1 for the Function Module name.
Procedure
-
A properly completed SAP connection document to read table KNA1is shown
below.
-
Create an activity document to use this connection.
-
The first example shows how to use a Direct Transfer activity. The second
example shows how to prepare a Virtual Fields activity.
-
Create a new Direct Transfer activity, and select your SAP connection document
as the data Source.
-
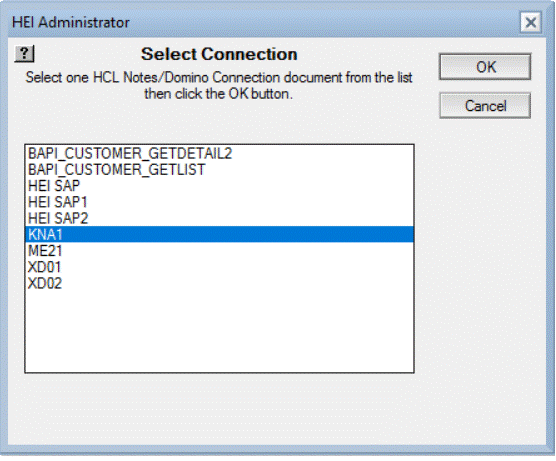
Click the Select Metadata option button (down arrow button) in the Source
section.

A dialog box with a list appears. Even though KNA1 is not a table found in
the interface of RFC_READ_TABLE, it appears in the list.
-
Select the table KNA1 as your metadata.
- After you have selected your Target connection document, you may do field mapping. The SAP
connector will now supply only the KNA1 column names in the mapping dialog
box.
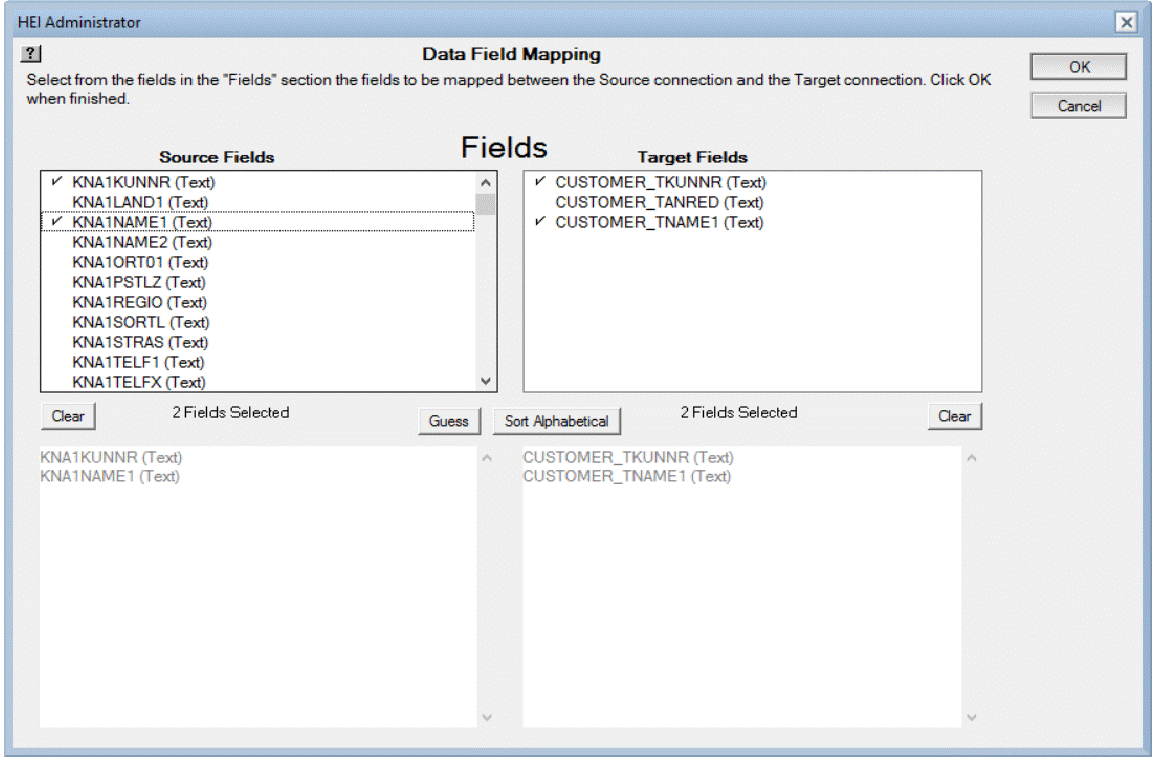
The field names follow the same syntax as any other table -- the field name
is the table name concatenated with the column name.
Do not use Automatic Field Mapping unless you plan to read every single
column available in your table. In order to maximize performance, the
non-wanted columns of the wanted table are not initialized, KNA1 in this
case, with valid data for each possible data type. You must specify in the
Select Statement which columns you actually want to get from your table.
The Select Statement behaves like that of any other RFC/BAPI, except that the
only required parameters are values for the FIELDS table. You must enter the
field names to be read from your table.

Note: In this example, the connection needs to read two columns, KUNNR and
NAME1, from each row in table KNA1. You can also add additional criteria
in the OPTIONS table.
Note: If you specify that the Number of Records to Transfer Concurrently is
1000 or 5000, instead of the default of 1, your performance will be much
better.





