Problem Management
Process Overview
- Problem Management aims to manage the lifecycle of a problem and to minimise both the number and severity of incidents and potential risks to the Business/ Organisation.
- It is the responsibility of the Problem management process to ensure that incident
information is documented in such a way that it is readily available to support all
problem management activities.
Problem Management activities include:
- Problem Identification
- Problem Logging
- Problem Categorization and Prioritization
- Problem Investigation and Diagnosis
- Problem Resolution
- Problem Closure and Evaluation/ Review
Key Definitions
- IT Service: A service provided to one or more customers by an IT Service Provider. An IT Service is based on the use of Information Technology and supports the customer’s business processes. An IT Service is made up from a combination of people, processes and technology and should be defined in a Service Level Agreement (SLA).
- Incident: An Incident includes any event which disrupts, or which could disrupt a service. Incident can be raised as a reactive or proactive work item on an existing service request by a Consumer.
- Problem: A problem is the underlying cause that leads to an incident. A problem may be something that could lead to the same incident occurring again or lead to another incident entirely. It is essentially the root cause of an incident.
- Change: Any addition, deletion or modification in IT Infrastructure which can cause positive or negative impact to IT Services.
- PIT (Problem Investigation Team): Problem Investigation Team (PIT) aims to investigate and diagnose the root cause of a problem.
- Known Error: A Known Error is a problem that has a documented root cause and a workaround.
- KEDB: Known Error Database (KEDB) is a repository that holds information about problems for which the root cause is known but a permanent solution doesn't. Either the permanent solution does not exist or has not been implemented yet. KEDB must be maintained outside HCL BigFix Service Management.
- Workaround: A workaround is a temporary way to restore Service failures to a usable level.
- Task: Tasks are designed to perform specific level of work with a specific output.
- Impact: Impact is a measure of the effect of an Incident, Problem, or Change on business processes. Impact is often based on how service levels will be affected.
- Risk: It is an uncertain event that can either have a positive or negative impact on the business process.
- Configuration Item (CI): CIs are the components or service assets that needs to be managed to deliver an IT service. Information about each configuration item is recorded in a configuration record within the configuration management system and is maintained throughout its lifecycle by service assets and configuration management.
- Root Cause Analysis (RCA): An Activity that identifies the Root Cause of an Incident or Problem. RCA typically concentrates on IT service failures.
- Reactive Problem Management: Reactive Problem Management reacts to incidents that have already occurred and focuses effort on eliminating their root cause and reoccurrence. The focus of Problem Management is to increase long-term service stability and consequently, customer satisfaction. It deals with an existing problem, mostly in response to one or more Incidents, to find a solution as the permanent fix.
- Proactive Problem Management: Recognising a potential problem and finding a solution that prevents it occurring in the first place. Proactive Problem Management is a continuous process that doesn’t wait for an incident (or series of incidents) to happen to react; it’ is always active and on guard. Even though Reactive Problem Management relies heavily on other Service Management components, Proactive Problem Management relies even more.
Roles and Responsibilities
| HCL BigFix Service Management Roles | Permissions |
| Problem User | To be able to see Problem tickets of own Problem Management Groups. |
| Problem Manager | To be able to see Problem Tickets across Problem Management Groups of own/ associated companies (to which it provided support). |
| Problem Investigator | Read/ Write access to assigned problem work items in HCL BigFix Service Management. |
| Problem Submitter |
Identify potential problems and create Problem records in the Service Management tool. ▪ Relate the configuration item, incidents, related problem records (if existing already), change records and any Known Error Database (KEDB)/ Knowledge base (KB) articles in the problem ticket. ▪ Add all additional information about any temporary fixes or workarounds already used in service restoration for incidents. ▪ Append any system log files, screenshots or any other form of technical information that may help the investigation team understand the issue better and if required, re-create the scenario in lower environments for investigation purposes. ▪ Use discretion and ‘Pain Value’ principles while submitting the Problem records. ▪ Provide any further information during the course of Problem Investigation and resolution and remain available for additional support during the lifecycle of the Problem record, as required. |
| Process Owner |
Approves Problem Process and policies. ▪Understands the underlying principles, processes, enabling tools and technologies. ▪Reviewing and approving Problem management policy and Process. ▪Owns the Problem Management Module & KEDB. ▪Participates in Global/ regional Problem Management review meetings to prioritize the resolution of Problems. |
| Problem Investigation Team (PIT) |
Aggregate and correlate all available information to suggest a meaningful direction for the root cause investigation. ▪Perform root cause analysis and adequately document within the service management tool the root causes as well as the rationale used in determining the root causes. ▪ Review the temporary fixes and workarounds already used and validate them for future use. ▪ Evaluate and propose options for permanent solutions and advise on the viability and cost effectiveness of the various available options. ▪ Design in sufficient detail, the technical aspects of the solutions that are finalized for fixing the identified problems. ▪ Whenever required, raise Change requests for implementation of the proposed solutions. ▪ Participate in the Change Management Post Implementation Review for the changes requested for Problem Management activity, to ensure that the changes have been implemented correctly and completely. |
| Problem Manager |
▪ Receive and act timely on all Problem records by evaluating, analyzing and accepting or rejecting the newly requested Problem records. ▪ Constituting correctly skilled teams for investigating and resolving the Problems. ▪ Understanding the tasks that will be required from various teams and creating/adding such tasks against appropriate teams for all activities required to complete the work on Problem record. ▪ Follow criteria for prioritization of problems, in accordance with agreed priority Levels. ▪ Convene and lead the discussions required across teams in their Tower, in order to establish initial clarity on the course of investigation, solution definition, solution implementation and KEDB/KB updates required for each Problem record. ▪ Specify the time-task expectations from each engaged group/task owner and if required, follow up or escalate if the progress is not made as per the expected time/ quality. ▪ In a timely manner, actively engage other roles of Problem Management Process (Investigator, KEDB Administrator, Solution implementer etc.). ▪ Manage end-to-end problem lifecycle including detection, diagnosis, root cause analysis, known error recording, repair and recovery (if approved). ▪ Provide inputs and feedback to the Technical Management staff on the resource quality as well as sufficiency, policies and any other operational optimizations as may have been witnessed incidentally while working on Problem records with various teams. ▪ Escalate to Stakeholders if corrective actions are not being taken and foresee the Problem Team to improve services. |
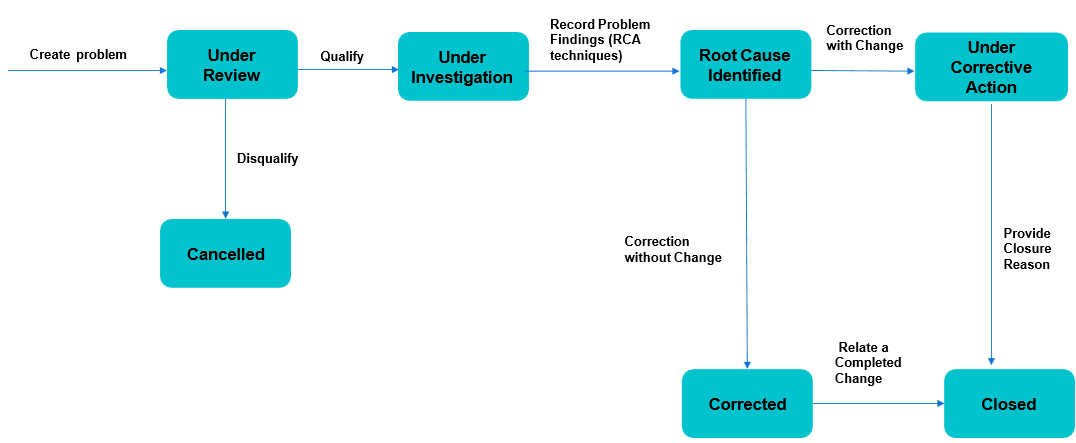
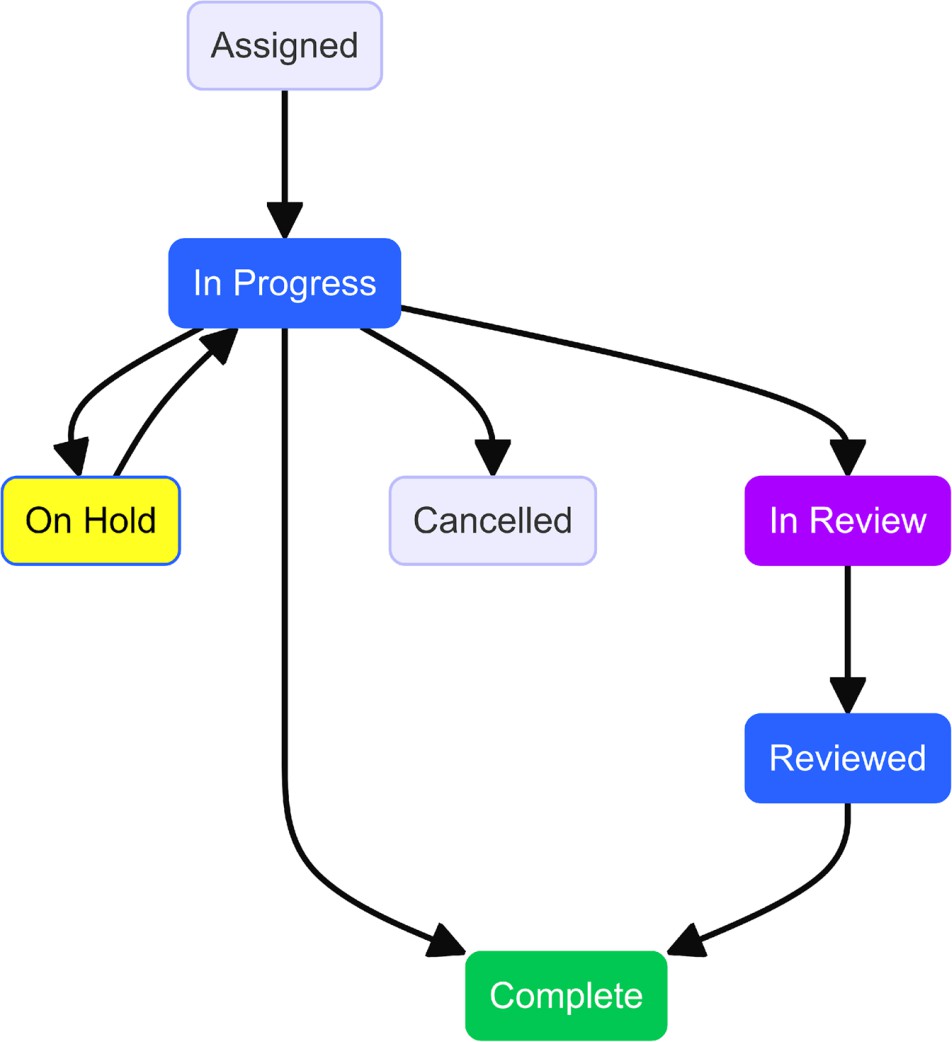
Problem Status Transition
Product Walkthrough (Problem Work Item)
Logging into HCL BigFix Service Management
To login, the user should:
- Open internet browser (Edge, Chrome) and enter the URL: https://support.dryice.ai
- Provide login credentials to authenticate and login to HCL BigFix Service Management.
.png)
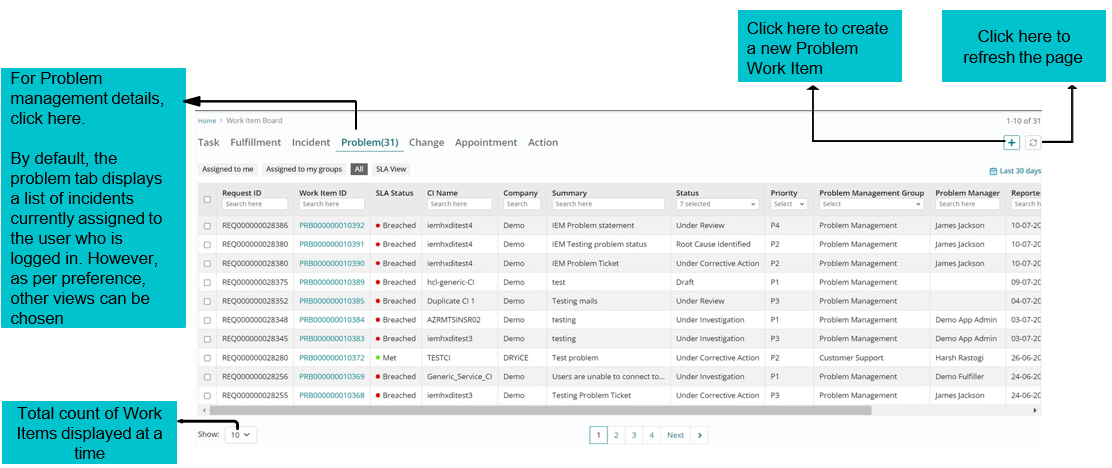
Landing page of Work Item Board
From the Application Menu, click on the Work Item Board.
Click here to refresh the page
Click here to create a new Problem Work Item
The User will be presented with the current Work Item Board.
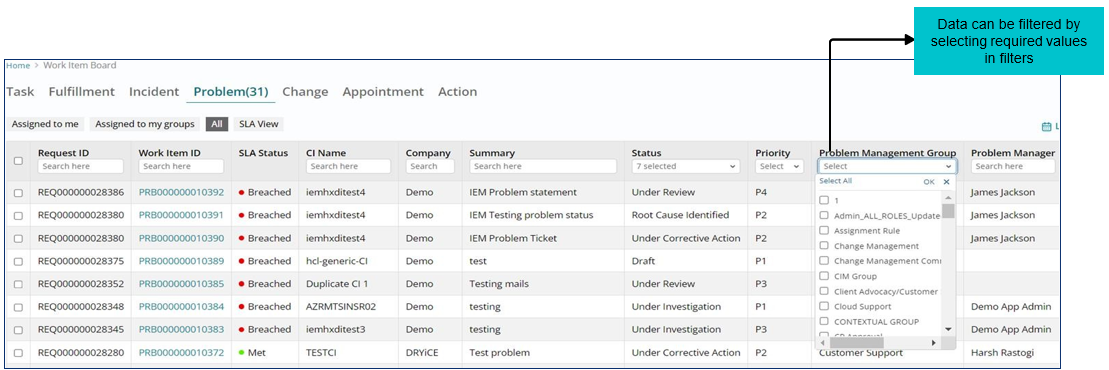
Sorting of Problems on Landing Page
Support users can sort Problem Work Items based on various filters available on the landing page of work item board.
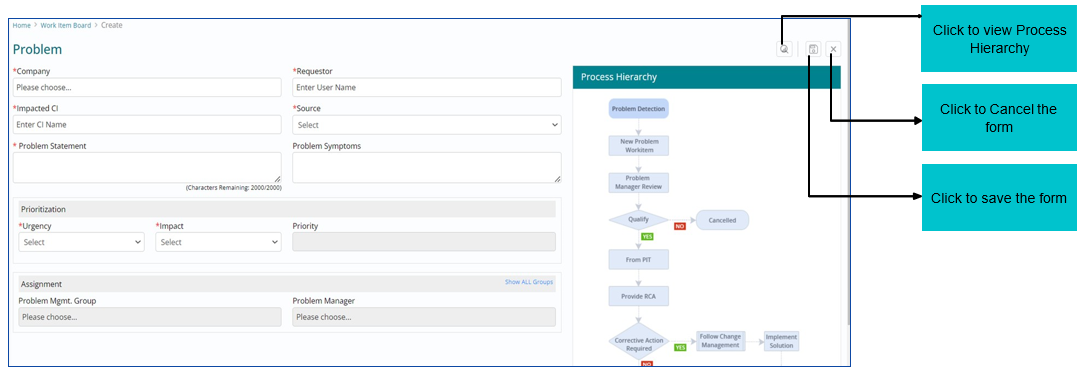
Creating a Problem Work Item
To create a Problem Work Item, all mandatory fields need to be filled in the below form.
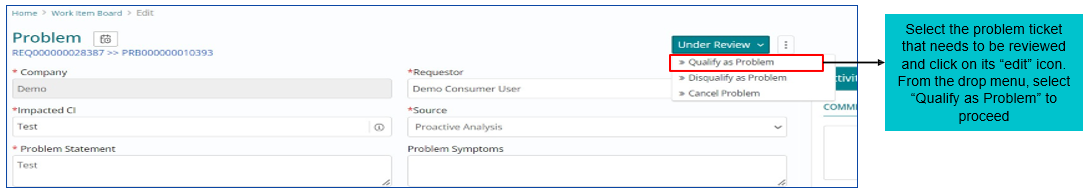
Qualifying a Problem Work Item
Work Item needs to be reviewed for correctness and consistency by the Problem manager who will have to Qualify as Problem to move ahead with the lifecycle.
Problem Ticket can be Qualified, Disqualified or Cancelled by Problem Manager.
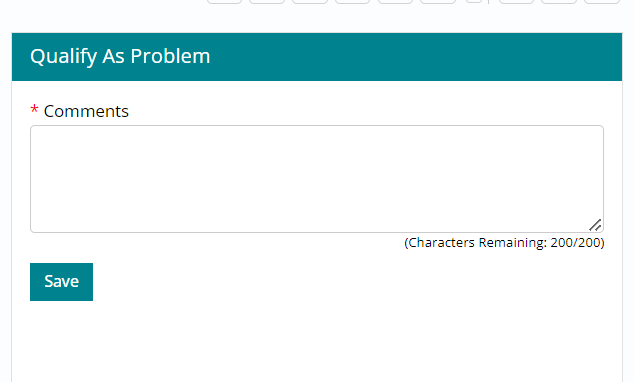
 Justification needs to be entered
in the Comments box. Click ‘Save’. Problem ticket will move to Under
Investigation
Justification needs to be entered
in the Comments box. Click ‘Save’. Problem ticket will move to Under
Investigation
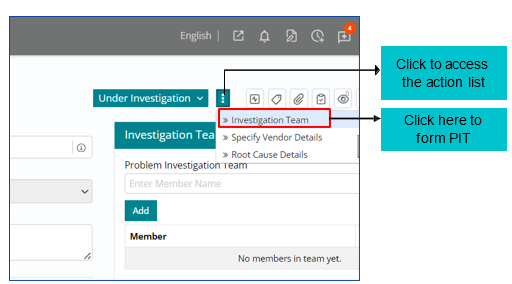
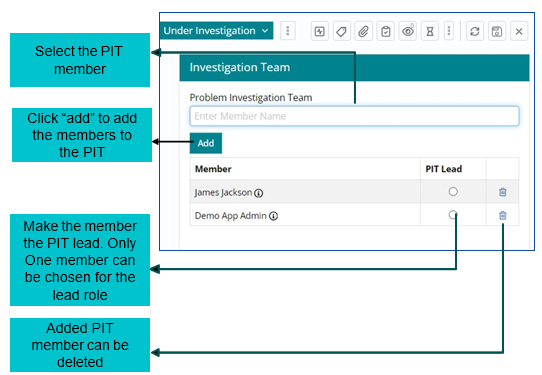
Forming a Problem Investigation Team (PIT)
Once the problem is qualified, Problem Investigation Team (PIT) is formed to investigate and diagnose the root cause of the problem, identify a fix and implement it to restore services to normal as early as possible.
As soon as support user clicks on ‘Investigation Team’ a window will appear on the right where PIT members need to be chosen.
Updating Root Cause
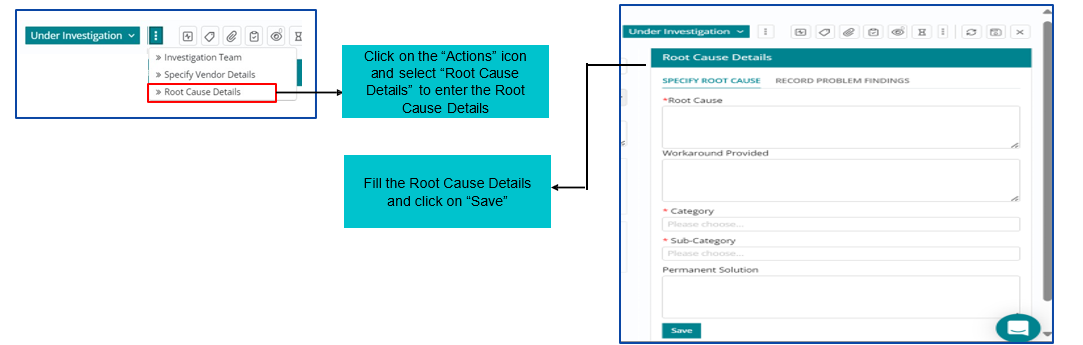
A Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is performed by the support user to identify the key points of the problem and fix the problem.
RCA once done needs to be updated in the tool by clicking on ‘Root Cause Details’ option.
After that user can fill in the Root Cause details in Root Cause Details section of the form and click on Save.
Post adding Root cause Details users can click on Root Cause Identified option to move forward with the Problem Management Workflow.
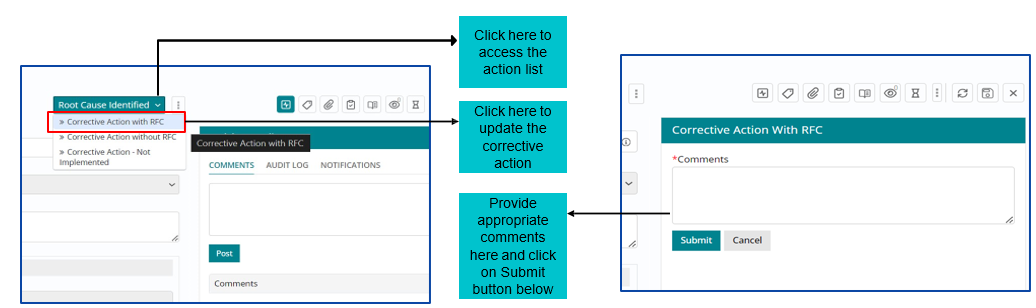
Corrective Action Required
Post adding Root cause Details, user can click on Root Cause Identified option to move forward with the Problem Management Workflow.
Once RCA is completed, Corrective Action needs to be implemented and captured in the tool. Problem fix can require Change/RFC to be implemented.
Proposing a Change from a Problem Work Item
A Change can be proposed to implement the corrective actions for fixing a Problem Work Item. This can be done via a feature available in the tool as shown below.
Once work item is under corrective action then problem manager should Propose a Change.
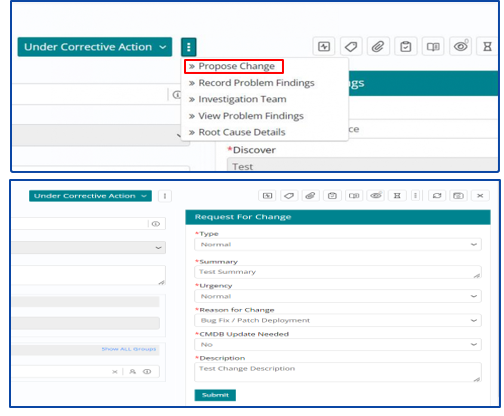
Once the mandatory fields are filled and support user clicks on
Submit, an RFC number will be generated with a message –

As soon as RFC (Request for Change) is created, it will be routed to the Change Management team and will be catered through the Change Management Process based on its priority.
Once Change is Implemented and Completed successfully as per the process, the lifecycle of Problem Work Item will move to ‘Corrected’.
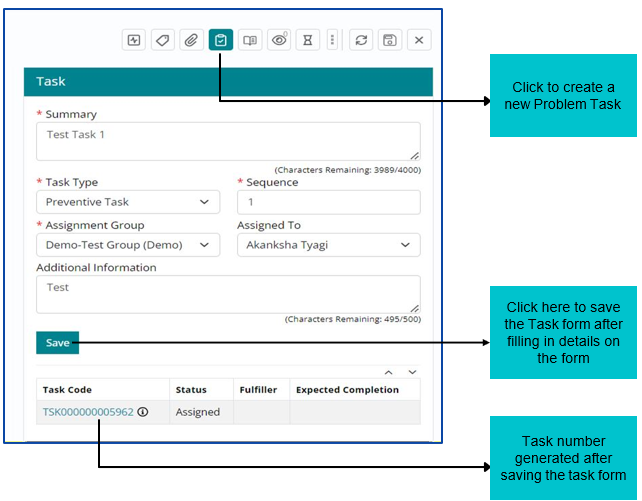
Creating and Assigning Tasks to other support groups
Support User can create and assign tasks for multiple support groups if needed to work on same Problem Work Item.
Tasks can be created and assigned based on following attributes:
- Summary
- Sequence
- Task Type
- Assignment Group – This tab will include all the available groups
- Assignment to – Individual to whom Work Item will be assigned
- Additional Information for tasks being created
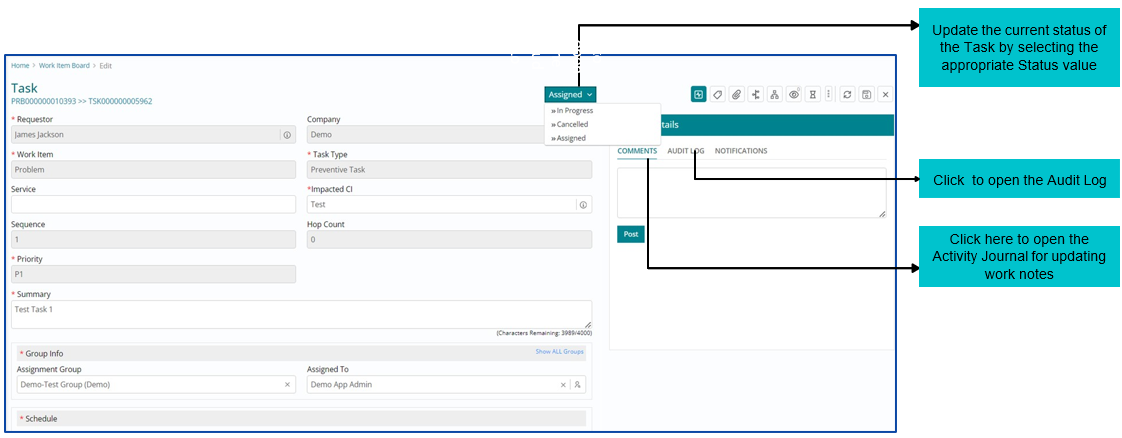
Implementing an assigned Problem Task
Support user will select the Task option on WIB and then he will be presented with the Task Module homepage.
The Support User can view all the Tasks assigned to them on the Task List View page.
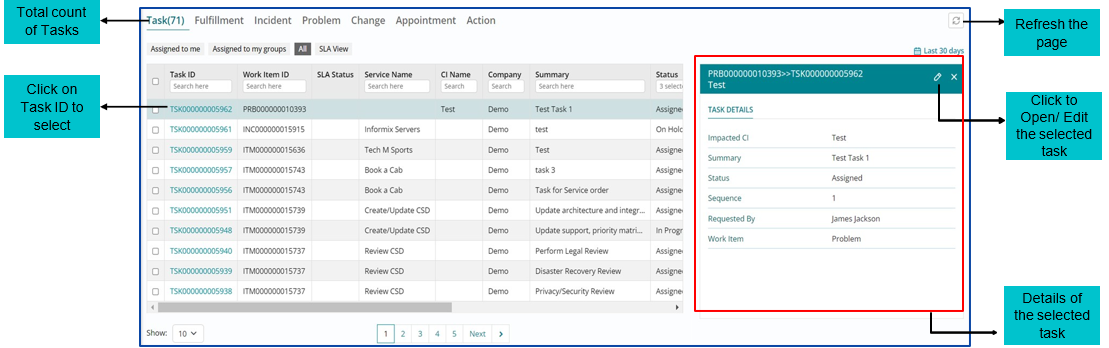
After implementing the Task, the Support User must update the Task status to ‘Completed’.
Corrective Action Without Change
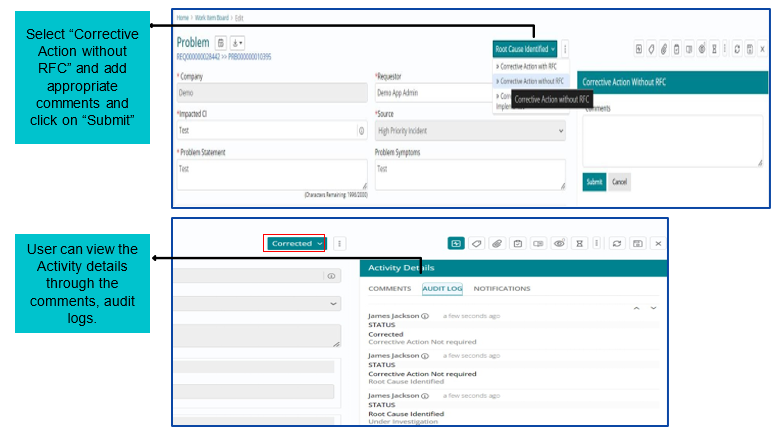
If Corrective Action- without Change is required, then Problem work item will be Corrected. Problem fix does not require any Change/ RFC.
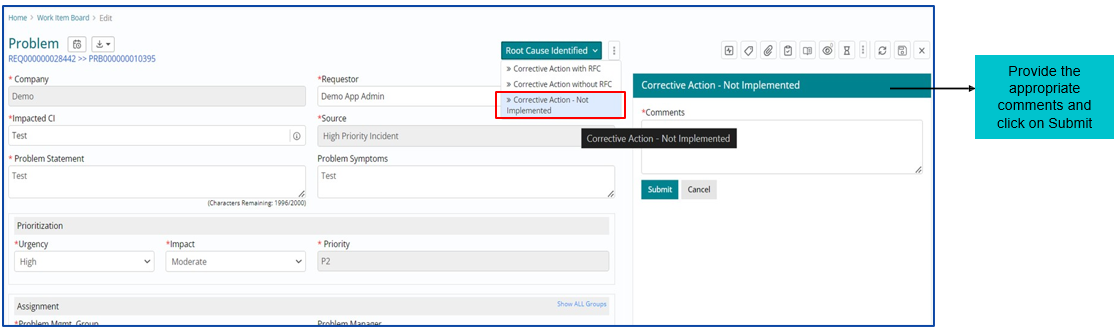
Corrective Action- Not Implemented
If Corrective Action – Not Implemented is required, then Problem work item will be Closed. Problem fix does not require any Change/ RFC.
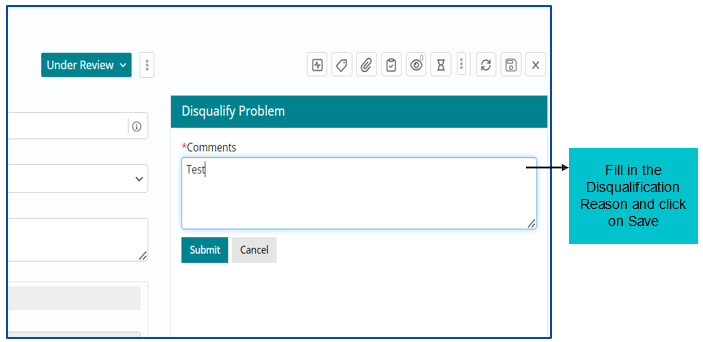
Disqualifying a Problem
Click on the “Action” button to link the appropriate Incident
Problem ticket can also be disqualified and in that case, user needs to attach an incident with the problem to proceed. The user gets a pop up on the screen requesting to link an appropriate incident to the problem to continue.
Under the “More” option, select “Related Work Items” option to attach the incident
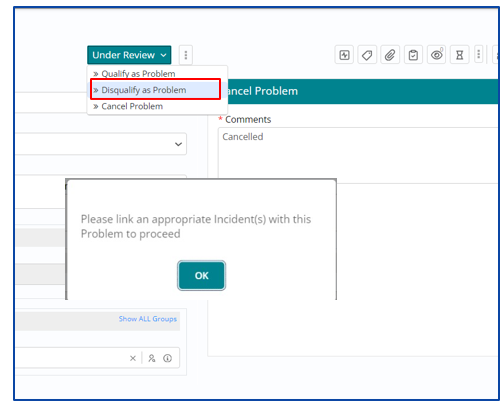
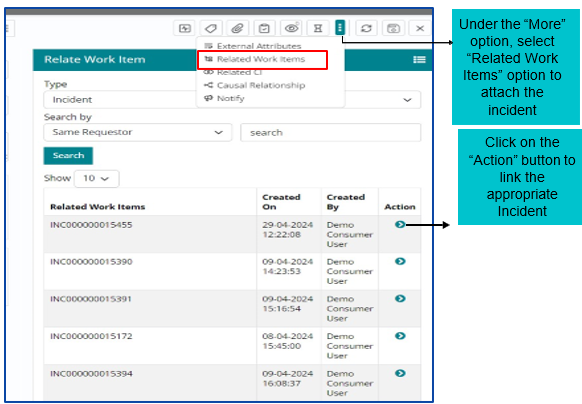
After attaching a related Incident, user must click on Disqualify Problem and then fill in the reason to disqualify post which the problem work item is automatically Closed.
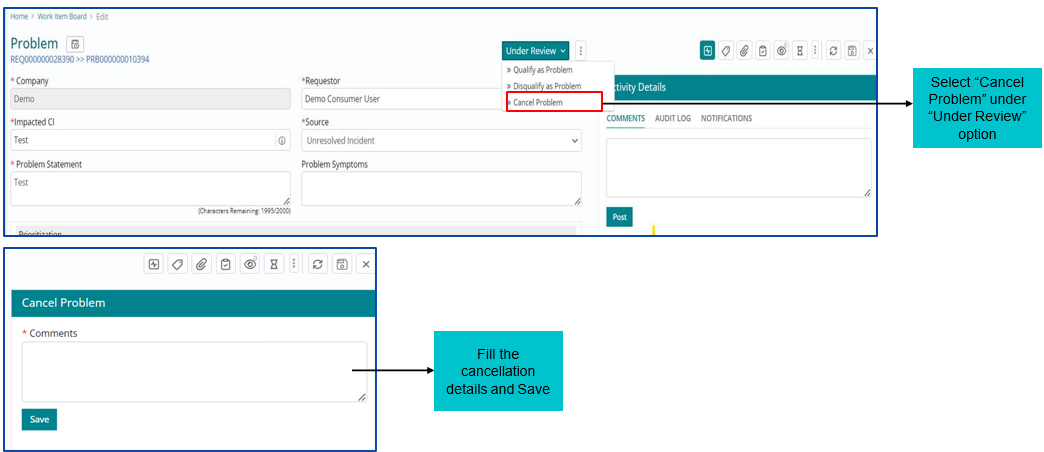
Cancelling a Problem Work Item
A Problem Work Item can be cancelled, in ‘Under Review’ Stage by selecting the option ‘Cancel Problem”.
After providing the reason and saving the form, the problem Work Item is set to Cancelled status.
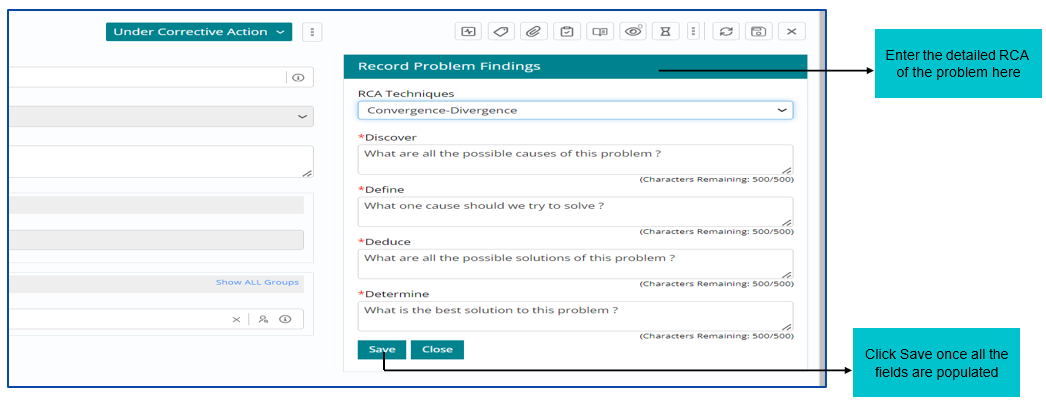
Updating the Problem Findings
Once investigation is completed, support user needs to update the findings under ‘Record Problem Findings’ option.
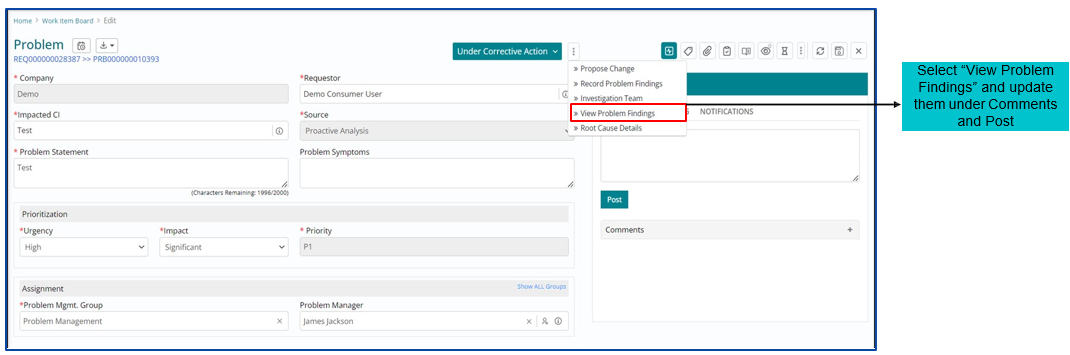
Fill the required details based on RCA Technique selected and click on Save.
Closing a Problem Work Item
Work Item can be Closed once it is
Corrected.
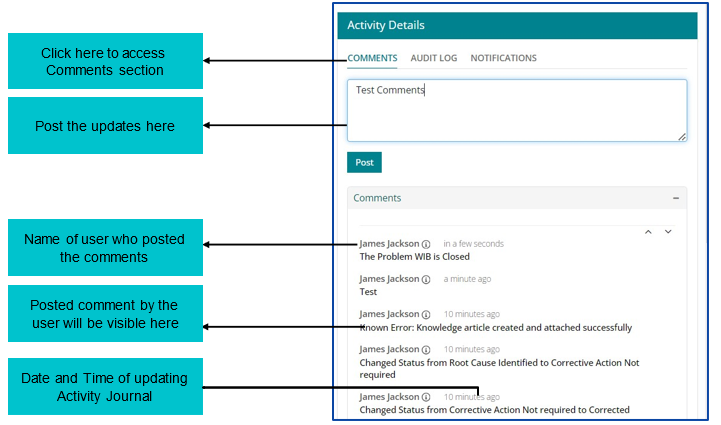
Updating Activity Journal
Support User can update ‘Activity Journal’ for Problem Work Item from the Comments tab under Activity Details section available on the left of the page.
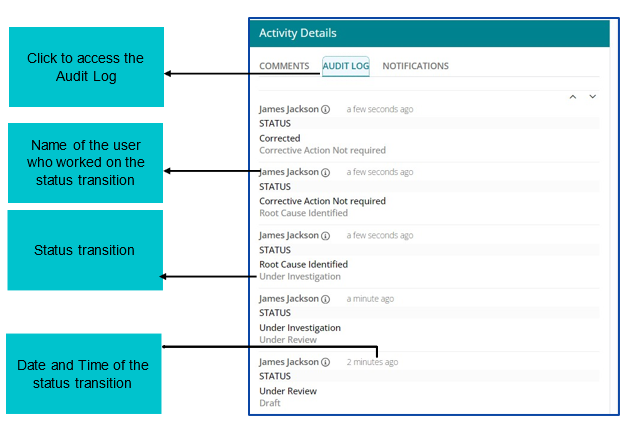
Audit Log
Audit Log captures the status changes throughout the lifecycle of a Problem Work Item.
Custom Attributes
Users can add various Custom Attributes in the form of key-value combination on the Problem Work Item to add any details which the Problem Work Item form does not contain.
Users can do so by clicking on Tags icon on the right.
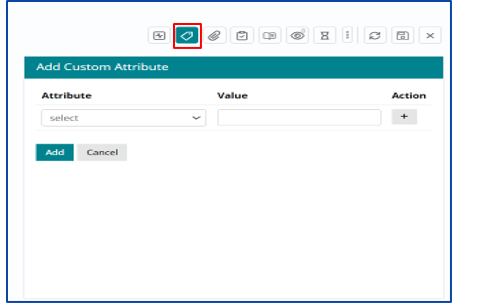
Relating other Work Items or CI with Problem Work Item
Support User can relate other Work Items with existing Problem Work Item anytime if required based on following attributes:
Type – Problem, Incident, Fulfilment and Change
Search by – Item ID, Same Requester and Same Impacted CI
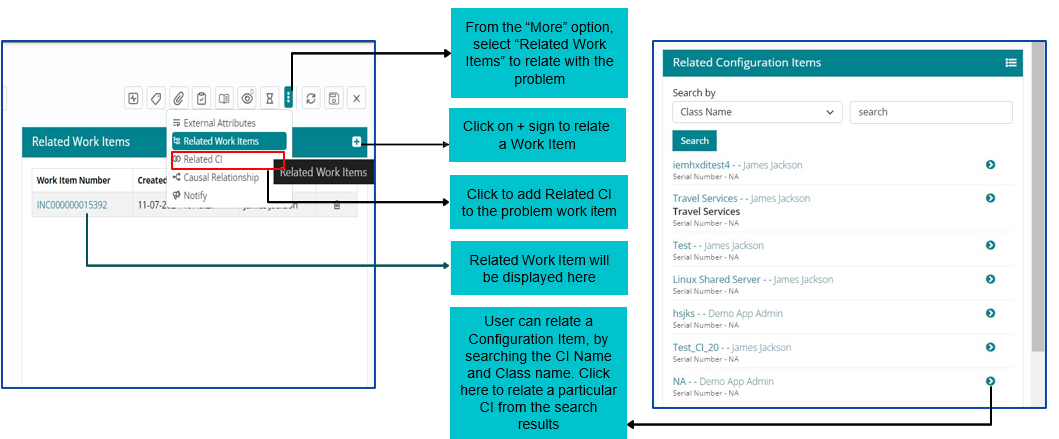
View SLA Details and Related Knowledge Topics
Users can view the SLA details by clicking on SLA icon available on the right side of the page. Users can also view the attached Knowledge Topics by clicking on Relate Knowledge Articles icon.
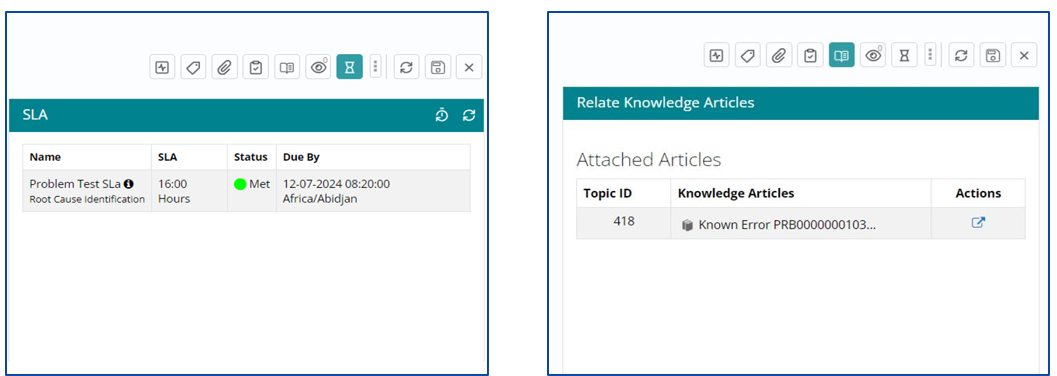
Uploading Attachments
A support user can Provide Attachments supporting the Work Item throughout the Lifecycle of the Problem via the ‘Attachments’ functionality available at each stage.
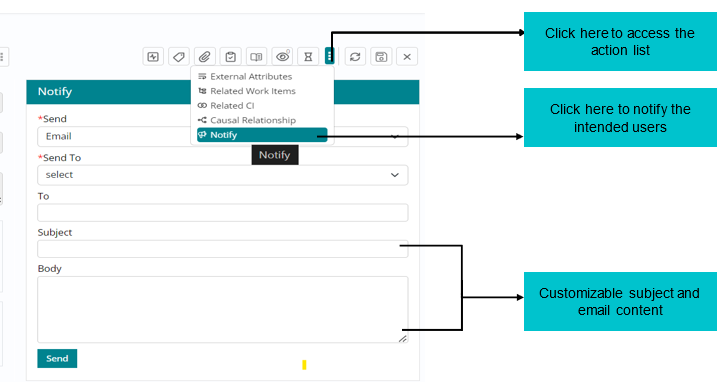
Notifying intended audience about the Work Item
Support User can Notify the intended audience by sending emails to the respective recipients through the Notify feature.
Emails can be sent to a ‘Requester’ or ‘Assigned Group. Support users also have a provision to mention the email ID of any intended individual/ group by selecting the ‘Specify Group’ or ‘Specify Individual’ option under ‘Send To’ field.
Change Management Process Overview
- A change is defined as the addition, modification, or removal of an authorized, planned, or supported service or CI.
- The purpose of the Change Management Process is to maintain the integrity of
the production environment. Change management provides a gateway through which every
change must pass on its way to the production environment. The Change Management Process
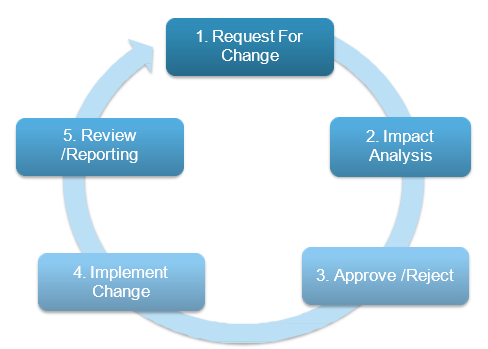
ensures the implementation of changes with minimum risk to the business.Change Management process is broadly fragmented into following steps:
- Preparing for Change
- Define your Change Management Strategy
- Prepare your Change Management Team
- Managing Change
- Develop Change Management Plans
- Take Actions and Implement Plans
- Reinforcing Change
- Collect and Analyse Feedback
- Diagnose Gaps
- Implement Corrective Actions
- Preparing for Change
Change Management Objective
Primary goal of the Change Management Process is to maintain the integrity of the production environment. Change management provides a gateway through which every change must pass on its way to the production environment. The Change Management Process ensures the implementation of changes with minimum risk to the business.
The objectives of Change Management Process are:
- Ensure efficient and prompt handling of changes.
- Provide accurate and regular information about all planned changes.
- Ensure consistent change implementation procedures
- Ensure adequate control measures are in place to minimize failure of change implementation.
- Ensure risk and impact analysis to assess and minimize the risk of implementing changes.
- Monitor and track the lifecycle of all changes.
- Ensure proper categorization of changes and that proper procedures are followed for each type of change.
- Ensure that changes are consistent with business and technical plans.
- Eliminate bureaucracy without compromising change implementation controls.
- Ensure that the Change Management Process complies with statutory requirements.
High Level Process Workflow
Key Definitions
- Change: A Change is defined as the addition, modification, or removal of an authorized, planned, or supported service or CI.
- Normal Change: Normal Change is a change to a service for which the approach is pre-authorised by the Change Management and has an accepted and established procedure to provide a specific change requirement.
- Emergency Change: These are the changes that are required to restore service due to an incident or a change that needs to be implemented immediately to avoid impact. An ECAB is triggered in case of an emergency change which supervises on the approvals, prioritization etc.
- Standard Change: Standard Change (a pre-approved Change) is a Change to a service or infrastructure for which the approach is pre-authorized by Change Management, that has an accepted and established procedure to provide a specific Change requirement. A Standard Change is of low risk, low impact, relatively common and follows a SOP (Standard Operating Procedure) or Work Instruction.
- Change Work Item: It contains all the details of a Change. It carries a formal request for a Change to be implemented.
- Task: Tasks are designed to perform specific level of work with a specific output. Many changes are divided into group of tasks to achieve desired results.
- Impact: Impact is a measure of the effect of an Incident, Problem, or Change on business processes. Impact is often based on how service levels will be affected.
- Request For Change (RFC): A change request is a formal proposal for an alteration to a product or system or an environment.
- Configuration Item (CI): CIs are the components or service assets that need to be managed to deliver an IT service. Information about each configuration item is recorded in a configuration record within the configuration management system and is maintained throughout its lifecycle by service assets and configuration management.
- Post Implementation Review (PIR): Purpose of PIR is to analyse the success of the Change and to make sure the Change is implemented as expected. PIR also contributes to the knowledge base for the team to learn from the experience.
- Downtime: It is the span of time during which Services will be interrupted or unavailable.
- Risk: It is an uncertain event that can either have a positive or negative impact on the business process.
- Rollback (Back Out Plan): It is the process of restoring Services or Business Operations to a previously defined workable state or to design a new Implementation plan to bring Services back to normal.
- Change Advisory Board (CAB): CAB delivers support to a Change Management team by approving requested Changes and assisting in the assessment and prioritization of Changes. This body is generally made up of IT and Business representatives that typically includes - a Change Manager, Technical Experts and Third-Party representatives & Customers (if required). As and when a CAB is convened, members should be chosen who can ensure that all Changes within the scope of the CAB are adequately assessed from both a business and a technical viewpoint.
- Emergency Change Advisory Board (E-CAB): E-CAB is responsible for assessing, authorizing and implementing an Emergency Change as quickly as possible. This process is invoked if normal Change Management procedures cannot be applied because an emergency requires immediate action.
- Lead Time: The Time between Change submission to Change implementation.
- Change Freeze/Blackout Window: Time interval during which an organization wants to avoid Changes in the production environment. Changes during this freeze need to have a special approval and will be approved by the members of the ECAB.
3-Tier Structure
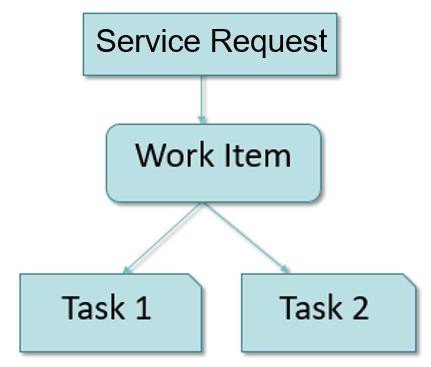
HCL BigFix Service Management has a 3-Tier structure for any ticket:
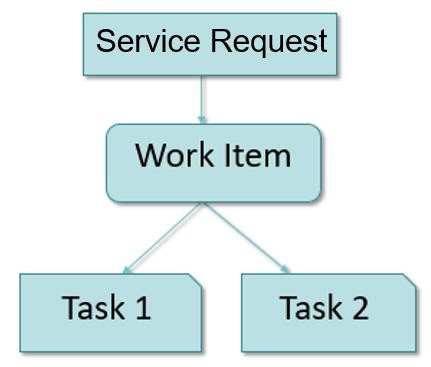
- Service Request: Service requests are placed by Consumers for purchasing new Services. Service requests have prefix REQ#
-
Work Item: Work Items are created for Service Providers for fulfilment of Service
requests. Work Items such as Incident, Problem, Change and Fulfilment Work Item are
associated with Service Request followed by work item number. For example:
- For Incident -> REQ# - INC#
- For Fulfilment -> REQ# - ITM#
- For Change -> REQ# - RFC#
- For Problem -> REQ# - PRB#
- Task: Each Work Item can have one or more tasks allocated to individual Service Provider groups. Task Numbers have prefix TSK. Tasks are optional and can be created manually if needed.
Process Input and Output
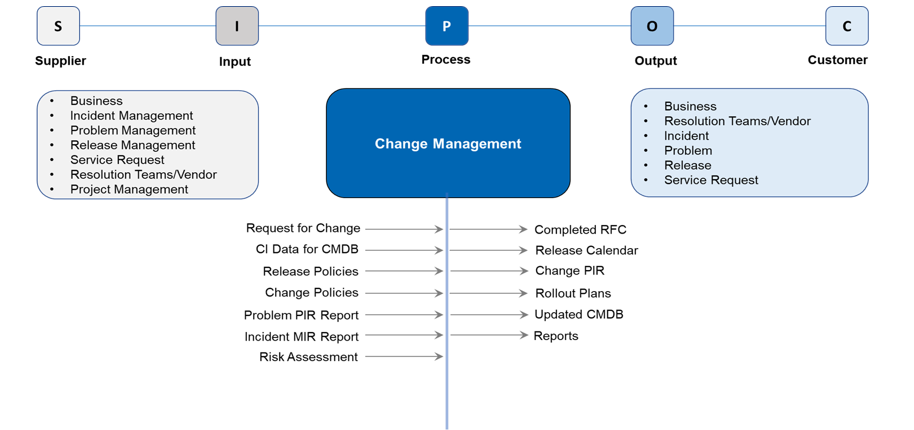
Classification of Change Types
Following types of changes are available in HCL BigFix Service Management
- Standard Change: Frequently performed changes with documented implementation procedures. Their implementation is tested and proven, and their success can be determined and reported quickly. Standard Changes will have predefined workflows and tasks created in HCL BigFix Service Management in the form of templatized catalog items.
- Normal Change: Normal Changes are planned regular changes. These changes will require a formal review and approval by the Change Advisory Board. The risk of this change may vary from low to high, depending on the criticality of the affected CI, the complexity of the change, and the impact on the business. It includes project or service improvement opportunities. Normal Changes will follow a defined lead time for testing, implementation and validation. Lead times can be configured for Normal Changes based on recommended policies of Customer Organization.
- Emergency Change: Emergency Change refers to RFCs that circumvent the normal RFC process to resolve critical incidents, security patches or services that need an RFC for immediate repair. Emergency Changes do not have any lead times and will require Emergency CAB approval process for implementation.
RFC Submission Policy
All members of a support group (Service Provider/Service Supporter) who have the change user or change manager role are authorized to initiate RFCs. Consumers have the option to raise Standard Change Requests.
Anyone may identify the need for a change. However, creation of an RFC can only be initiated when proper justification exists. If the requester is not an authorized change initiator, they must contact the authorized change initiator to initiate an RFC.
All mandatory information related to an RFC must be complete.
An RFC can be submitted at any time.
Risk Assessment Policy
- The risk involved in a Change is determined by assessing the following parameters and based on two criteria which is Technical Risk & Business Risk.
- The risk assessment must be performed by the Change Initiator at the time of Change submission. Overall risk on a Change is automatically computed based on the values selected for ‘Risk Occurrence Probability’, ‘Impact if risk is realized’ and ‘Control Effectiveness’, respectively.
- Risk assessment will be based on one or more of the following factors:
- Criticality of the affected application.
- Change schedule (maintenance window, business or non-business hours).
- Adequacy of release testing.
- Skill requirements.
- Conflicts with other change(s).
- Compatibility of components.
- Change complexity.
- Availability and adequacy of back-out and implementation plans.
- Downtime or outage in the case of a back-out.
- The risk will be assessed by the Change Initiator (an internal IT Operations person) but reviewed by the Change Manager for that change and verified and validated by the Approver.
- An Approver can change the risk level or advise the Change Manager of the risk level.
- Additional controls, such as those in the following checklist, should be enforced
before execution of high-risk changes.
- All affected users and the IT service desk have been informed and information posted on the bulletin board.
- The change has been fully tested, and the reports have been documented.
- The back-out plan has been documented and understood.
- The appropriate business owner has been informed.
RFC Acceptance Policy
Change acceptance criteria in the initial review include, but are not limited to:
- Is it within the scope of IT service?
- Is it within IT Governance policy?
- Are there any conflicts with security policies?
- Are there any conflicts with IT strategy (such as deviations from standards or the IT roadmap)?
- Is it technically feasible?
- Is the information in the RFC complete and accurate?
- Are the effects on DR, if any, accounted for and required action plans included in the RFC?
If the information in the RFC is not adequate, it can be referred-back – a notification email is triggered to the Change Initiator or the concerned user requesting further details.
Change Approval Policy
- No Change, even an Emergency Change, can be implemented without approvals.
- By default, HCL BigFix Service Management allows to configure 4 level of approvals,
however for Normal Change minimum two level of change approvals should be configured:
- Level 1 RFC Approval (Change Manager)
- Level 2 RFC Approval (CAB Approver)
- RFC Approvals are configured against each CI at the time of CI creation. Additional approvals can be configured as & when needed.
- An Emergency RFC that requires fixing a high-priority outage can be executed after appropriate approval from an authorized person. Written approval (e-mail) is preferred.
- The Change Approver may reject scheduled or unscheduled changes due to inadequate planning, inadequate back-out plans or a negative impact of the timing of the Change on a key business process.
- When RFC is rejected, the reason for rejection must be mentioned.
- If the Change Initiator and the Approver are same, the change ticket is auto approved and moves to next approval.
- Besides granting approval, the Change Approver can also perform the following actions
on an RFC:
- Change the risk assessments
- Change the planned dates and
-
Provide additional instructions
Conflict or Collision Detection Policy
- Collision Detection is a procedure to identify the conflict between various changes scheduled during the same window
- Collision Detection is useful to identify other changes that are scheduled at the same time or impact the same configuration items (CIs) as a change request.
- Collision or conflict detection happens for normal and emergency changes. The tool will identify a conflict if the start and end time of the new change is falling between the start and end time of a change that is in Scheduled status.
- Conflict information will be visible as a pop-up window before the new change can be submitted. Conflict can be resolved by either changing the planned start and end time or by ignoring the conflict by providing a justification.
Multi Supplier Change
- Changes involving multiple suppliers would require active participation from all the
suppliers involved, which will include:
- Day-to-day change coordination activities, which will be performed by the Supplier Change Manager.
- Sharing the required details as part of the change implementation activity and deployment plan.
- Representing the Supplier and enabling successful implementation of the overall change.
- Working with the Change Manager to execute the CAB discussions and approval.
- Providing timely approvals for the tasks assigned to each supplier to achieve the estimated change implementation date.
- Providing detailed justification for the tasks rejected or referred-back to the Change Initiator.
-
Active participation in identifying improvement opportunities as part of PIRs conducted for the changes.
Emergency Changes
- An Emergency RFC will only be created under the following situations:
- To fix a high-priority incident or problem.
- To avoid an imminent outage.
- Emergency is the highest RFC urgency level. An Emergency RFC must be responded to immediately because it may relate to a service interruption that is classified as high impact, either because it affects a large number of users or involves systems or services critical to the organization.
- The process, workflow and approval levels for an emergency change are the same as those for a normal change. However, in the case of Emergency changes, all activities, including approval, must be conducted as soon as possible.
PostImplementation Review
- All types of changes to production CIs must go through Post Implementation Review.
- Details will be recorded within the RFC ticket and Change Manager will review this.
- In the event of failed or backed out change, a detailed PIR report is created to document lessons learnt, deviation from solution and follow- up action. Change Manager ensures this is tracked and all follow-up actions are addressed, documented and brought to closure. Change Manager organizes a PIR meeting for each with all stakeholders including Change Initiator, Implementation team and Change Manager.
- PIR is conducted by Change Manager in HCL BigFix Service Management by completing the online form Post Change Implementation.
Change Completion
- RFC can be marked as completed only after the Change Initiator has agreed that the change achieved its purpose or the CAB has conducted a Post-Implementation Review.
- If CMDB update is required, it must take place before the RFC can be considered as “Completed”.
- Configuration Manager will update the CMDB and notify the change manager who would then perform the PIR and mark the change as Completed.
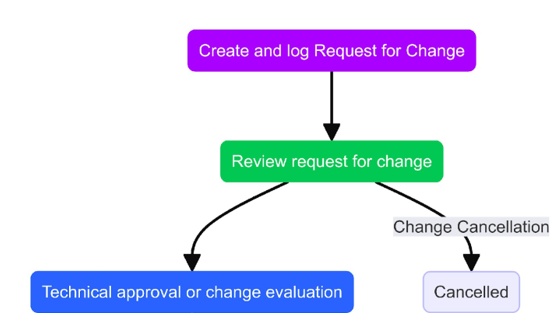
Change Cancellation
- The Change Initiator can cancel an RFC any time during its lifecycle. A request for
cancellation is governed by the following policies:
- If it is cancelled before approval, the RFC will move to cancelled stage
- If it is cancelled after approval then Change Manager will check the implementation status, if it’s in ‘Scheduled’ and the implementation is not yet started, then it will be cancelled immediately by Change Manager.
- If the change is under implementation and roll back is possible, then the implementer will roll back the Change. For these RFCs also, standard closure process will be applicable after back-out.
- In case the change cannot be rolled back, then they will go through the implementation and closure process. The records will state that the cancellation did not occur, and the implementation was successful.
Preventing Unauthorized Changes
- An Unauthorized Change is a change implemented without approval(s) as defined by the
Change Management Process. Unauthorized changes can be of two types:
- Changes implemented without submission of an RFC. The Change Management Process is not designed to prevent, detect, or report unauthorized changes. These changes can be detected only during configuration audits.
- An RFC is submitted but not approved and yet the change is implemented. The Change Management Process can facilitate detection of these unauthorized changes through an audit of RFCs submitted during a specific period.
- Any unauthorized change identified in the environment must be investigated to determine the reason the change was implemented.
- Reviews of unauthorized changes may be an additional CAB agenda to identify controls necessary to prevent unauthorized changes.
Change Process Workflow
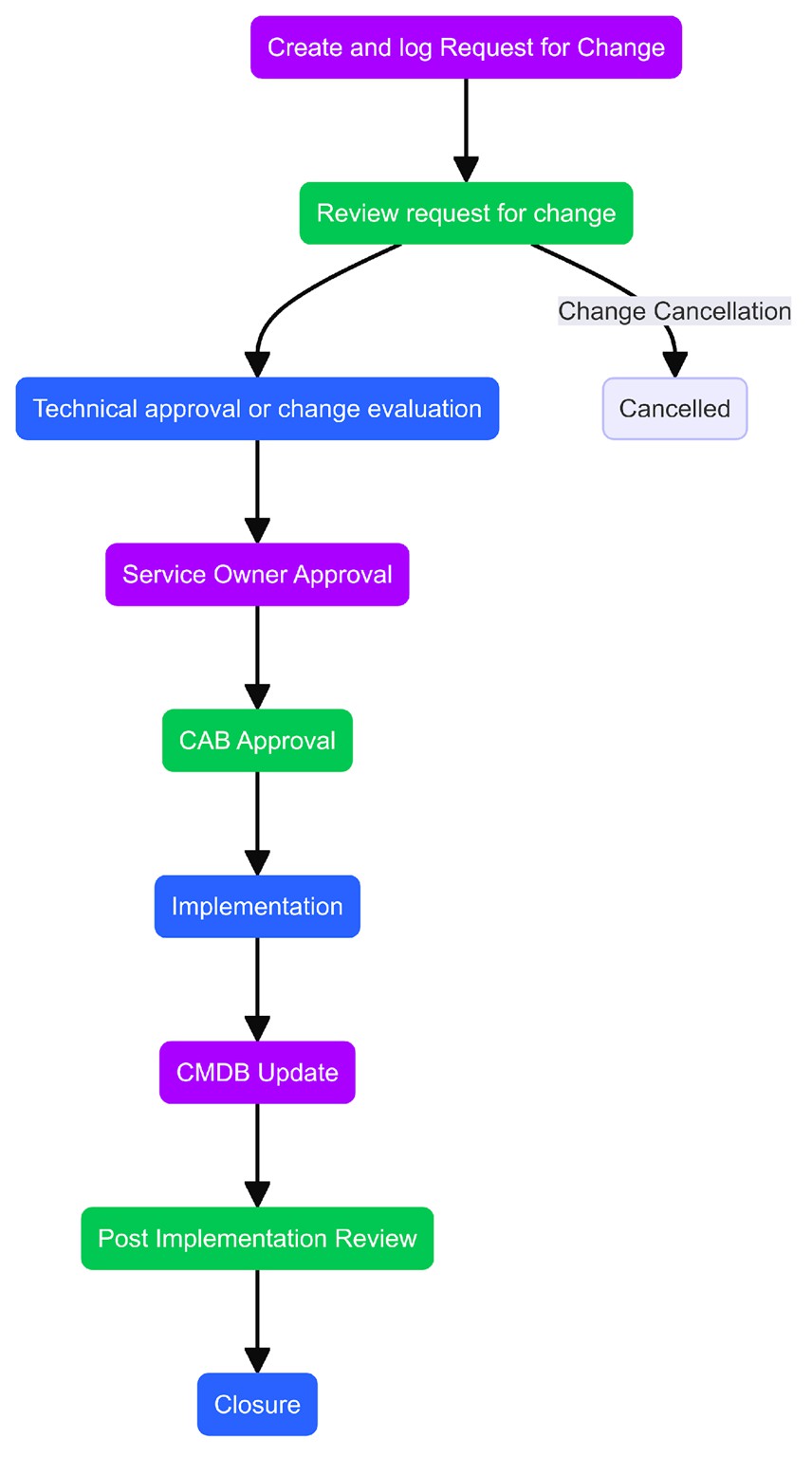
Change – Request and Submission
- Projects can undergo change at any stage. To ensure change flows smoothly, the change lifecycle should be governed end to end.
- As soon as the need for change is identified via Investigation work Item or any other source, RFC must be created immediately. However, creation of RFC can only be initiated when proper justification exists.
- If the requester is not an authorized change initiator, they must contact the authorized change initiator to initiate an RFC. All mandatory information related to RFC must be complete.
- An RFC can be submitted at any time but with valid reasons and Business Justification.
- Change Initiator needs to do provide Change Implementation, Test and Backout Plan before change submission.
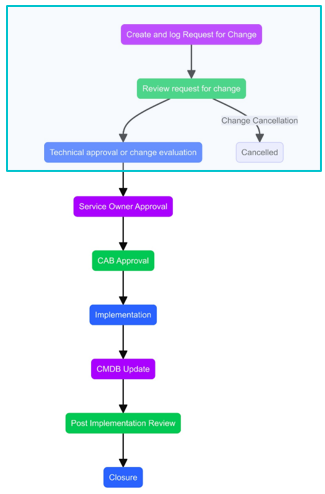
Change – Approval, Implementation and Closure
- Once a Change is submitted, notification is sent to the designated Level 1 Approver. This could be a technical approval. Technical approvers validate its risks and make an impact assessment. Then approver will approve or reject a change.
- If the change is approved, it will move ahead for Level 2 Approval. This could be a CAB approval.
- Once both the approvals are granted change will move ahead with its lifecycle. The change implementer(s) will initiate the implementation of the change. If the implementation is successful, the change implementer(s) provide the CMDB update information. All RFCs do not necessarily lead to a CMDB update.
- If a change is unsuccessful and a correction is possible, then the change implementer(s) will perform an appropriate correction step and provide the CMDB with updated information.
- If the change is unsuccessful and correction is not possible, then the back-out is performed to restore the system to its previous working state.
- If the RFC is rejected at any of the Levels of approval (Level 1 & 2), the approvers will specify the reasons for rejection and the Change will move to Rejected stage, where implementer can Re-plan the change.
- Downtime and Start and End date can be modified at Re-plan stage.
- After a change is re-planned, it will again undergo process of review and approval, and the same cycle will follow.
- After a successful implementation, the CMDB is updated, and the RFC status is updated as Completed. Configuration Manager shall be informed via email notification or by creating a manual ad hoc task for making the necessary changes in CMDB.
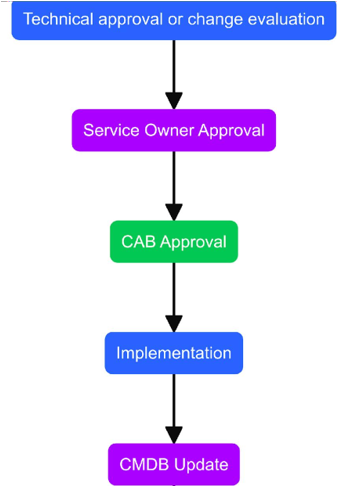
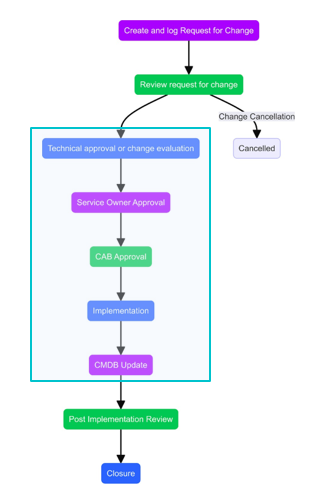
Change – Post Implementation Review (PIR) and Closure
- The Change Manager for that change prepares a PIR report and initiates the review with the CAB and the Change Initiator before closing of the RFC.
- The report includes review outputs containing any lessons learned and devised action plans.
- If the change is rejected, or the change fails during testing and is determined not feasible, the RFC is closed without review.
- PIR will be conducted by the Change Manager in HCL BigFix Service Management.
- PIR Form will be available on the change form in Related Links which needs to be filled in by Change Manager before closure.
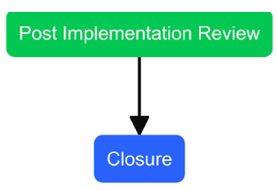
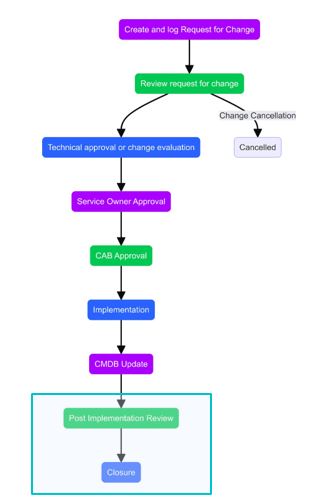
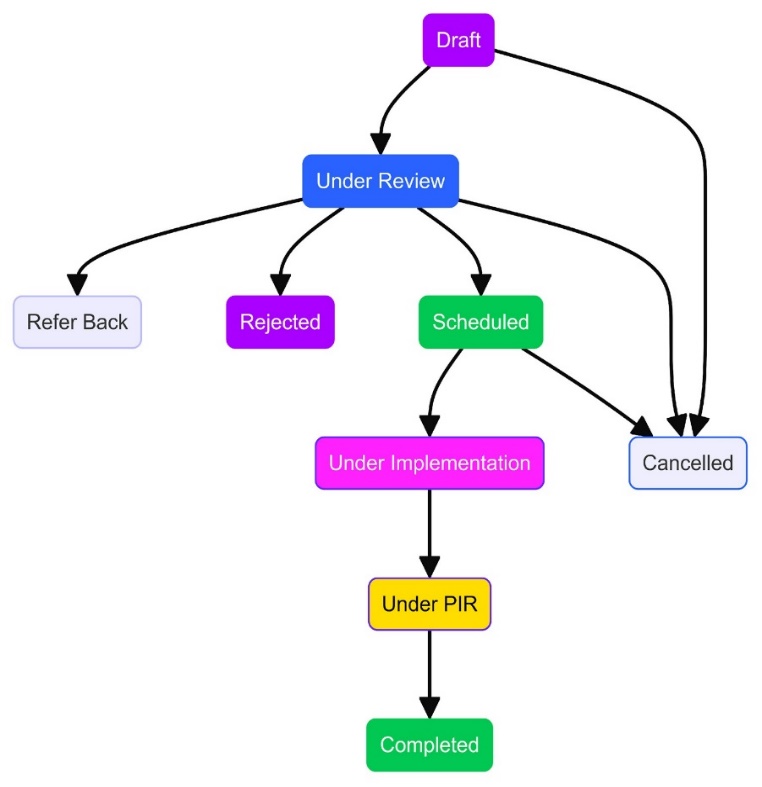
RFC Status Transition
Change Task Status Transition
| Key Activities | Roles | |||||
| R – Responsible | ||||||
| A - Accountable | Change Process Owner | Technical Support Group (Implementer) | Supplier Change Manager / Process SPOC | |||
| S - Supported (Own within area of Key Supplier responsibility) | Change Initiator | Change Manager | Change Approver | |||
| I - Informed | ||||||
| C - Consulted | ||||||
| Process Ownership | I | AR | I | I | I | |
| Process definition | C | AR | I | I | I | |
| Create RFC | R | AR | R | |||
| Ensure day-to-day process operation & compliance | R | R | I | AR | ||
| Provide accurate minimum dataset for RFC | AR | CI | AR | |||
| Change Evaluation | C | CI | AR | AR | ||
| Technical Review | I | C | R | AR | AR | |
| RFC Approvals | I | I | RS | AR | AR | |
| Overall Change Coordination (across suppliers) | AR | I | S | SR | ||
| RFC Lifecycle Management within area of supplier | SC | S | AR | |||
| responsibility | ||||||
| Manage CAB | AR | IC | S | R | S | |
| Manage ECAB | AR | IC | S | R | S | |
| Analyze Change Trend and propose additions to Standard | C | IC | RS | AR | AR | |
| Change Catalogue | ||||||
| Change Implementation | I | I | R | A | A | |
| Post Implementation Review | AR | IC | S | AR | S | |
| Change Dispute Handling | SI | AR | CS | I | S | R |
| Change Escalation Handling | C | CS | I | AR | ||
| Change Ageing & Backlog | S | I | I | S | AR | |
| Change Audits | S | AR | CI | I | S | S |
| Change Reviews | S | AR | C | I | AR | S |
| PIR Action Tracking | S | CI | RS | AR | AR | |
| Manage reporting | S | S | I | I | S | AR |
| Inter-process touch points management | AR | I | I | C | S | |
| Training and implementation of processes | R | A | I | CI | R | |
| Continual Service Improvement | S | R | A | I | CI | R |
Task Lifecycle
- For Standard Changes, the tasks can be pre-defined along with auto-routing rules at the time of standard change template creation. This can be enabled in the Fulfillment Plan on the Service Board.
- Tasks can also be pre-defined for a normal change or Emergency change from the Asset/Config board which can be auto routed to relevant groups based on CIs.
- Ad-hoc parallel and sequential tasks can also be created for a change from the ‘Work item board’. The lifecycle of the tasks is same.
- It is mandatory to close the tasks before the PIR is performed by the change manager.
- If a change is cancelled, all underlying tasks will be cancelled automatically.
Change Management – RASIC Matrix
Change Module Roles Configured in HCL BigFix Service Management
| HCL BigFix Service Management Roles | Permissions |
| Change User | Read/Write access to Incidents of his own groups. |
| Change Manager | To be able to see RFC tickets across Change Management Groups of his own/associated companies (to which it provided support). |
| Implementation User | To be able to view tickets of his own Implementation Groups. |
| Implementation Manager | To be able to see RFC tickets across Implementation Groups of his own/associated companies. |
| Functional Role | Description |
| Change Process Owner | ▪ Owns the Change management process and is responsible for the efficiency and effectiveness of it. |
| ▪ Owns the Change Management Module. | |
| ▪ Reviews and approves all process related enhancements. | |
| ▪ Actively participates in the Change compliance review activities. | |
| Change Manager | ▪ Take the ownership to oversee the day-to-day operations relating to Change Management. |
| ▪ Ensure Change Requests are assessed properly and effective impact assessment of Changes across Service Providers. | |
| ▪ Ensure Change Process compliance, audit process, provide necessary feedback to Service Providers for improvement. | |
| ▪ Ensure Changes are implemented within scheduled time and reviewed post implementation. | |
| ▪ May chair the CAB, Convene the emergency CAB as required. | |
| ▪ Evaluate impact, risk assessments, potential conflicts with other Requests for Change, submission of implementation, test, back out plans from Service Providers before approving Changes and in preparation for the Change Advisory Board. | |
| ▪ Ensure Change Management KPIs are reviewed at agreed frequency for improvement. | |
| ▪ Regular monitoring to avoid backlog/ageing of change tickets, ensuring implementation as per schedule and change process | |
| effectiveness. | |
| ▪ Consolidate reports related to Change Management from all Service Providers, as applicable. | |
| ▪ Take the ownership of process data, maintenance & update along with defining functional requirements for changes, enhancements in the Change Management Process workflows. | |
| ▪ Conduct regular trainings for process awareness and improve process compliance. | |
| Change Implementer | ▪ Implements and tests the change documented in the RFC according to the implementation plan and schedule. |
| ▪ Develops the back-out plan and performs a rollback if the change fails. | |
| ▪ Records the activities performed during change implementation. | |
| ▪ Records the implementation results. | |
| ▪ Once the RFC has been implemented, provides information for the CMDB update before the change is closed. | |
| ▪ Works with the Supplier Change Manager to document the remarks when the change is closed. | |
| ▪ Monitors the assignment of changes. | |
| ▪ Designs and develops tests used to assess the quality and usefulness of change. | |
| Change Advisory Board (CAB) | ▪ Assists the Change Manager in reviewing the changes. |
| ▪ Ensures that business justification for all changes are submitted for approval. | |
| ▪ Ensures that a viable change plan exists. | |
| ▪ Ensures that implementation and back-out plans exist. | |
| ▪ Ensures that business and technical impact assessments are done. | |
| ▪ Ensures that a plan is developed to communicate the impact of the change to all the relevant users. | |
| ▪ Approves minor and major changes. | |
| ▪ Approves implementation and back-out plans and test reports. | |
| ▪ Assists the Change Manager in assessing the change, risk and impact. | |
| Change Initiator | ▪ Identifies the need for initiating a change in an environment. |
| ▪ Develops plans and executes the steps necessary to initiate an RFC. | |
| ▪ Creates an RFC and provides necessary details to execute a change. | |
| ▪ Ensures that the request for change is complete with accurate information at a sufficient level of detail to implement the change without intervention. | |
| Technical Approver | Technical Approver is from support team to assess the technical feasibility which includes CI and technical risk, change window, RFC technical documentation and provides approval on basis of the following aspects: |
| ▪ Technical aspects of the change | |
| ▪ Impact on the Configuration Items in the CMDB | |
| Emergency Change Advisory Board | An Emergency CAB (ECAB) is required for Emergency changes. The ECAB performs the same functions as a CAB, except that it approves and authorizes Emergency changes. |
Product Walkthrough (Change Work Item)
Logging into HCL BigFix Service Management
To login, the user should:
- Open internet browser (Edge, Chrome) and enter the URL: https://support.dryice.ai
- Provide login credentials to authenticate and login to HCL BigFix Service Management
.png)
Landing page of Work Item Board
From the Application Menu, click on the Work Item Board. The User will be presented with the current Work Item Board.
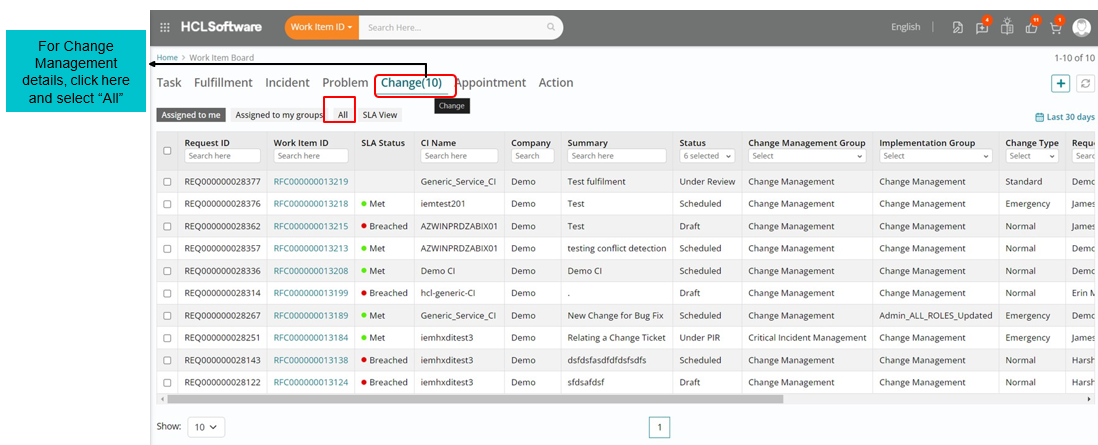
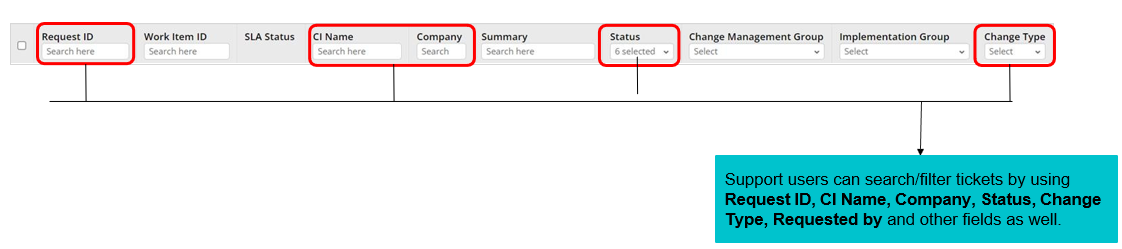
Support users have a capability to sort Work Items based on various filters available on the landing page.
Alternatively, the change request can be searched from the global search at the top of the page.

Creating a Change Work Item
To create a Change (Normal, Emergency or Latent) Work Item, click on the  icon on the landing page of Work Item
Board. It will open a form that needs to be filled to create a Change Work Item.
icon on the landing page of Work Item
Board. It will open a form that needs to be filled to create a Change Work Item.
Once all the Change request related details are filled, on the same page, click to Save or Cancel the form.
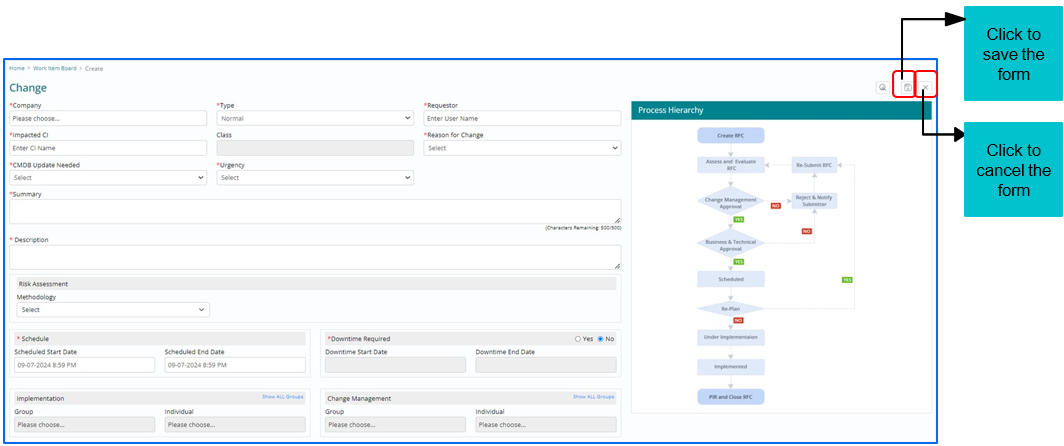
Lifecycle of a Change Work Item
Lifecycle of a Change Work Item is divided into several phases:
-
Draft:
As soon as the Change Work Item is created, the first stage is ‘Draft’. In
this stage Support User will assess and examine the Change. Change User/Implementer will
draft an Implementation Plan with the course of action that are required to execute a
change.
A support user can perform the following actions at this stage.
- Cancel a Work Item
- Submit a Change Work item for review
- Draft a detailed Implementation Plan.
- Upload Attachments
- Notify Intended Audience
-
Under Review:
Once an Implementation plan is submitted for review to a Change Manager or an
accredited Approving Authority, lifecycle moves to ‘Under Review’ stage. A change
Work Item has to undergo two levels of approvals. Change Manager or any other accredited
Approving Authority will be responsible for reviewing the Implementation Plan and
subsequently Approving or Rejecting it.
A support user can perform the following actions at this stage.
- Cancel a Work Item
- View the Implementation Plan
- Approve/Reject a Work Item
- Upload Attachments
- Notify Intended Audience
-
Under Approval:
As soon as the Level 1 approval is granted, lifecycle moves to its next stage based
on levels of approval set up. Appropriate approvers will Approve/Reject the Work Item
after review and ticket moves to next stage.
A support user can perform the following actions at this stage.
- Re-Plan an Implementation Plan
- Cancel a Work Item
- View Implementation Plan
- Approve/Reject a Work Item
- Upload Attachments
- Notify Intended Audience
-
Scheduled:
After Level 1 and 2 approvals are granted, Change lifecycle moves to
‘Scheduled’ stage.
A support user can perform the following actions at this stage.
- Re-Plan an Implementation Plan
- Cancel a Work Item
- Start Implementation
- View Approvals
- Upload Attachments
- Notify Intended Audience
-
Under Implementation:
As soon as the change User/Implementer starts executing the Implementation Plan,
the lifecycle of the Change Work Item moves to ‘Under Implementation’ stage. If
the Change Implementation review policy is enabled, then it is required for the
change assignee to select a reviewer on the implementation task. The reviewer will then change the implementation task status to “Reviewed”.
A support user can perform the following actions at this stage.- End Implementation
- View Approvals
- Upload Attachments
- Send Notifications
- Implemented: Once the Implementation plan is executed and Support user clicks on End Implementation lifecycle of a Change Work Item moves to ‘Implemented’.
-
Under PIR:
After Implemented stage, lifecycle of a Change Work Item moves to ‘Under
PIR’. Purpose of PIR is to analyses the success of the Change and to make sure the
Change is implemented as expected.A support user can perform the following actions at this stage:
- Document PIR
- View Approvals
- Upload Attachments
- Send Notifications
- CMDB Update (If CMDB Update Needed=Yes)
- Completed: Once the PIR is documented and saved, Lifecycle of a Change Work Item moves to final stage which is ‘Completed’.
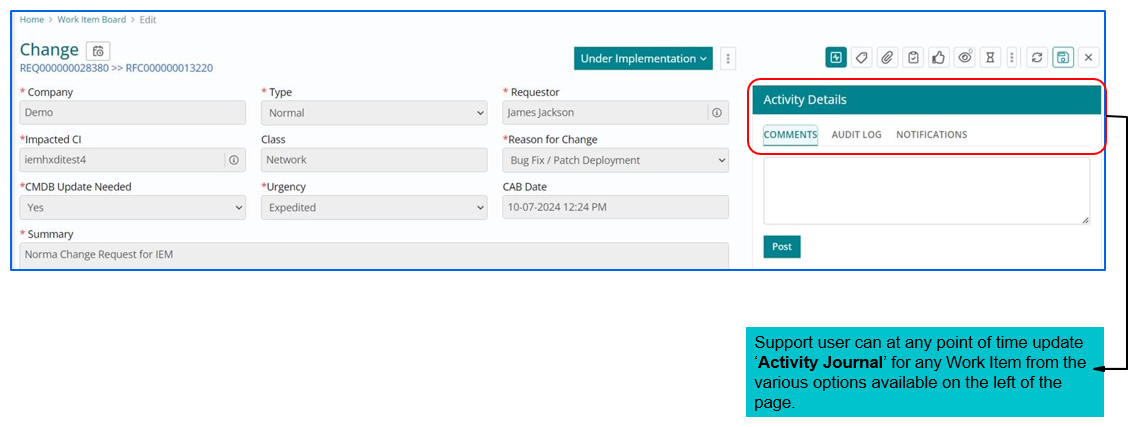
Updating Activity Journal
Relating other Work Items with Change Work Item
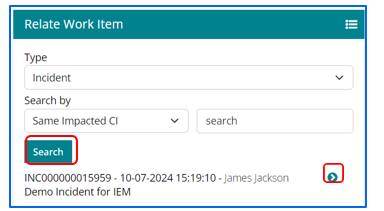
Support users can relate existing Change Work Items with Other Work Item if required based on following attributes:
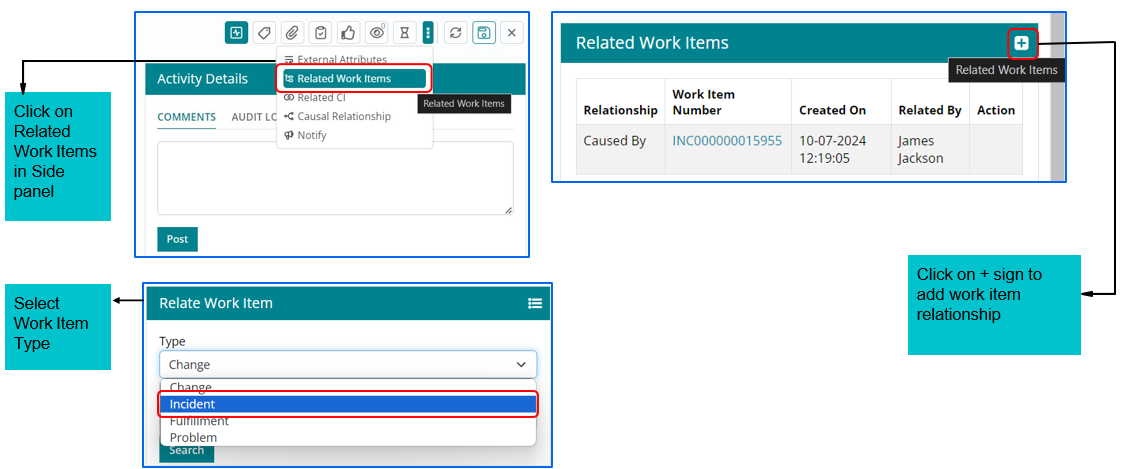
Relating other Work Items with Change Work Item
Support user can relate existing Change Work Items with Other Work Item if required based on work item Type such as Change, Incident, Fulfilment and Problem.
Relationship can be removed using Delete icon
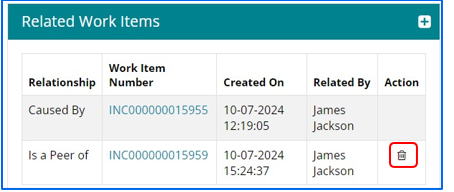
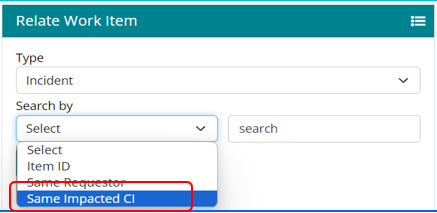
Search by – Item ID, Same Requester and Same Impacted CI. Click on Relate button to relate the work item.
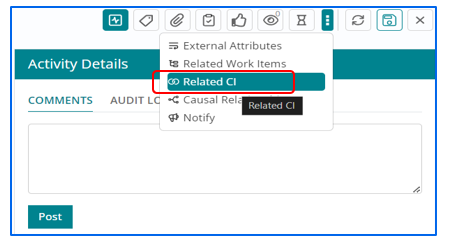
Relating Configuration Items with Change Work Item
Support users can relate Configuration Item with Change Work Item whenever required by selecting Related CI from side panel.
User needs to click on + icon to search the Cis.
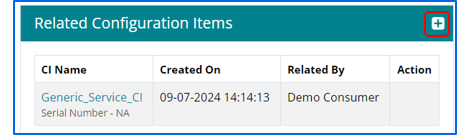
Configuration Items can be searched based on two parameters – CI Name and Class Name. Once the CI list is visible, users can select the CI and click on relate.
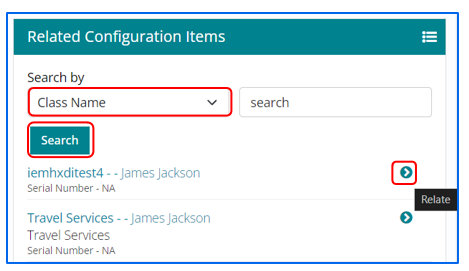
Identifying Applicable Approvals associated with a Work item
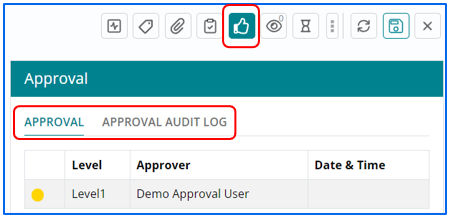
- Support user can check the Approving authority name’s applicable to a specific Work Item by the options explained in the snapshot below.
- Approval Audit log contains the history of approvals executed on the change request
Audit Log
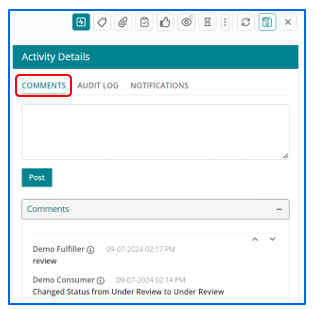
Activity Details capture the details of the change ticket lifecycle:
- Comments contain the comments posted by support users.
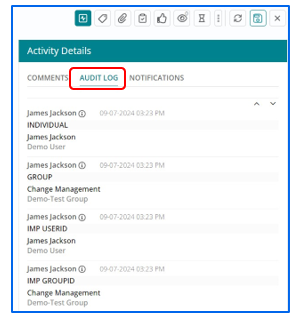
- Audit log captures the changes in various fields throughout the lifecycle of a Change
Work Item.
- Notifications contains the notifications sent for the change ticket.
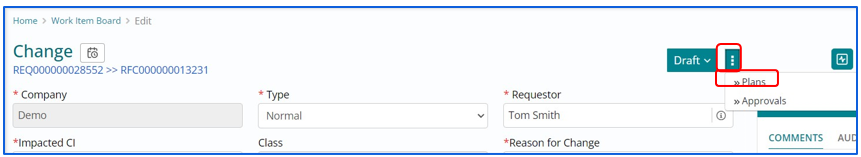
Drafting an Implementation Plan/ Back out Plan
Change User/Change Manager are required to draft an Implementation plan explaining how the change will be implemented.
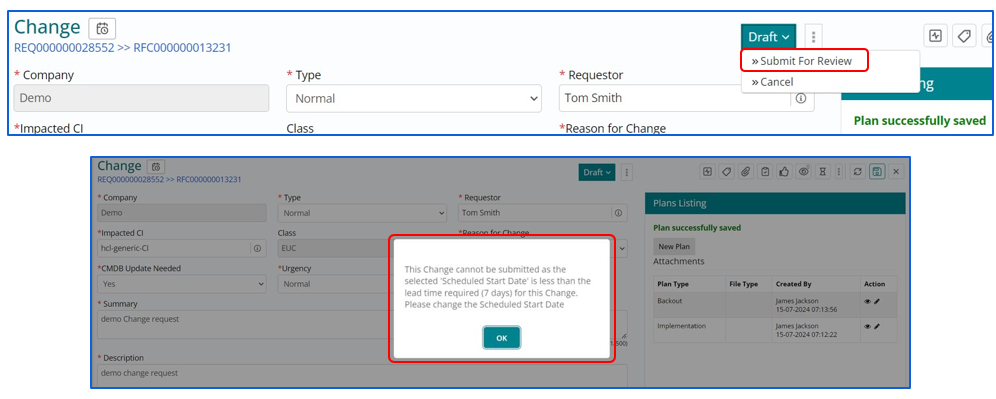
Submitting the change for review
Implementation Plan needs to be reviewed by the Change Manager or any authorized Approving Authority before its being executed by the
Change implementer. Once it's sent for review the lifecycle stage of Change Work Item changes to ‘Under Review’
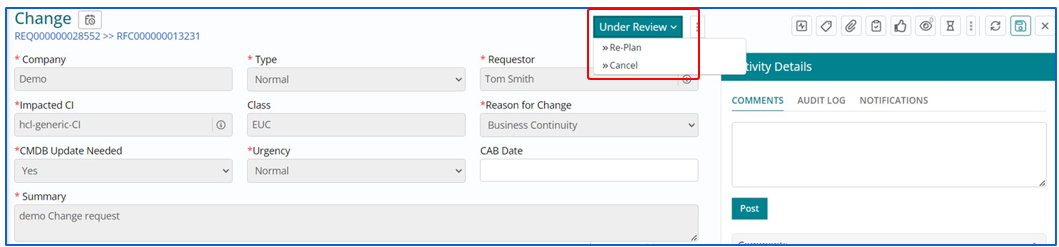
Replan or cancel the change under review
Implementation Plan needs to be reviewed by the Change Manager or any authorized Approving Authority before its being executed by the Change implementer. Once it’s sent for review the lifecycle stage of Change Work Item changes to ‘Under Review’.
Approving/ Rejecting/ Referring back a Change Request from ‘My Approvals’ page
There is one more option to Approve/ Reject and Refer Back to the changes and that is from ‘My Approvals’ page:
- As any Approving Authority clicks Approve, a window will popup asking for confirmation. Click Yes if you want to Approve.
- In case Approving Authority is not satisfied with the documented Implementation Plan and needs modifications to be done to it, Click Reject, a window will popup asking for Reason of Rejection. Enter the same and click Submit.
- If the approving authority feels that if anything is missing and needs to be updated/modified, ‘Refer Back’ option should be used, and the Change Initiator must update the required details. The approvals in this case will start from Level 1 again.
Implementing a change
- Implementation Plan must go through two Levels of Approval- Level 1 and Level 2.
- Change Manager or any other Approving Authority will be able to view the submitted RFC in their bin for approval. They need to
- review the Implementation Plan before it gets implemented and suggest
amendments/correction if required before approval.
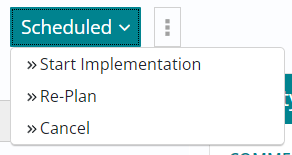
Re-planning an Implementation
- In case a support user wants to Re-Plan an Implementation for a
valid reason, they can do so by selecting Re-Plan option from the list below as
shown in the snapshot.
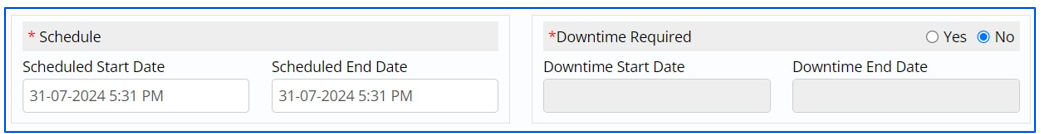
- Re-planning an Implementation provides user with options to amend Start and End Date of Implementation along with alterations in Downtime.
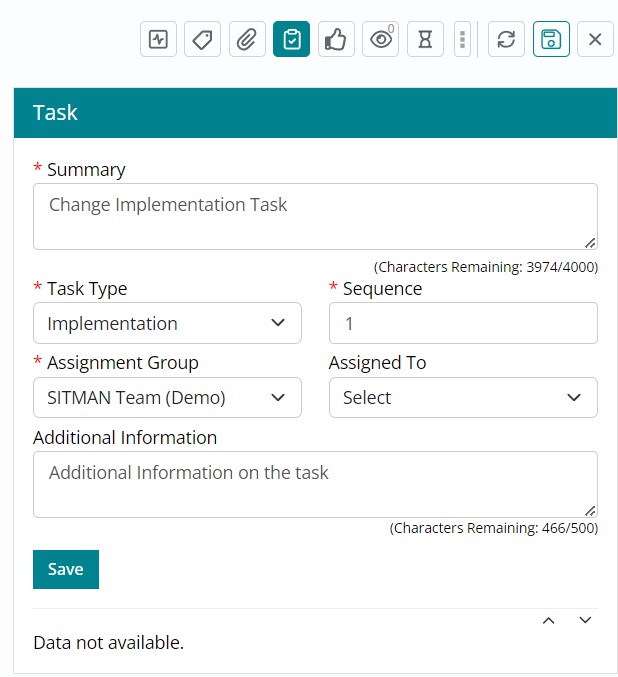
Creating and Assigning Tasks to other support Groups
Support users can create and assign tasks for multiple support group if needed to work on same Change Work Item.
Tasks can be created and assigned based on following attributes:
- Sequence Number – 1,2,3 and 4.
- Sequence Type – Sequential and Parallel.
- Status – Assigned, In Progress, Completed and Cancelled.
- Assignment Group – This tab will include all the available groups (available in the
dropdown list).
- Assignment to – Individual to whom Work Item will be assigned (available in the
dropdown list).
Implementing an assigned Change Task
- Once a Task has been assigned to the Support User, it will be visible in the Task List
View page of that User.
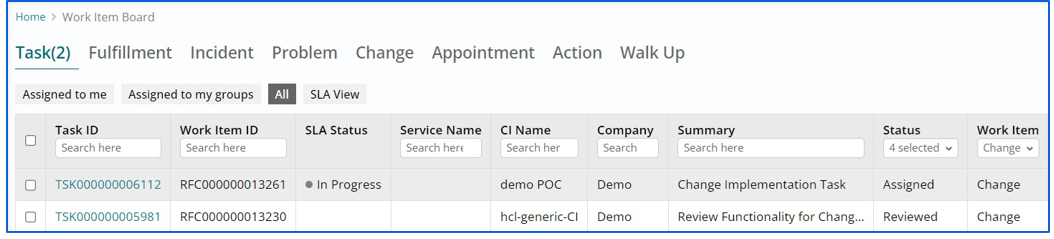
- Support User can view Task from the Task List View page by clicking the ‘Edit’ or ‘Pencil’ icon.
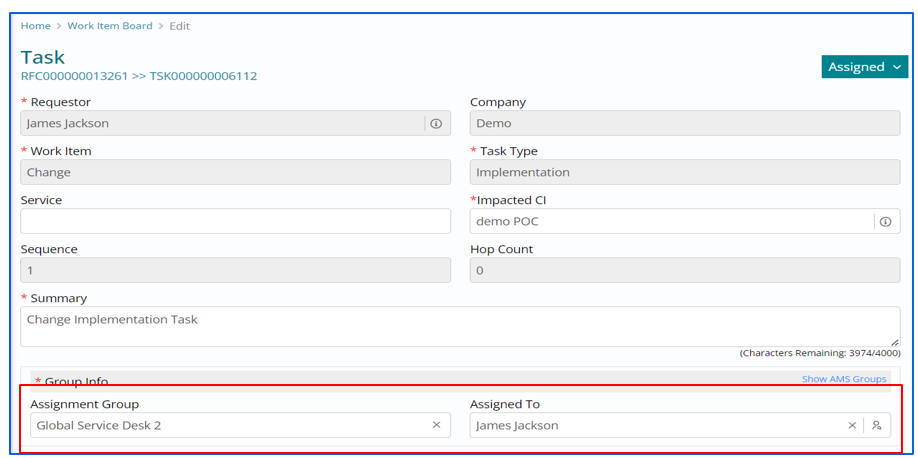
Assigning/Viewing the Task
On Clicking Edit, the form will appear, and changes can be made.
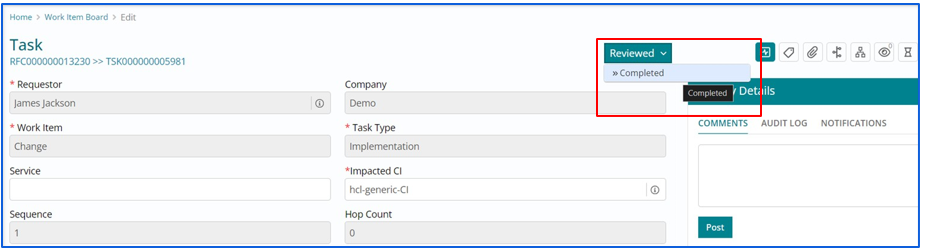
Implementing/Completing assigned Change Task
After implementing the task, the Support User must update the Task Status to ‘Completed’
Performing a Post Implementation Review (PIR)
Select ‘PIR’ is selected from the drop down list. 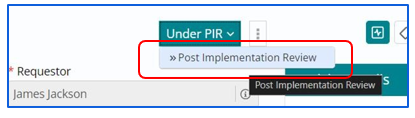
A template will open on the right which needs to be filled by the Change user to document PIR.
Support User needs to enter remarks in all the fields and Click Save. As soon as user clicks on it, PIR will be saved, and a message will pop up confirming the save.
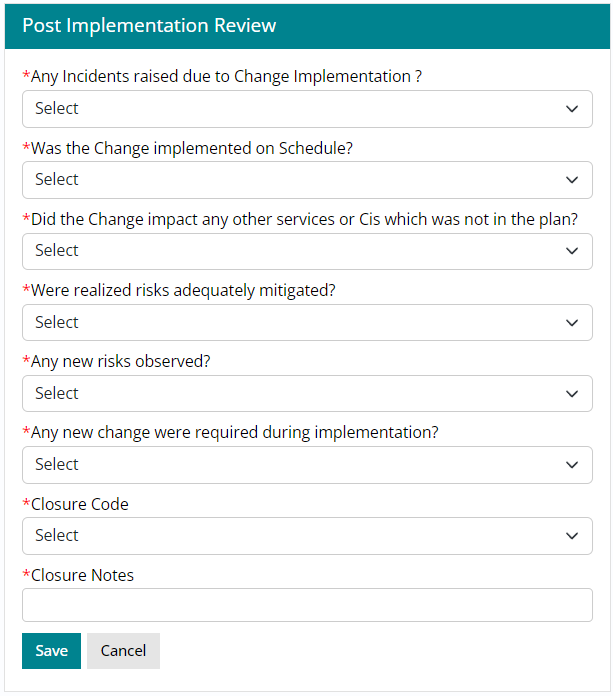
Once PIR is completed, status of Change Work Item Lifecycle moves to ‘Completed’.
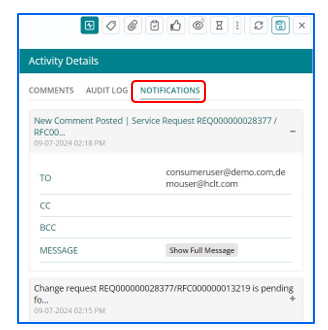
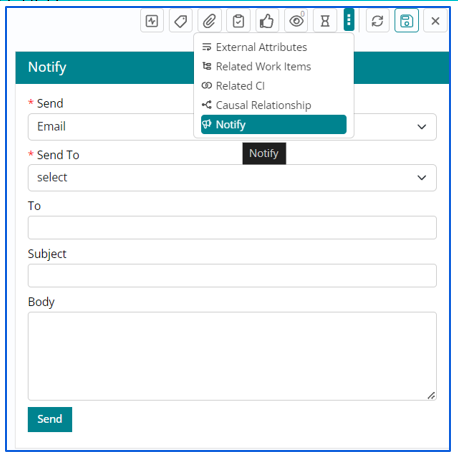
Notifying intended audience about the Work Item
- Support User can Notify the intended audience by sending emails to the respective recipients through the Notify option.
- Emails can be sent to a ‘Requester’ or a ‘Group’. Support User also has
a provision to mention the email id of any intended individual/ group by selecting the
‘Specify’ option under ‘Send To’ field.
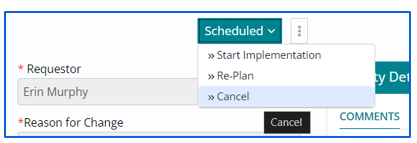
Cancelling a Change Work Item
- A Change Work Item can be cancelled, in various stages of a Lifecycle by selecting the ‘Cancel’ option.
- Support user can ‘Cancel’ the Change in following 3 Stages : Draft, Under Review,
Scheduled stage.
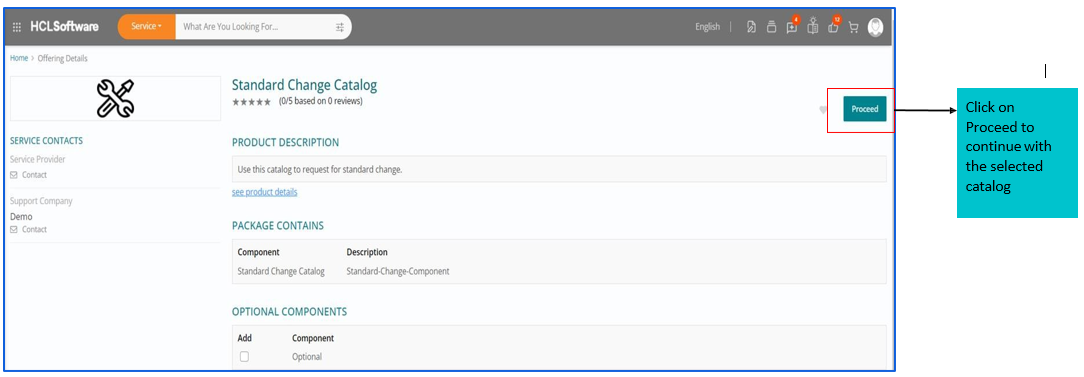
How to raise Standard Change Request?
- In HCL BigFix Service Management, catalog manager exposes “Standard Change” catalog item in the Home page of “Shopping Catalog”.
- From where requestor can raise Standard Change Request.
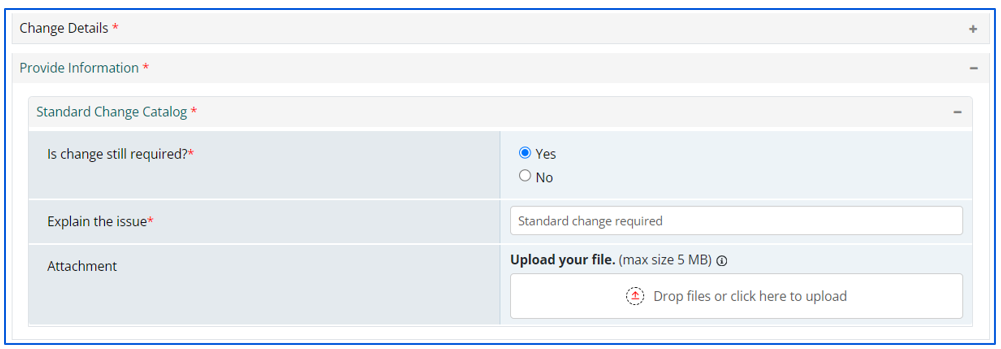
Raise a Standard Change Request
The below form will be displayed on the screen. User needs to fill in the details to move ahead.
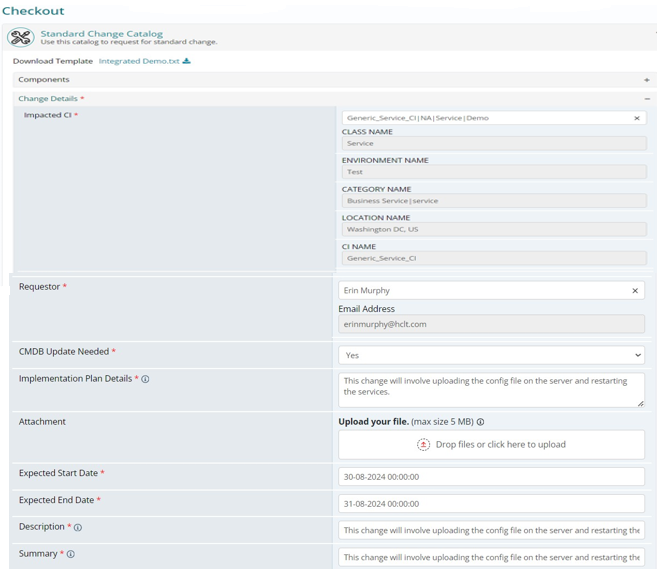
Once requestor submits the request, a RFC Number will generate from the system. The workflow of standard change will be same as Normal/Emergency which has described in above slides.