Configuring the agent and target system
To deploy applications with HCL DevOps Deploy (Deploy), you need one or more agents. The server uses the agents to deploy the application components on target systems.
Before you begin
About this task
Procedure
- Prepare a computer for use as the target system.
-
Install an agent on the target system.
See Installing agents.
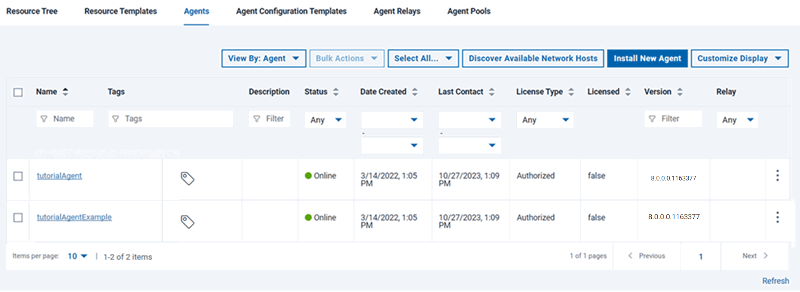
- On the Deploy server,
verify that the agent is installed by clicking . Your agent must appear
in the list of agents with a status of Online,
as shown in the following figure:
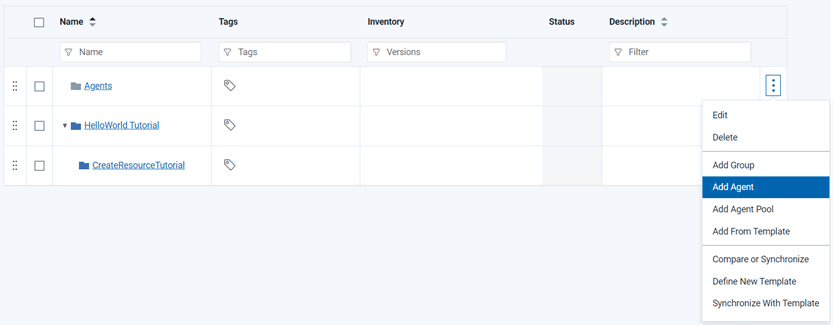
- Add the agent as a resource:
The agent is now listed as a child of the resource group. You must add agents to resource groups in this way so that applications can access the agents through the resource group.
-
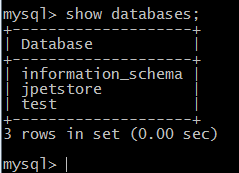
Install and start the MySQL/MariaDB server on the target system.
The application uses a MySQL/MariaDB database.If you are using a Linux™ operating system, you can use the package manager to install and start MySQL/MariaDB. For example, on Red Hat Enterprise Linux™ version 7, run the following commands:
yum install mariadb mariadb-serversystemctl enable mariadbsystemctl start mariadbOn Windows™, you can use a graphical installer or download a binary package for the database server. Then, start the server by going to the bin folder and running the mysqld command. - Create an empty database for the application to use:
- Verify that the user can access the database:
-
Install Apache Tomcat on the target system.
You can use Tomcat version 6 through version 9.A simple way to install Tomcat on a Linux™ operating system is to download and install the binary distribution of Tomcat, as in the following steps:
- Add an administrative user to the Tomcat server in the conf/tomcat-users.xml file.
This user account is necessary to deploy applications to Tomcat.For example, for Tomcat version 6, open the file conf/tomcat-users.xml and uncomment the
roleandusertags at the bottom of the file. Then, add the following lines of code to those tags:
The end of the file looks like the following example:<role rolename="manager"/> <user username="tomcatmanager" password="tomcatmanager" roles="manager"/><role rolename="tomcat"/> <role rolename="role1"/> <user username="tomcat" password="tomcat" roles="tomcat"/> <user username="both" password="tomcat" roles="tomcat,role1"/> <user username="role1" password="tomcat" roles="role1"/> <role rolename="manager"/> <user username="tomcatmanager" password="tomcatmanager" roles="manager"/> </tomcat-users>For Tomcat version 7 or 8, open the file conf/tomcat-users.xml and uncomment theroleandusertags at the bottom of the file. Remove the text<must-be-changed>and replace it with passwords for the default user accounts. If you do not remove this text, the configuration file is unreadable and your sample application will not be able to access Tomcat. Then, add the following lines of code to those tags:
The end of the file might look like the following example:<role rolename="manager-script"/> <role rolename="manager-gui"/> <user username="tomcatmanager" password="tomcatmanager" roles="manager-script,manager-gui"/><role rolename="tomcat"/> <role rolename="role1"/> <user username="tomcat" password="tomcat" roles="tomcat"/> <user username="both" password="tomcat" roles="tomcat,role1"/> <user username="role1" password="tomcat" roles="role1"/> <role rolename="manager-script"/> <role rolename="manager-gui"/> <user username="tomcatmanager" password="tomcatmanager" roles="manager-script,manager-gui"/> </tomcat-users> - In the conf/server.xml file, modify
the default HTTP ports to avoid conflicts.