
Considerations when using Basic Natural Language Processing
Natural Language Processing (NLP) can be used in two modes, Basic NLP and the default mode, Advanced NLP. Advanced NLP is enabled by default.
In certain circumstances you may want to use the Basic mode
instead, for example, when your language is not supported by CoreNLP, because you
want to reduce the size of your Query containers, or to reduce required heap memory
for the Query container in the runtime environment. The NLP mode and its scope are
controlled by the environmental variable
NLP_ENABLE_LANGUAGE_CODE or Vault key
nlpEnableLanguageCode. This variable supports a list of up to
eight languages that are supported by a Stanford CoreNLP module, . If you add
languages beyond the eight supported by CoreNLP, as described in Adding languages to the NLP service, the extra languages are evaluated by the
Basic NLP module.
The eight languages that are supported in Advanced NLP are Arabic (ar), Chinese (zh), English (en), French (fr), German (de), Hungarian (hu), Italian (it), and Spanish (es). The eighteen languages supported by Basic NLP are Arabic (ar), English (en), Chinese (zh), Danish (da), Dutch (nl), Finnish (fi), French (fr), German (de), Greek (gr), Hungarian (hu), Italian (it), Norwegian (no), Portuguese (pt), Romanian (ro), Russian (ru), Spanish (es), Swedish (sv), and Turkish (tr).
Basic NLP provides all of the features of Advanced NLP, except for Dependency Parsing and Word to Number transformations. Eighteen languages are supported for Basic NLP. These languages are listed in the Basic NLP Properties file. If languages beyond these eighteen are specified, the Basic NLP flow is used for those languages, but without Stemming. In other words, Stemming is only applied to languages that are listed in the properties file, so if you do not wish to use Stemming with a particular language, remove it from the file.
- Only English defined in NLP_ENABLE_LANGUAGE_CODE.
- There is no need to add Greek to the Basic NLP properties file. When any given language is passed to the API that is not part of the support eighteen languages, Stemming will not be performed, but the rest of the Basic NLP flow still continues.
Adding new snowball stemmers when using Basic NLP
[ar_EG = Arabic, da_DK = Danish, de_DE = German, en_US = English, es_ES = Spanish,
fi_FI = Finnish, fr_FR = French, hu_HU = Hungarian, it_IT = Italian, nb_no = Norwegian, nl_NL = Dutch, pt_BR = Portuguese,
ro_RO = Romanian, ru_RU = Russian, sv_SE = Swedish, tr_TR = Turkish]PATCH http://dataQueryHost:dataQueryPort/search/resources/api/v2/configuration?nodeName=ingest&envType=auth
Request Body:
{
"global": {
"connector": [
{
"name": "attribute",
"property": [
{
"name": "stemmer.language",
"value": "
{\"nb_NO\": \"Norwegian\", \"nl_NL\": \"Dutch\"}
"
}]}]}}For assistance in acquiring the stemmer for a particular language, see the topic Snowball token filter on the Elasticsearch documentation website.
/configuration REST
endpoint.GET - http://dataQueryHost:dataQueryPort/search/resources/api/v2/configuration?nodeName=ingest&envType=auth{
"name": "stemmer.language",
"value": "
{\"ar_EG\": \"Arabic\", \"da_DK\": \"Danish\", \"de_DE\": \"German\", \"en_US\": \"English\", \"es_ES\": \"Spanish\", \"fi_FI\": \"Finnish\", \"fr_FR\": \"French\", \"hu_HU\": \"Hungarian\", \"it_IT\": \"Italian\", \"nb_no\": \"Norwegian\", \"nl_NL\": \"Dutch\", \"pt_BR\": \"Portuguese\", \"ro_RO\": \"Romanian\", \"ru_RU\": \"Russian\", \"sv_SE\": \"Swedish\", \"tr_TR\": \"Turkish\"}
"
},
{
"name": "stopword.language",
"value": "
{ \"ar\": \"_arabic_\", \"da\": \"_danish_\", \"de\": \"_german_\", \"el\": \"_greek_\", \"en\": \"_english_\", \"es\": \"_spanish_\", \"fi\": \"_finnish_\", \"fr\": \"_french_\", \"hu\": \"_hungarian_\", \"it\": \"_italian_\", \"ja\": \"_cjk_\", \"ko\": \"_cjk_\", \"nb\": \"_norwegian_\", \"nl\": \"_dutch_\", \"pt\": \"_portuguese_\", \"ro\": \"_romanian_\", \"ru\": \"_russian_\", \"sv\": \"_swedish_\", \"tr\": \"_turkish_\", \"zh\": \"_cjk_\"}
"
}If the stemmer.language or
stopword.language properties are not present in the
Ingest node, update these using the /configuration endpoint
asdescribed in Manually adding languages when using Basic NLP
Enabling category search for non-leaf categories
HCL Commerce allows Shoppers to find products based on their associated parent category name, orin the case of a list of category names. This situation can arise when linked categories or a full category path search are enabled for searching. Once a category name match is found, all products within this category are returned in the search result. Additional refinement can be performed together with other terms in the same search phrase. For example, a search phrase "Gusso dresses" includes a Gusso brand name and a category name (as well as a product name) called "dresses". This search will return all products under those categories that have "dresses" in their name that are of the Gusso brand, followed by other products that only match "Gusso" or "dresses" in their name or short description.
Category search is disabled in Basic NLP. This means that while
performing keyword searches, only leaf level categories are considered when matching
the input term to categories. You can configure the system to match the input term
for non leaf categories as well, using the following configuration endpoint. Set the
value of the Ingest property flow.basic.nlp.category.search to
true. By default category search is disabled; to enable it,
perform the following steps.
- Execute a PATCH request to the Ingest configuration API with the included
request
body.
PATCH - http://dataQueryHost:dataQueryPort/search/resources/api/v2/configuration?nodeName=ingest&envType=auth { "global": { "connector": [ { "name": "attribute", "property": [ { "name": "flow.basic.nlp.category.search", "value": "true" } ] } ] } } - Perform a full reindex. See Building the Elasticsearch index for the procedure.
- Restart the Query service. For more information, see Starting the Query Docker container with default configurations.
Boosting results in Basic NLP
"Boost":"com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchBasicNLPBoostQueryProviderHelper"{
"profileName": "HCL_NLPProfile",
"provider": {
"PartNumber": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPCustomPartNumberHelper",
"BlankSpace": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPWhiteSpaceProviderHelper",
"CurrenySymbol": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPCurrencySymbolProviderHelper",
"SpellCorrect": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPSpellCorrectionProviderHelper",
"ExcludeSearchTerm": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPExcludedTermProviderHelper",
"NumberFormatter": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPNumberFormatterProviderHelper",
"STA": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPSTAExpansionProviderHelper",
"DependenciesParsing": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPDependenciesParsingProviderHelper",
"MultiWordSearchTerm": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPMultiwordTermProviderHelper",
"LowerCase": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPLowerCaseProviderHelper",
"DMM": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPDMMProviderHelper",
"SpecialCharacter": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPSpecialCharacterProviderHelper",
"MultiWordPriceFilter": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchMultiwordFilterProviderHelper",
"Stopword": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPStopwordProviderHelper",
"WordToNumber": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPWordToNumberProviderHelper",
"PriceFilter": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPPriceFilterProviderHelper",
"POS_NER": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPPOSAndNERProviderHelper",
"Color": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPColorMMProviderHelper"
},
"classification": {
},
"termDroppingPriority": {
"1": "FILTER",
"2": "MEASUREMENT",
"3": "BRAND",
"4": "COLOR",
"5": "ADJECTIVE",
"6": "CATEGORY",
"7": "NOUN"
}
} Note: You can disable term dropping by setting
termDroppingPriority to a null value. For more information,
see Disabling term dropping.
Note: You can disable term dropping by setting
termDroppingPriority to a null value. For more information,
see Disabling term dropping.{
"profileName": "HCL_Basic_NLPProfile",
"provider": {
"PartNumber": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPCustomPartNumberHelper",
"CategorySearch" : "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchBasicNLPCategorySearchProviderHelper",
"BlankSpace": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPWhiteSpaceProviderHelper",
"CurrenySymbol": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPCurrencySymbolProviderHelper",
"LowerCase": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPLowerCaseProviderHelper",
"SpellCorrect": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPSpellCorrectionProviderHelper",
"ExcludeSearchTerm": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPExcludedTermProviderHelper",
"Fractional": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPFractionalNumberHelper",
"DMM": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPDMMProviderHelper",
"MultiWordPriceFilter": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchMultiwordFilterProviderHelper",
"Stopword": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchBasicNLPStopwordProviderHelper",
"PriceFilter": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPPriceFilterProviderHelper",
"POS_NER": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchBasicNLPPOSAndNERProviderHelper",
"Color": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchNLPColorMMProviderHelper",
"Boost": "com.hcl.commerce.search.internal.expression.provider.SearchBasicNLPBoostQueryProviderHelper"
},
"classification": {
},
"termDroppingPriority": {
"1": "FILTER",
"2": "MEASUREMENT",
"3": "BRAND",
"4": "COLOR",
"5": "ADJECTIVE",
"6": "CATEGORY",
"7": "NOUN"
}
}{
"name": "basic.nlp.boost.fields",
"value":"NOUN=nlp.natural.categories.[catalogId].normalized,BRAND=nlp.natural.names.raw,CATEGORY=nlp.natural.categories.[catalogId].raw"
}
- Before ‘=’ is the classification.
- After ‘=’ is the field on which you perform boosting if it is identified as NOUN, BRAND, or CATEGORY classification.
‘basic’.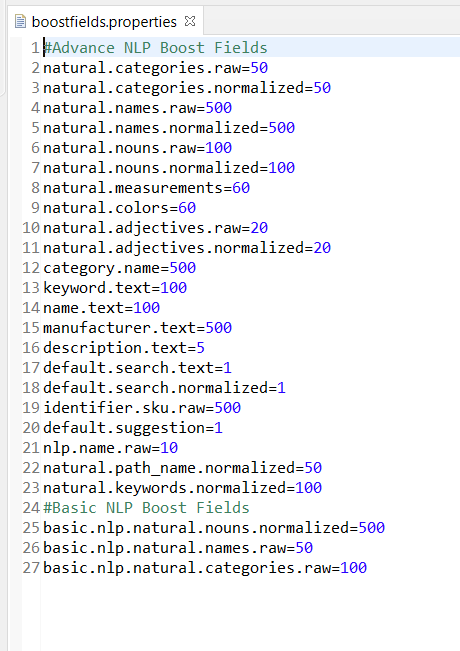
Disabling Basic NLP in Versions 9.1.15.2+
To completely disable Natural Language Processing when the Basic NLP option is being used in Versions 9.1.15.2 and upward, perform the following steps.
- Remove all the languages from NLP_ENABLE_LANGUAGE_CODE by setting the value of this environment value to null.
- Add a new empty Basic NLP profile in Zookeeper using the data
query endpoint
/search/resources/api/v2/documents/profiles/. Include the
following content:
Configure this new NLP profile as explained in Configuring the NLP profile.{ "profileName": "HCL_Basic_NLPProfile1", "provider": {}, "classification": { }, "termDroppingPriority": {} } - Set the flow.disable.basic.nlp attribute to
trueusing the following REST endpoint:
Use the following content to change the attribute:PATCH API https://data-query-host:data-query-port/search/resources/api/v2/configuration?nodeName=ingest&envType=auth
For more information about the flow.disable.basic.nlp attribute, see Ingest configuration via REST.{ "global": { "connector": [ { "name": "attribute", "property": [ { "name": "flow.disable.basic.nlp", "value": "true" } ] } ] } }

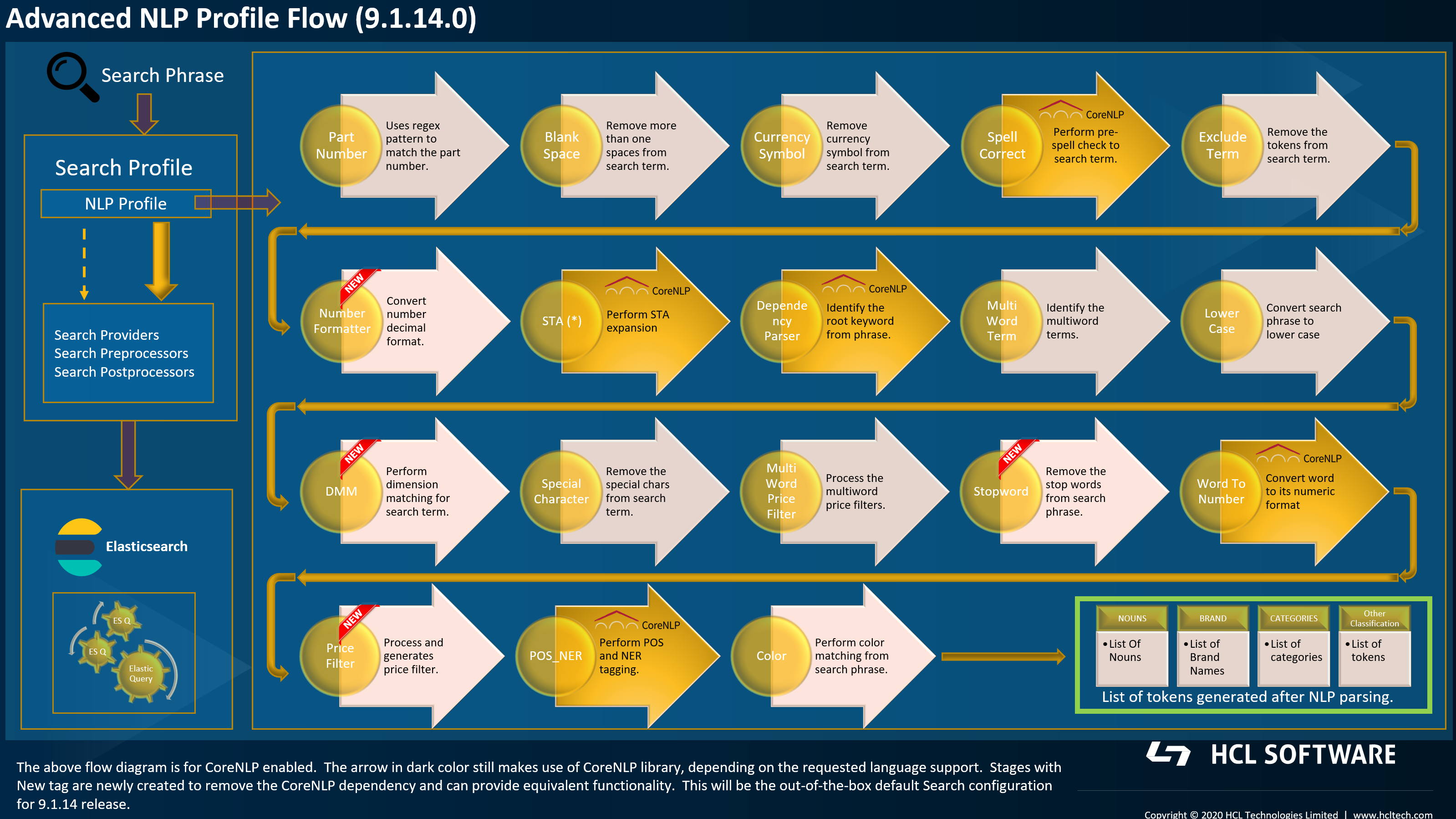
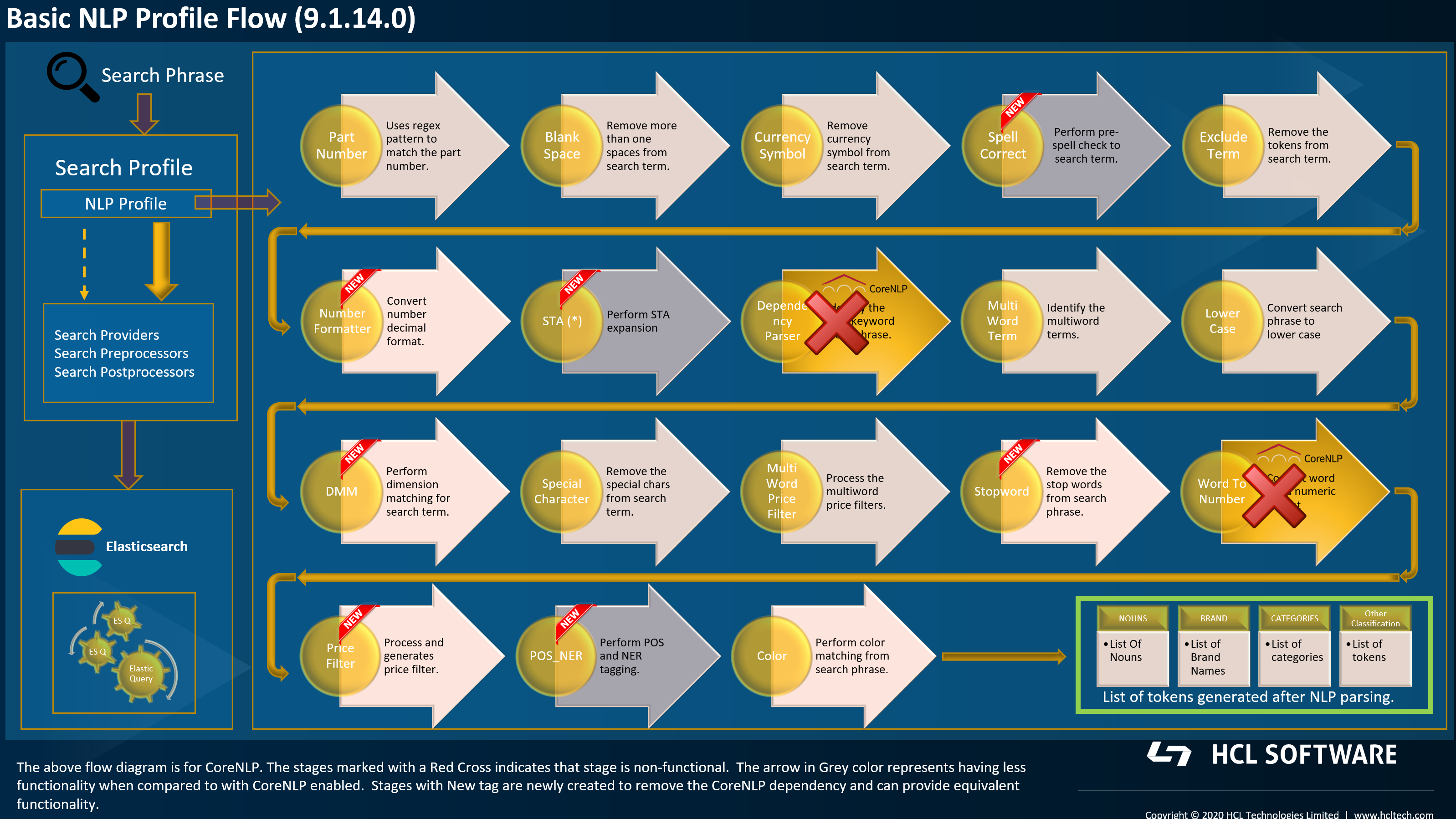
Advanced NLP vs. Basic NLP
When configuring search in HCL Commerce Search, you can choose between Advanced NLP (CoreNLP-enabled) and Basic NLP. Basic NLP runs without the Stanford CoreNLP engine and therefore disables several NLP stages. This section explains the differences and the impact on search and relevancy when switching from Advanced to Basic NLP.
- Overview of the NLP Processing Differences
- The following diagrams illustrate the complete NLP pipeline for Advanced NLP
and Basic NLP. Stages marked with a red cross in the Basic NLP flow are not
functional without CoreNLP. Key differences include:
- No dependency parsing.
- No word-to-number conversion.
- Functional Comparison Table (Advanced vs. Basic NLP)
-
Table 1. NLP Stage Advanced NLP Basic NLP Impact Part Number YES YES No impact Blank Space Normalization YES YES No impact Currency Symbol Removal YES YES No impact Spell Correct YES (CoreNLP) YES (limited) Less functionality when compared with core NLP enabled Exclude Search Terms YES YES No impact Number Formatter YES YES No impact Search Term Association (STA) YES (CoreNLP) YES (limited) Less functionality when compared with core NLP enabled Dependency Parsing YES NO Disabled in Basic NLP Multiword Search Term YES YES No impact Lowercase YES YES No impact Dimension Match Maker YES (CoreNLP) YES No impact Special Character Removal YES YES No impact Multiword Price Filter YES YES No impact Stop Word Removal YES YES No impact Word to Number YES (CoreNLP) NO Disabled in Basic NLP Price Filter YES YES No impact POS and NER YES (CoreNLP) YES (limited) Less fuctionality when compared with core NLP enabled Color Extraction YES YES No impact
Search Behavior and Relevancy Changes When Using Basic NLP
- Reduced Relevancy Accuracy. Without dependency parsing, the system
cannot extract the "root term" from complex queries. Example:
- Advanced NLP: "red women running shoes" -> running shoes become the core token.
- Basic NLP: Root keyword is not extracted -> matches may be less targeted.
- No Word-to-Number Conversion. Advanced NLP converts words like
"fifty" or "hundred" into numeric values. Basic NLP does not perform this
conversion, which affects queries like:
- "dress under fifty"
- "laptop above thousand"
- "camera under one fifty"
Advanced NLP can convert "fifty" → 50, enabling proper price-range filtering. Basic NLP cannot, which may reduce relevancy for price or numeric range queries.
- Reduced accuracy for Spell Correct, STA, and POS/NER. These stages
are functional in Basic NLP but run with limited logic because CoreNLP is
not available.
- Spell Correct. Less accurate suggestions.
- STA. Reduced matching for singular/plural variants or similar terms.
- POS/NER. Advanced NLP identifies brands, categories, product types, and nouns from the query. Basic NLP treats all tokens equally, which may weaken categorization and filter scoring.
When to use Basic and Advanced NLP
- Performance and resource usage need to be optimized.
- The environment cannot support CoreNLP dependencies as your site uses languages that are not supported by Advanced NLP (CoreNLP).
- Your product catalog relies on simpler query patterns.
- You primarily use keyword-based searches.
- You require accurate semantic matching.
- Queries frequently include numbers, ranges, or units.
- You depend on brand/category recognition through NLP.
- You require high accuracy STA and synonym.
- Relevancy tuning is critical for your business.