
NLP processing details in API responses
NLP Processing Details
Details of the current search request's Natural Language Processing (NLP) parse are available in the term search API response's metadata section. This metadata is generated after any applicable search term dropping logic has been applied to the query. Along with these details in the metadata, the final Elasticsearch query is provided. These details are returned when you use the request parameter esQueryWithGrouping. This parameter returns the grouping query if grouping is enabled. esQueryWithoutGrouping will return the query without grouping in case grouping is disabled.
- What was the search term
- Spell correction details
- Excluded terms
- Synonym expansion or replacements made for any keyword
- Price filters
- Part of speech tagging / Name Entity Recognition
- Color Filter
The following example supposes that you have synonyms and replacement setup as follows.
{
"chair => sofa": "",
"sofa, couch": ""
}
Suppose that a search is made using the string red style home cheir under
$500, where the keyword chair is misspelled as
cheir. The nlpParsing list includes two JSON
objects, which show that in the first iteration the query returned with zero result.
In the next iteration, the Query service applies search term dropping logic based on
the dropping priority defined in the NLP profile. The second JSON object in the
parsing list contains the result from parsing with that logic applied. If this
fails, the process continues until a result is returned, or there is no result. In
this case, cheir is matched to chair. The
nlpParsing list is populated in each iteration. During the
NLP parse, each token is given a map classification. When Search Term Asssociation
(STA) is applied, chair is replaced with sofa and
then sofa gets expanded with sofa OR couch,
under $50 is analyzed as a price filter, and
[LTE:50] is considered as less than or equal to $50.
The complete contents of nlpParsing are shown in the screenshot below.

chair will be classified as as
CATEGORY.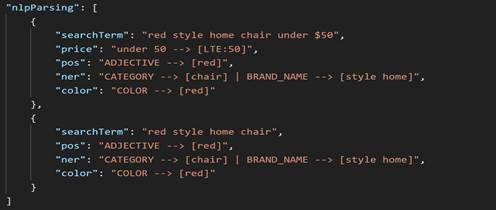
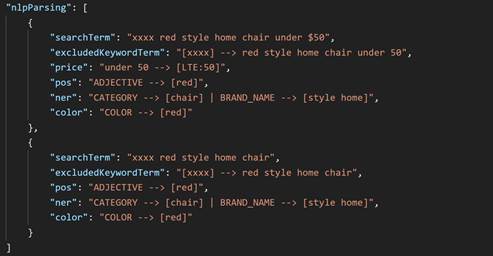
xxxx. This parameter
is passed on as an excluded term.
In all the screenshot images above, the red text is mapped onto the ADJECTIVE (pos) section, as well as COLOR. In this case color is first analyzed as an adjective. In the later stage of NLP processing, all the adjectives from the adjective list are scanned, and color names are extracted and sent to the color filter.
If you want the generated Elasticsearch query in the response, for troubleshooting
purposes, pass
esQueryWithGrouping=
or
trueesQueryWithoutGrouping=
parameter in the term search API request.The query is returned in the metadata
section of the API response. This query is generated based on the last iteration of
the NLP parsing cycle. This Elasticsearch query can be directly executed in
Elasticsearch.true

Boosting search terms in Basic NLP
When boosting search terms of types NOUN, CATEGORY, and BRAND_NAME, boost information
can be included in the search response within the
metaData.nlpParsing node. This boost factor is customizable.
pos and ner are added to both search
terms with a boost factor of 100.0. The information is only adding to the search response,
and the overall process of boosting remains unchanged. Before being boosted, it is defined as:{
"metaData":
{
"price": "1",
"nlpParsing":
[
{
"searchTerm": "Stonehenge gifts"
}
]
}
...
}{
"metaData":
{
"price": "1",
"nlpParsing":
[
{
"searchTerm": "Stonehenge gifts",
"pos": "NOUN --> [bath~bathing] (boosted by 100.0)",
"ner": "BRAND_NAME --> [stonehenge] (boosted by 100.0)"
}
]
}
...
}