Payments subsystem architecture
The Payments subsystem contains three main parts: Payment rules engine, Payment plug-in controller, and payment plug-ins.
Review the following concepts related to the Payments subsystem:
- Payment methods
- Refund methods
- Payment, refund, and return payment business policies
- Payment instructions
- Payment events and task commands
- Payment actions
- Financial transactions
The Payments subsystem contains three main parts:
- Payment rules engine
- The Payment rules engine determines which action to take based on the payment instruction, payment method and the payment event.
- Payment plug-in controller
- The Payment plug-in controller is a component of the Payments subsystem. It determines which plug-in to use (based on the payment method) and which plug-in API method to call (based on the action).
- Payment plug-ins
- A payment plug-in is a self-contained software component that serves as a proxy for a payment back-end system.
Payment processing flow
The following diagram shows how a payment is processed by the Payments subsystem.
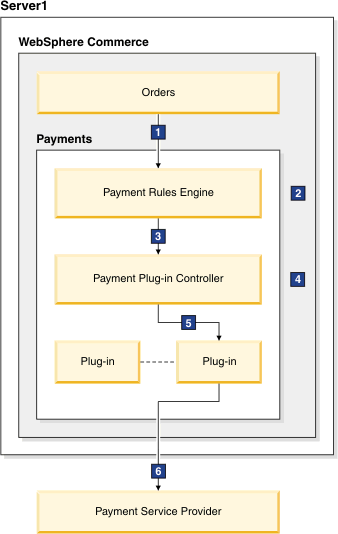
- The shopper or CSR completes an order. When the order is submitted, the OrderProcess command runs, then invokes the PrimePayment payment task command.
- The Payment rules engine determines the payment action that needs to be performed, for example, Approve.
- The payment action is wrapped into an event, which is passed to the Payment plug-in controller. For example, for the approve action, the Payment plug-in controller API Approve is called.
- The Payment plug-in controller determines which plug-in to use.
- The payment action is invoked against the plug-in. For example, for approve action, the API approve of the corresponding plug-in is called.
- The plug-in interacts with the Payment Service Provider.
- The plug-in sets the transaction state according to the transaction execution results with the Payment Service Provider. This transaction state will return to the Payment plug-in controller.
- The Payment plug-in controller updates the payment related records in the database according to the state of transaction execution returned by the plug-in.