Configuring the data load environment settings
Configure the environment variables that are used by the Data Load utility in an XML file called wc-dataload-env.xml.
Procedure
-
Create a file that is called wc-dataload-env.xml. You can create this file
within any directory. Ensure that any other Data Load utility configuration file that must reference
this file includes the path to your new file.
Sample environment configuration files are provided for different component objects within the component-specific directories within the following directory:
- WC_installdir/samples/DataLoad
- WCDE_installdir/samples/DataLoad
-
Change the values of the business context attributes inside the
<_config:BusinessContext>element to match your store settings:- storeIdentifier
- The identifying name of the store that owns the object data, for example, Aurora.
- langId
- The language ID for the language of the data, for example, -1 for English.
If you are configuring the utility to load catalog data, configure the following settings:- catalogIdentifier
- The catalog that includes the catalog entry or category data, for example, Aurora.
- currency
- The currency code for the price data, for example, USD.
For example:<_config:BusinessContext storeIdentifier="AuroraESite" catalogIdentifier="Extended Sites Catalog Asset Store" languageId="-1" currency="USD"> </_config:BusinessContext> - Required:
Change the attribute values inside the
<_config:Database>element to match your database environment.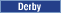
<_config:Database type="derby" name="..\..\db\mall" />
<_config:Database type="db2" name="database name" user="user" password="encrypted password" server="server" port="50000" schema="schema name" />
<_config:Database type="Oracle" name="database name" user="user" password="encrypted password" port="1521" schema="schema name" driverType="thin" />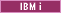
<_config:Database type="os400" name="database name" user="user" password="encrypted password" server="server" remoteDB="true" driverType="toolbox" />
- type
-
 derby
derby db2
db2 oracle
oracle os400
os400
- name
- The name of the database
- user
- The database user ID.
 If you are using an Oracle database, the user you specify should be
identical to the schema. If you specify an invalid schema in the settings, the user is used as the
database schema if the user is different and valid. The utility displays a warning, which explains
that a change occurred and then the utility continues to run.
If you are using an Oracle database, the user you specify should be
identical to the schema. If you specify an invalid schema in the settings, the user is used as the
database schema if the user is different and valid. The utility displays a warning, which explains
that a change occurred and then the utility continues to run.  If you use DB2 and you specify an invalid schema, an error message displays.
This message indicates that a valid schema is required before the utility runs.
If you use DB2 and you specify an invalid schema, an error message displays.
This message indicates that a valid schema is required before the utility runs.
- password
- The database password is necessary to connect to the database. For security purposes, the password is always encrypted. If the password field is empty, you are prompted to enter the password on the command line when you run the utility.
- server
- The name of the server the database is on. The server name can be the IP address or the fully qualified DNS name of the server the database is on.
- port
- The port to connect to the database.
- remoteDB
- Indicates whether the database is remote.
 If your system uses DB2 for IBM i with a remote iSeries database, set the value
for this parameter to be
If your system uses DB2 for IBM i with a remote iSeries database, set the value
for this parameter to be "true".
- driverType
- Optional: The database driver type.
 The default value for the
The default value for the
driverTypeisthin. Another possible option for thedriverTypeisoci8, which is the oracle thick driver. The supported values for the
The supported values for the driverTypeare2and4.
 If you are configuring your
development environment to use DB2 for IBM i, set the value for this parameter to be
If you are configuring your
development environment to use DB2 for IBM i, set the value for this parameter to be
"toolbox". - schema
- The name of the database schema.
- Required:

 Encrypt the password of the database user:
Encrypt the password of the database user:
- Enter the following command:

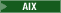 ./wcs_encrypt.sh db_password
./wcs_encrypt.sh db_password
 wcs_encrypt.bat
db_password
wcs_encrypt.bat
db_password
- Use the encrypted password next to ASCII encrypted string as the
value for the
passwordattribute inside the<_config:Database>element.
- Enter the following command:
-
Find the
<_config:IDResolver>element. - Optional:
Modify the cache size inside the tag. The cache size that you specify here does not apply to a
specific database table, but is instead divided between all database tables that are participating
in a data load.
- cacheSize
- This attribute sets the cache memory allocation for the ID resolver. The ID resolver performs faster when unique ID data in retrieved from cache memory instead of from the database.
Note: If you do not specify a<_config:IDResolver>element, the default cache size value is 0 bytes. - Optional:
Identify any database tables that are to be excluded from having IDs from those tables included
within the IDresolver cache. When a table is excluded from this cache, the Data Load utility
resolves the ID for business objects information directly against the database table.
Note: For Non-ATP inventory model.
If you plan to perform multiple inventory updates that include a delete and a reinsert for the same catalog entry, then you need to exclude the INVENTORY database table. Otherwise the catalog entry is not reinserted after a delete due to a IDresolver cache limitation.
To exclude a table from the ID resolver cache, use the<_config:ExcludeCache>element within the<_config:IDResolver>element. Specify the table with thetableNameattribute. Specify each table that is to be excluded in a separate<_config:ExcludeCache>element. For example,<_config:IDResolver className="com.ibm.commerce.foundation.dataload.idresolve. IDResolverImpl" cacheSize="2000" > <_config:ExcludeCache tableName="BASEITEM" /> <_config:ExcludeCache tableName="CATENTRY" /> <_config:ExcludeCache tableName="INVENTORY" /> </_config:IDResolver> - Optional:
Set the data writer class. Find the
<_config:DataWriter>element. Add the class name of the data writer inside the tag.Option Description 
 native load data writerWrites WebSphere Commerce physical objects to database loadable files. The files are specific to the selected database management system. These files must be written to the database with the native database loading utilities in a separate operation.
native load data writerWrites WebSphere Commerce physical objects to database loadable files. The files are specific to the selected database management system. These files must be written to the database with the native database loading utilities in a separate operation. The native data writer supports both insert mode and replace mode. In insert
mode, it uses the DB2 load utility to load the native loadable files. In replace mode, it uses the
DB2 import utility to load the native loadable file.
The native data writer supports both insert mode and replace mode. In insert
mode, it uses the DB2 load utility to load the native loadable files. In replace mode, it uses the
DB2 import utility to load the native loadable file. The native data writer supports only the insert mode. In insert mode, it
uses the Oracle sqlldr utility to load these native loadable files.
The native data writer supports only the insert mode. In insert mode, it
uses the Oracle sqlldr utility to load these native loadable files.
Use the native load data writer for faster performance than JDBC batch jobs, such as when a large amount of data is being loaded during initial loads.
<_config:DataWriter className="com.ibm. commerce.foundation.dataload.datawriter.NativeDBDataWriter" />

 JDBC data writer
JDBC data writerWrites physical objects directly to a database in a JDBC batch job. The JDBC data writer has the following advantages over the native load data writer: - The JDBC data writer supports insert, delete, and replace modes. The native load data writer supports only the insert mode.
- The native load data writer bypasses database triggers, requiring data to be loaded separately to both production and staging servers. The JDBC data writer does not bypass database triggers.
- The JDBC data writer provides more error reporting than the native load data writer.
Use the JDBC data writer for greater flexibility, such as when you replace and delete data during the same load.
<_config:DataWriter className="com.ibm. commerce.foundation.dataload.datawriter.JDBCDataWriter" />Note: If you do not specify a<_config:DataWriter>element, the JDBC data writer is used by default. - Save and close the configuration file.