Local-loopback connections
A network connection between a client application and a database server on the same computer is called a local-loopback connection.
The networking facilities used are the same as if the client application and the database server were on different computers. You can make a local-loopback connection provided your computer is equipped to process network transactions. Local-loopback connections are not as fast as shared-memory connections, but they do not pose the security risks of shared memory.
In a local-loopback connection, data seems to pass from the client application, out to the network, and then back in again to the database server. The internal connection processes send the information directly between the client and the database server and do not put the information out on the network.
An example of a local-loopback connection
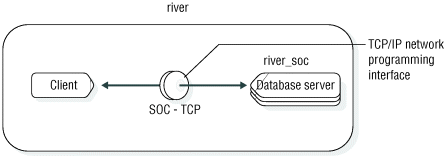
#dbservername nettype hostname servicename options
river_soc onsoctcp river riverolontlitcp instead
of onsoctcp.DBSERVERNAME river_socThis example assumes that an entry for river is in the hosts file and an entry for riverol is in the services file.