Shared-memory connections (UNIX)
A shared-memory connection uses an area of shared-memory as the channel through which the client and database server communicate with each other. A client cannot have more than one shared-memory connection to a database server.
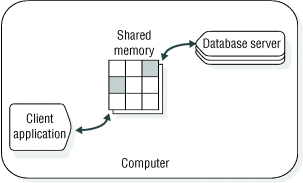
Shared memory provides fast access to a database server, but it poses some security risks. Errant or malicious applications might delete or view message buffers of their own or of other local users. Shared-memory communication is also vulnerable to programming errors if the client application performs explicit memory addressing or over-indexes data arrays. Such errors do not affect the database server if you use network communication or stream pipes.
Example of a shared-memory connection
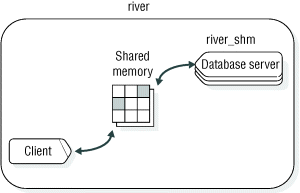
DBSERVERNAME river_shm
#dbservername nettype hostname servicename options
river_shm onipcshm river rivershmCONNECT TO '@river_shm'For
a shared-memory connection, no entries in network configuration files
are required. Use arbitrary values for the hostname and servicename fields
of the sqlhosts file.