Installing AMQ Streams Operator for Kafka
This section provides a detailed guide to installing and configuring the AMQ Streams Operator for Kafka on Red Hat OpenShift.
AMQ Streams simplifies the deployment and management of Apache Kafka clusters in a Kubernetes environment, enabling reliable real-time data streaming and messaging capabilities.
The guide includes steps for installing the AMQ Streams Operator from the OpenShift Operator Catalog, deploying a Kafka cluster, configuring essential resources like secrets and users, and setting up a sample Kafka cluster with Zookeeper.
- In the OpenShift Operator catalog, search and install the AMQ Streams operator.

- In the Operators > Installed Operations, deploy a Kafka Cluster Instance.
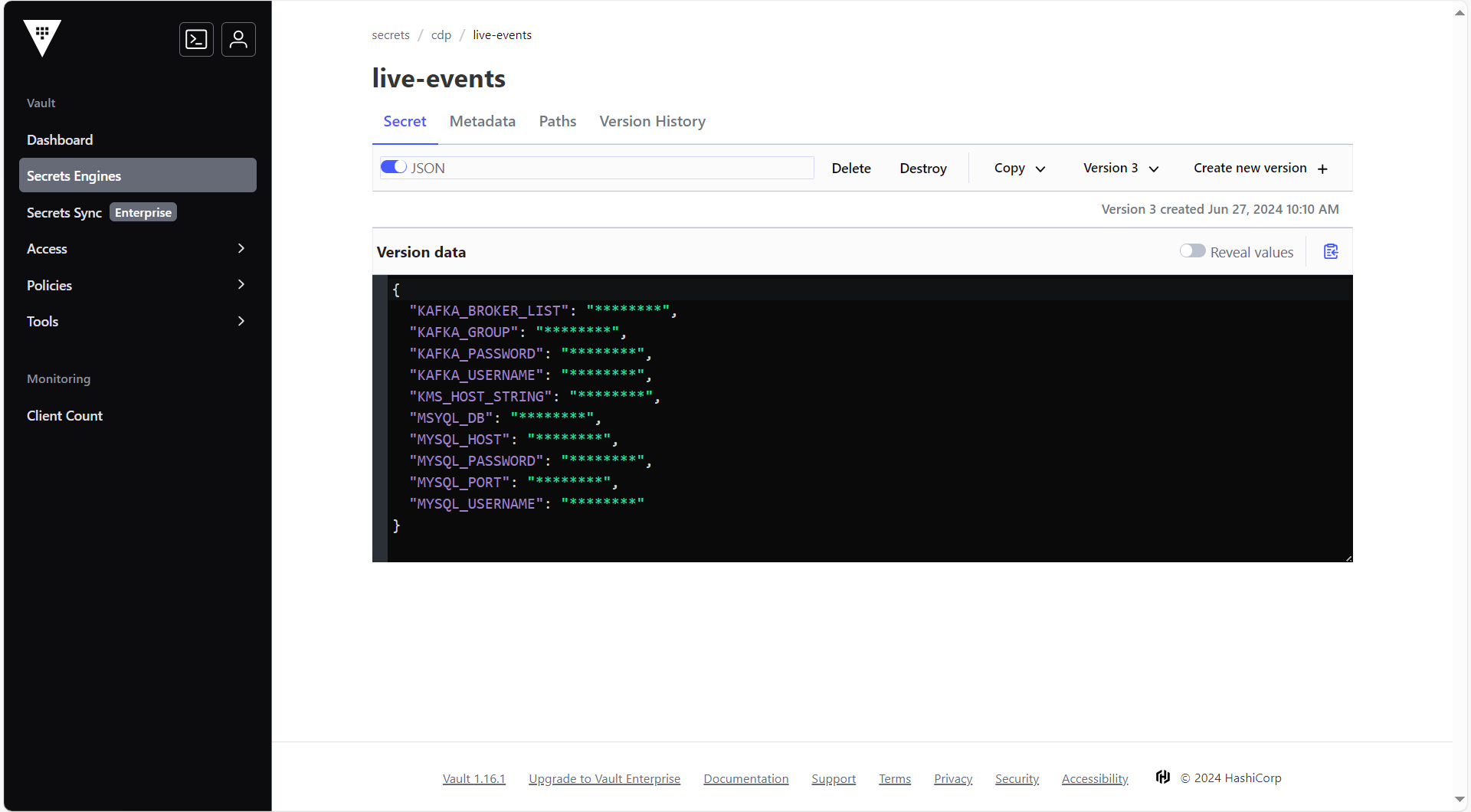 Note: Make sure to create a secret with username and password for Kafka user and create a Kafka user. For more information on creating user and secrets, refer and .
Note: Make sure to create a secret with username and password for Kafka user and create a Kafka user. For more information on creating user and secrets, refer and . - After creating the user account and secrets, in the Operator details section, for the AMQ
Streams, select Kafka and click Create Kafka.
.png)
- In the Create Kafka section, click the YAML View option, and create a Kafka cluster
instance with zookeeper. A sample config.yaml file is provided
below.
apiVersion: kafka.strimzi.io/v1beta2x kind: Kafka metadata: labels: app: sbi-kafka name: hclsw-sbi-dev-kafka namespace: kafka-ns spec: entityOperator: topicOperator: {} userOperator: {} kafka: authorization: superUsers: - hclsw-sbi-kafka-user type: simple config: default.replication.factor: 2 inter.broker.protocol.version: '3.6' min.insync.replicas: 2 offsets.topic.replication.factor: 2 transaction.state.log.min.isr: 2 transaction.state.log.replication.factor: 2 listeners: - authentication: type: scram-sha-512 configuration: preferredNodePortAddressType: Hostname name: external port: 9094 tls: false type: nodeport - authentication: type: scram-sha-512 name: internal port: 9092 tls: false type: internal replicas: 2 resources: limits: cpu: '4' ephemeral-storage: 20Gi memory: 8Gi requests: cpu: '2' ephemeral-storage: 20Gi memory: 2Gi storage: class: nfssc deleteClaim: false size: '20' type: persistent-claim version: 3.6.0 zookeeper: replicas: 3 resources: limits: cpu: '4' ephemeral-storage: 20Gi memory: 8Gi requests: cpu: '2' ephemeral-storage: 20Gi memory: 2Gi storage: class: nfssc deleteClaim: true size: 20Gi type: persistent-claim - On successful deployment of cluster, the two broker pods and three zookeeper pods will be
created.
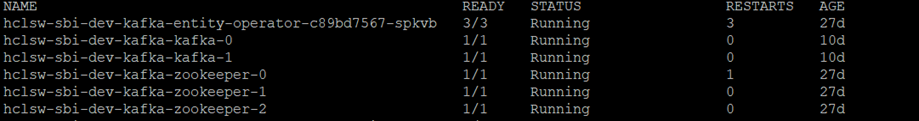
- To access the Kafka within the cluster, the Bootstrapper URL will be created as shown
below.
<Your-cluster-name>-kafka-bootstrap.cdp.svc:9092 - Similarly, to access the Kafka from outside the cluster (DMP Producer application), the
Bootstrapper URL will be created as shown below.
<hostname1>:31571,<hostname2>:31571 - Once a Kafka instance is deployed follow below steps to create a secret and user for accessing Kafka.
Creating secret for Kafka User
The
Secret object type provides a mechanism to hold sensitive information
such as passwords, OpenShift Container Platform client configuration files, private source
repository credentials, and so on. You can create a kafka-cdp-secret on the OpenShift
cluster for Kafka User.Note: Make sure that the username and password
must be in base64 format.
apiVersion: v1
data:
password: WWQ4cXloWmNuREpXUUpMMzg2dGZ4UQ==
username: aGNsc3ctc2JpLWthZmthLWNkcC11c2Vy
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: kafka-cdp-secret
namespace: cdp
type: OpaqueCreating Kafka User
To create a Kafka user, follow the steps below:
- In the AMQ Streams section, select Kafka User and click Create KafkaUser
for accessing Kafka and performing operations on topics and create consumer
groups.
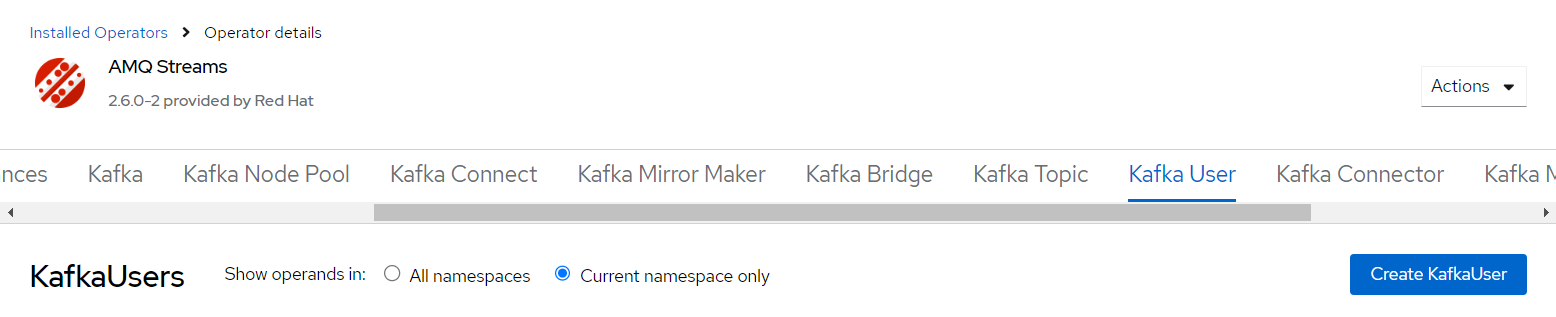
- Create the user with label having Kafka cluster name e.g.
hclsw-sbi-dev-kafka.
strimzi.io/cluster: hclsw-sbi-dev-kafkaapiVersion: kafka.strimzi.io/v1beta2 kind: KafkaUser metadata: labels: app: sbi-kafka strimzi.io/cluster: hclsw-sbi-dev-kafka name: hclsw-sbi-kafka-user namespace: kafka-ns spec: authentication: password: valueFrom: secretKeyRef: key: password name: kafka-cdp-secret type: scram-sha-512 authorization: acls: - host: '*' operation: All resource: name: '*' patternType: literal type: topic type: allow - host: '*' operation: All resource: name: '*' patternType: literal type: group type: allow type: simple - In the YAML view, update the authorization block to allow permissions to user on topic
and Group.
spec: authentication: password: valueFrom: secretKeyRef: key: password name: hclsw-sbi-kafka-secret type: scram-sha-512 authorization: acls: - host: '*' operation: All resource: name: '*' patternType: literal type: topic type: allow - host: '*' operation: All resource: name: '*' patternType: literal type: group type: allow type: simple