REST service annotations
WebSphere Commerce REST services and Search REST services are annotated so you view
and test the APIs with Swagger, an interactive REST service interface. The REST Discovery API
generates a list of REST resources and APIs by parsing annotations on a resource handler. By
documenting your custom REST resource handlers with the same annotation standards as WebSphere Commerce REST services, your custom REST services can be viewed and tested with
Swagger.
Available REST annotations
WebSphere Commerce REST service and Search REST services are annotated with a combination of
custom REST and JAX-RS annotations available from the Apache Wink implementation. You can use these
annotations when you are creating your custom REST services. For more information about the
available JAX-RS annotations, see:
Note: WebSphere Commerce REST and Search REST services use the
standard Swagger specification (version 1.2). For more information about this Swagger specification,
see Swagger RESTful API Documentation
The following code illustrates a POST method that was annotated with a combination of the
supported WebSphere Commerce REST annotations:
@POST
@Path("catalogEntryUpdate")
@Description("A sample REST POST that executes the CatalogEntryUpdateCmd based on the request parameters and profile specified.")
@Produces({ MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON, MediaType.APPLICATION_XML, MediaType.APPLICATION_XHTML_XML, MediaType.APPLICATION_ATOM_XML })
@AdditionalParameterList({
@ParameterDescription(name = ParameterDescription.BODY_NAME, paramType = ParameterDescription.BODY_TYPE,
description = "CatalogEntryUpdate request body.", typeClass = CatalogEntryUpdateRequest.class)
})
@ResponseSchema(valueClass = CatalogEntryUpdateResponse.class, responseCodes = {
@ResponseCode(code = 200, reason = RESPONSE_200_DESCRIPTION),
@ResponseCode(code = 400, reason = RESPONSE_400_DESCRIPTION),
@ResponseCode(code = 401, reason = RESPONSE_401_DESCRIPTION),
@ResponseCode(code = 403, reason = RESPONSE_403_DESCRIPTION),
@ResponseCode(code = 500, reason = RESPONSE_500_DESCRIPTION)
})
public Response processRequest(
@PathParam("storeId") @ParameterDescription(description = PARAMETER_STORE_ID_DESCRIPTION,
valueProviderClass = StoreIdProvider.class, required = true) String storeId,
@QueryParam(value = "responseFormat") @ParameterDescription(description = PARAMETER_RESPONSE_FORMAT_DESCRIPTION,
valueProviderClass = ResponseType.class) String responseFormat,
@QueryParam(value = "profileName") @ParameterDescription(description = PARAMETER_PROFILE_NAME_DESCRIPTION) String profileName)
{
Response result = executeConfigBasedCommandWithContext(CatalogEntryUpdateCmd.class.getName(), profileName, responseFormat,
storeId, null);
return result;
}The Swagger user interface
The Swagger interface is composed of static HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, and it is accessed through
your web browser. The Swagger framework queries the REST Discovery API to display your REST resource
handlers in alphabetical order. The following screen capture shows the Swagger interface,
specifically the sample resource handler that was annotated earlier:
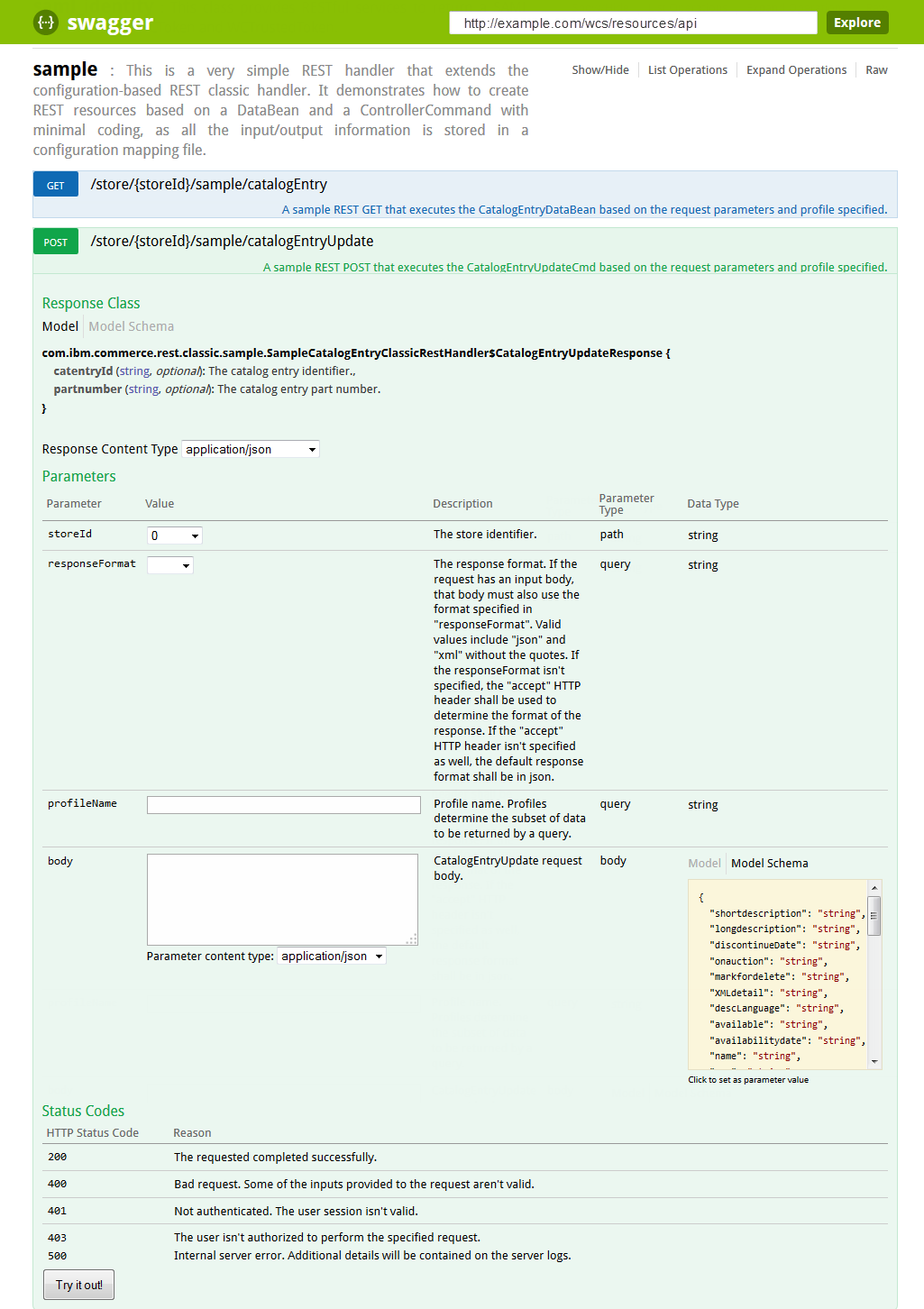
Where

Where
- Each resource handler class has a short description of the service.
- Show/Hide expands or collapses the API content of each class.
- List Operations displays a summarized view of the API content, where a row is displayed for each method's path, with a short description of the service.
- Expand Operations displays an expanded view of the API content, where rows are displayed for each method's response class, parameters, and status codes. The API can be dynamically tested by selecting Try it out! in the expanded view.
- Raw displays the raw information that the Swagger UI uses to populate the page.