The Java Emitter Template (JET) is an Eclipse-enabled template engine for generating
applications based on model-driven architecture transformations. By defining an XML file that
describes your module, the JET plug-in for Rational Application Developer (RAD) can generate the
basic WebSphere Commerce service module code for you. Afterward, you can complete the module by
completing your specific business logic to start directly with the service module implementation.
You do not need to spend hours with the setup and configuration of a service module.
About this task
In this lesson, you use the Java Emitter Template (JET) provided by WebSphere Commerce to
generate the base code for your Project service module. The Java code for a WebSphere Commerce
service module is abstracted and generated. You can then focus on implementing the code specific to
each service module, for example, the nouns and the business logic.
Procedure
- Start WebSphere Commerce
Developer.
- In the Enterprise Explorer view, create the application
definition file to create the base code for the TutorialStore service
module.
- Create the service module input file.
- Right-click the WebSphereCommerceServerExtensionsLogic project;
select .
- Enter ServiceModuleDefinition as the folder
name. This step creates a single location to store all service module
input files.
- Right-click ServiceModuleDefinition; select .
- Enter project.xml as the file name and
click Finish.
-
Paste the following application definition into the Source tab of
project.xml:
<_pattern:commerceComponent xmlns:_pattern="http://www.ibm.com/xmlns/prod/commerce/foundation/pattern"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.ibm.com/xmlns/prod/commerce/foundation/pattern ../../WC/xml/config/xsd/wc-component-pattern.xsd "
name="Project" packagenameprefix="com.mycompany.commerce" company="myCompany"
namespace="http://www.mycompany.com/xmlns/prod/commerce/9/project" nlsprefix="myprj" type="BOD">
<_pattern:noun name="Project" get="true" process="true" change="true" sync="false">
<_pattern:nounpart name="Material" xpath="/Material" />
<_pattern:nounpart name="Tool" xpath="/Tool[]" />
<_pattern:nounpart name="Instruction" xpath="/Instruction[]" />
<_pattern:nounpart name="Description" xpath="/Description[]" />
<_pattern:nounpart name="CollectionRel" xpath="/Collection[]" />
</_pattern:noun>
<_pattern:noun name="ProjectCollection" get="true" process="true" change="true" sync="false">
<_pattern:nounpart name="Description" xpath="/Description[]" />
</_pattern:noun>
</_pattern:commerceComponent>
Note: The definition indicates the name of the noun (ProjectCollection) and the verbs that are
enabled for the pattern (Get, Process, and Change, but not Sync). This file determines the assets
and code to be generated for you.
- Save the file.
- Right-click project.xml; select .
- In the Transformation section:
- Select the following ID:
- com.ibm.commerce.toolkit.internal.pattern.componentprojects
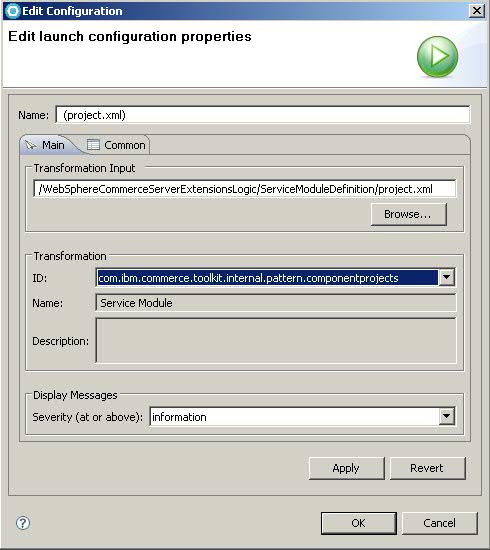
- Click OK.
- The pattern is applied. In the Navigator view, verify that
the following projects are created:
- Project-Client:
- This project contains client-specific code that is used to build requests and handle responses
from the Project Web service.
- Project-DataObjects:
- This project holds the XSD file that defines the Project noun
and the Service Data Objects generated from the Project and ProjectCollection
nouns.
- Project-Server:
- This project contains the server-side business logic for the
Project and ProjectCollection nouns.
- ProjectServicesHTTPInterface:
- This project enables the Project-Server for web services over
HTTP.
- ProjectServicesJMSInterface:
- This project enables the Project-Server for web services over
JMS.
- Project-UnitTests:
- This project contains ready built unit tests to verify the Project
component.
Note: Build errors occur in the projects at this stage because data objects are not yet generated.
Continue the tutorial to generate these objects and resolve the build errors.
- Update the WebSphere Commerce project.
- Right-click the WC project; select Refresh.
- Expand WC/xml/config/com.mycompany.commerce.project.
- Rename wc-component-client.xml to wc-component-client-J2SEWebService-example.xml
- Rename wc-component-client-local-example.xml to wc-component-client.xml
- Change the data source JNDI name:
- In the Enterprise Explorer view, expand Project-Server/ejbModule/META-INF.
- Right-click ibm-ejb-jar-bnd.xmi;
select .
- Verify that the following
jndiName values
are specified for the attribute <resRefBindings>:
- Update the build dependencies for the service module:
Note: This step is necessary as build dependencies are managed by using the Deployment Assembley
instead of the project class path.
- Add the service module to the WebSphere Commerce application.
- Expand WC, right-click WebSphereCommerceServer;
select .
- On the design pane, click Add; select Module,
then click OK.
Note: If Add is
grayed out and cannot be clicked, verify that Application,
the first option, is highlighted in the modules list.
- Under Module, select Project-Server, then
click Finish.
- Again, click Add; select Module,
then click OK.
- Under Module, select ProjectServicesHTTPInterface,
then click Finish.
- Under Actions, click . Select Project and
click Next.
- Select Project-Client and Project-DataObjects.
Click .
Note: If Actions is grayed out
and cannot be clicked, verify that Application,
the first option, is highlighted in the modules list.
- Save the changes that are made in the Application Deployment Descriptor Editor.
- Right-click the Project-Server project;
select Properties.
- Select Deployment Assembley.
Click Add.
- Select Java Build Path Entries.
Click Next.
- Select the following JAR files and projects:
- Click .
Results
In this lesson, you used the Java Emitter Template (JET) to generate the base code for
the Project component. Your next task is to generate the data objects that are required to
implement the logical data model of your Project noun. This noun is defined in the Project.xsd and
ProjectCollection.xsd files.

 jdbc/WebSphere Commerce DB2 DataSource
demo
jdbc/WebSphere Commerce DB2 DataSource
demo jdbc/WebSphere Commerce Oracle
DataSource demo
jdbc/WebSphere Commerce Oracle
DataSource demo jdbc/WebSphere Commerce Cloudscape
DataSource demo
jdbc/WebSphere Commerce Cloudscape
DataSource demo



