Date and time formatting
This section talks about the date and time formatting for globalization.
About this task
Date formatting
The date format presents the day, month, and year of a particular calendar system. Even when one specific calendar system is considered, there is no single world wide standard for the presentation of date information. Different languages represent dates in different ways. The following table lists some of the date formats used:
| Locale | Common format | Long format | Short format |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States English | 04/10/98 | April 10, 1998 | 04/10/98 |
| Simplified Chinese | 1998Year4Month10Day | 1998Year4Month10Day | 98-4-10 |
| French | 10/04/1998 | 10 avril 1998 | 10/04/98 |
| German | 10.4.98 | 10. April 1998 | 10.04.98 |
| Polish | 10.04.1998 | 10 April 1998 | 10.04.98 |
| Romanian | 10.4.1998 | 10 April 1998 | 10.4.98 |
| Russian | 10.04.1998 | 10 April 1998 | 10.04.98 |
The following are the elements of the date format that make the date unique in different regions of the world:
| Elements | Description |
|---|---|
| Date delimiter | Delimiters in date representation differ around the world.
The following are some examples of delimiters used in dates:
|
| Order of date components | The order of the day, month, and year differs around the world. |
| Day format | A zero may fill in the day if it is a single-digit day. |
| Month format | The month may be numeric, abbreviated, or fully spelled out. |
| Year format | The year format may have 2 digits or 4 digits. |
In WebSphere Commerce, either the long format or short format is usually used. Using the WebSphere Commerce Tools Framework Calendar UI element, developers can display a calendar to the user and allow them to graphically or manually enter a date. This date is then returned to the calling window and placed in the correct field. The user's input is presented in text boxes. Because those text boxes have labels attached to them, there is no ambiguity in identifying which numbers are the year, month, and day respectively. As a result, cultural formatting is not required. The following figure displays an example of an embedded calendar in WebSphere Commerce:
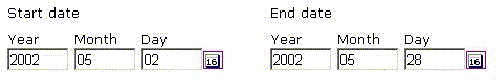
Time format
The formats used for time differ around the world. Even though a software product may manipulate time information using a Timestamp , it should display time information to, and accept time information from, the user in the correct cultural context.
The following table lists some of the time formats used:
| Locale | Common format | Long format | Short format |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States English | 2:45:16 PM | 2:45:16 PM EST | 2.45 PM |
| Simplified Chinese | 14:45:16 | 14hour45min16sec | 14:45 |
| French | 14:45:16 | 14:45:16 | 14:45 |
| German | 14:45:16 | 14:45:16 | 14:45 |
| Polish | 14:45:16 | 14:45:16 | 14:45 |
| Romanian | 14:45:16 | 14:45:16 | 14:45 |
| Russian | 14:45:16 | 14:45:16 | 14:45 |
The following are the elements of the time format that make the time format unique in different regions of the world:
| Elements | Description |
|---|---|
| Delimiter | Colon or period (Full stop) |
| Format | Some countries display the leading zero in hours. |
| 24-hour clock | Some countries use the 24-hour clock, while others such as the USA use the 12-hour clock with indicators AM/PM. |
In the WebSphere Commerce Tools Framework, the functions used to validate dates are included in the web/JavaScript/tools/common/DateUtil.js JavaScript file. Ensure this file is included in your JSP files.
Always give the user the option to launch a calendar UI element. If users enter the date manually, use the validDate (date) inside the DateUtil.js JavaScript file. The validTime() function is in the Util.js JavaScript file.
In WebSphere Commerce, the TimestampHelper class provides time and date formatting functions that are required by the WebSphere Commerce tools and store development.
The TimestampHelper() class is available in both com.ibm.commerce.utils (for tools framework) and com.ibm.commerce.ejb.helpers (for server runtime) packages to help perform the conversions described in the following table:
| From | To |
|---|---|
| Timestamp | Date in yyyy-mm-dd |
| Timestamp | Time in hh:mm |
| Date and time | Timestamp |
For example, TimestampHelper.getDateFromTimestamp(Timestamp t,Locale locale) extracts the date portion from the timestamp. The date is returned in a locale-specific manner.
Most of the WebSphere Commerce databeans are enabled to implicitly use the date or time formatting functionality of the TimestampHelper. The following example describes one such data bean:
<%@page import="com.ibm.commerce.utils.TimestampHelper"%>
...
...
Timestamp currentTime = TimestampHelper.getCurrentTime();
String date = (String)
TimestampHelper.getDateFromTimestamp(currentTime, ${locale});
...
...