
Search-based navigation
Search-based navigation enhances starter stores by performing searches against categories when browsing a storefront catalog. All immediate categories and products are returned in the results, and can also include its subcategories to increase its scope.
With search-based navigation enabled, the storefront benefits include improved search performance and accuracy, while enabling search rules and faceted navigation. As a result, the storefront delivers a perception of a personalized browsing experience in starter stores. Note: Disabling search-based navigation: Once WebSphere
Commerce search and search-based navigation are enabled, you cannot
simply disable it by clearing the selection in the Store Management
tool. Instead, in addition, you must clean up the wc-search.xml file.
Note: Disabling search-based navigation: Once WebSphere
Commerce search and search-based navigation are enabled, you cannot
simply disable it by clearing the selection in the Store Management
tool. Instead, in addition, you must clean up the wc-search.xml file.- Quick search
A search field with auto-suggest functions, integrated into the store's header at the top of the page. This allows shoppers to perform quick searches from any store page within the site.
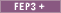 The auto-suggest menu contains suggested
keywords, categories, brands, site content, and search history.
The auto-suggest menu contains suggested
keywords, categories, brands, site content, and search history.- Category-based navigation
- A category-based navigation technique, driven by the header's top navigation menu. This is only effective when the shopper knows exactly which category their desired products are located.
- Faceted navigation
- A process of browsing information by filtering a set of topics by progressively selecting from only valid values of a faceted classification system, which is a predefined collection of facets.



 Advanced search
Advanced search



A variation of quick search, but allows for more detailed searching criteria to be specified. This is useful when the shopper knows their range of criteria or conditions to be used to narrow the scope of search results.


 The advanced search page
is available in the Madisons starter store by default.
The advanced search page
is available in the Madisons starter store by default. The advanced search page is available in
the Aurora starter store by default.
The advanced search page is available in
the Aurora starter store by default.
Catalog navigation service for the storefront
The Catalog navigation noun used with the storefront Catalog service is called the CatalogNavigationView. This noun represents a business response of a catalog browsing request. It contains a list of sub-products, called CatalogEntryView, and a list of subcategories, called CatalogGroupView.
- Component: Catalog
- Noun: CatalogNavigationView
- Namespace: http://www.ibm.com/xmlns/prod/commerce/9/catalog
- Prefix: _cat
- CatalogNavigationViewType
- Represents a business response of a catalog browsing request. Contains a list of sub-products, called CatalogEntryView, and a list of subcategories, called CatalogGroupView.
- CatalogEntryViewType
- Defines a list of catalog entries within the given catalog navigation view scope.
- CatalogGroupViewType
- Defines a list of catalog groups within the given catalog navigation view scope.
- FacetViewType
- Contains a list of facet entry view types.
- FacetEntryViewType
- Defines a label and a count for each facet entry.
- BreadCrumbTrailViewType
- Contains a list of bread crumb entry view types.
- BreadCrumbTrailEntryViewType
- Defines a label for this browsing history entry.
- PriceViewType
- Defines a price string used by storefront catalog entry view.
- AttributeViewType
- A view type definition of Catalog entry attributes which represents a group of catalog entry attributes.
- AttachmentAssetViewType
- A view type definition for an attachment asset.
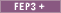 SuggestionViewType
SuggestionViewType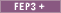 Represents a container for navigation suggestions, for example,
"Brand" or "Category" suggestions.
Represents a container for navigation suggestions, for example,
"Brand" or "Category" suggestions.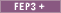 SuggestionEntryViewType
SuggestionEntryViewType Represents an entry in a navigation suggestion container. For
example, for the container "Brand," an entry might be "Sharpson."
Represents an entry in a navigation suggestion container. For
example, for the container "Brand," an entry might be "Sharpson."- PreviewReportType
- Contains a list of messages for creating a report within search preview.
 WebContentView
WebContentView Facilitates storing the search results used by the JSP file. It
helps the JSP file make service calls to the search server.
Facilitates storing the search results used by the JSP file. It
helps the JSP file make service calls to the search server.
See the CatalogEntry noun for more information, where the noun and its services are meant to be used in an Authoring environment only, while the storefront should use CatalogNavigationView.
When modeling the business data for browsing and search in the storefront, the approach is to model as many requirements from the storefront as possible using the search index. It is because most of the storefront browsing and search requests are read-only and therefore this access model fits best with a search index. However, if there exists additional personalized information that needs to be calculated at runtime based on certain user specific context, such as contract, then those information can be retrieved or recalculated on-demand through this Catalog browsing service's business object mediator. For example, overriding the indexed price amount with the calculated offer price for only the items on the current search result page.