Migrate User Settings
You can capture the user profiles and settings of a system before the reimaging process begins.
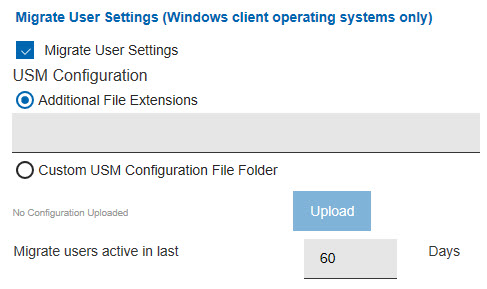
The Migrate User Settings capability captures multiple user profile directories from a system about to be reimaged. In most cases, the profile data stays on the migrated system. However, if the system does not have sufficient disk space to duplicate the migrated profiles, the data might overflow to a "USM Overflow Location" (SMB) and be restored to the system after the image task is complete. To avoid filling up your available storage on the specified USM Overflow location, perform multiple migrations.
Computer Managementoption of the Administrative tools. Alternatively, if you want the migrated users to be enabled during the deployment process, follow these steps:
- In the Image Library, select the image you want to deploy and click Deploy to Computer
- In the Deploy Image to Computer pane expand the Options section
- Select the Manual tab and scroll to USM Settings
- Modify the value of the LoadStateArgs parameter
as follows:
LoadStateArgs=/lac /lae
Note that by adding these values in the LoadStateArgs parameter, the restored users that were disabled in the source operating system (and that do not already exist in the image you are deploying) will be enabled in the final operating system. For more information about editing parameter values for capturing (ScanStateArgs) and restoring (LoadStateArgs) user settings in the Manual tab, see the documentation at the following links: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc749015%28v=ws.10%29.aspx (ScanState) and http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc766226%28v=ws.10%29.aspx (LoadState).
You cannot migrate user settings for server class operating systems. When you select server class operating systems, this option is disabled.
User State Migration behavior and capabilities might vary based on the original operating system, new operating system, or amount of storage space.
| From / To | Windows 7 | Windows 8 | Windows 8.1 | Windows 10 | Windows 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 7 | Uses 'hard link' to migrate the profile locally No disk or network impact |
Uses 'hard link' to migrate the profile locally
No disk or network impact |
Uses 'hard link' to migrate the profile locally
No disk or network impact |
Uses 'hard link' to migrate the profile locally
No disk or network impact |
Uses 'hard link' to migrate the profile locally No disk or network impact |
| Windows 8 | Not Supported | Uses 'hard link' to migrate the profile locally
No disk or network impact |
Uses 'hard link' to migrate the profile locally
No disk or network impact |
Uses 'hard link' to migrate the profile locally
No disk or network impact |
Uses 'hard link' to migrate the profile locally No disk or network impact |
| Windows 8.1 | Not Supported | Not Supported | Uses 'hard link' to migrate the profile locally
No disk or network impact |
Uses 'hard link' to migrate the profile locally
No disk or network impact |
Uses 'hard link' to migrate the profile locally No disk or network impact |
| Windows 10 | Not Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Uses 'hard link' to migrate the profile locally
No disk or network impact |
Uses 'hard link' to migrate the profile locally No disk or network impact |
| Windows 11 | Not Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Uses 'hard link' to migrate the profile locally No disk or network impact |