Introducing Computer Groups
Grouping your BigFix Client computers can simplify the maintenance of large networks.
There are many ways to group computers, from simple manual selection to more flexible automatic grouping based on properties.
A simple grouping technique is to manually select members of a group from the listing in the Computers List Panel. For a quick look at a manual selection, click View as Group from the right-click context menu. This opens an Ad-Hoc Computer Group document in the Work Area where you can quickly analyze various properties of the group. Ad-hoc groups are temporary, but you can create persistent groups by choosing Add to Manual Group from the same context menu. These techniques are simple, but in a network with many thousands of computers, they can be tedious.
For more details, see Creating Manual Computer Groups.
A more powerful technique is to define criteria for Automatic Grouping. From the Tools menu, select Create New Automatic Computer Group.
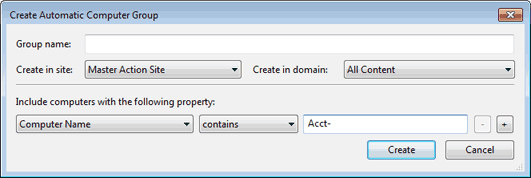
Here you can define membership in a group based on the values of specific computer properties. You could, for example, group computers by IP address ranges, operating systems, applications, and thousands of other criteria using Relevance expressions. Groups created this way have the benefit of automatic enrollment and expulsion, so that a computer that is repurposed to a different task or department automatically switches groups without operator intervention.
For more details, see Creating Automatic Computer Groups.
With the introduction of the Correlated devices, you might need to define a group based on properties coming from different representations of a correlated device or simply use the computer properties coming from one specific representation to include in the group the whole correlated device with all its representations.
For this purpose you can use a Server Based Computer group; Server Based Computer groups are evaluated by the BigFix Server based on the value of the properties reported by the devices and refreshed periodically.
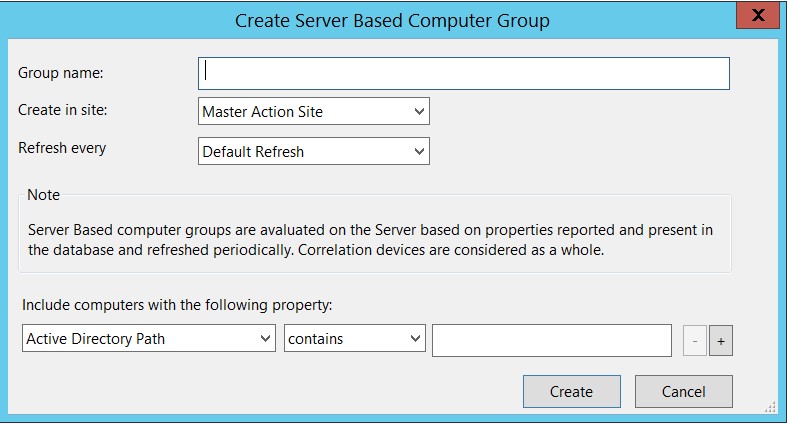
For more details, see Creating Server Based Computer Groups.
The following table summarizes the main differences among the 3 groups:
| GROUP TYPE | WHEN TO USE IT | HOW DOES IT WORK | EXAMPLES | COMMENTS |
| MANUAL | When the list of computers is static, you can add / remove “Computer Names” to / from a group | Membership evaluation is static based on the Computer Names |
QA-GROUP: computer1, computer2, computer3… |
In case of correlated devices, you should list all representations manually |
| AUTOMATIC | When you want to define criteria for group membership | Composing logical statements with properties. Membership is calculated at the agent through the client relevance |
DESIGNERS-GROUP: department equals design AND OS equals macos |
If your criteria include non-native properties, the BigFix agent representation might not belong to the group |
| SERVER BASED GROUP |
When criteria involve (also) non-agent properties
When you want to rely on the database information and avoid network traffic or save client evaluation cycle time
|
Membership is calculated with APIs to the server DB |
EU-AWS-REGION-GROUP: cloud region contains eu-central |
Devices with representations evaluating true the specified property will belong to the group along with all their correlated representations |