Flow of data
There are several different interactions that occur between the components of the BigFix Inventory infrastructure and between the user and tool.
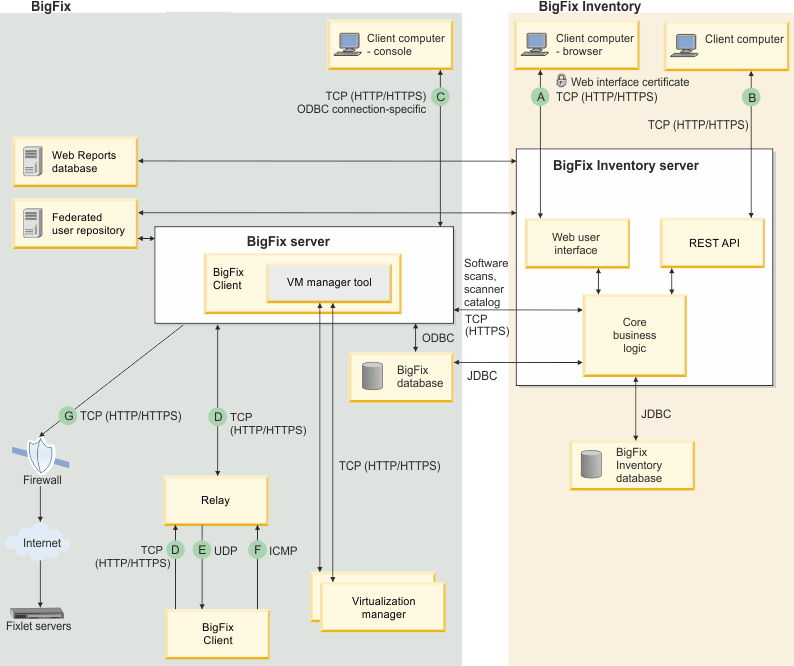
BigFix Inventory domain
| Interaction | Type | Connection | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Web browser data traffic | Port | By default, the web browser connects to the BigFix Inventory server using port 9081 (HTTPS). You can disable the SSL/TLS connection tunneling. |
| Origination | The web browser connects to the BigFix Inventory server. | ||
| B | REST API data traffic | Port | By default, the web browser connects to the BigFix Inventory server using port 9081 (HTTPS). You can disable secure connection. |
| Origination | A client that uses REST API connections. |
BigFix domain
| Interaction | Type | Connection | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | BigFix Console data traffic | Port | Consoles connect to root server using HTTPS 52311 for all interactions |
| Origination | The BigFix console connects to the RootServer service. | ||
| Network controls: | There is a "refresh rate" for each BigFix console user (default 15 seconds) | ||
| D | Gather, post, download | Port | Port 52311 is configurable by the BigFix administrator at installation time. |
| Origination | The BigFix client initiates the request to the BigFix relay or server. | ||
| Network controls: |
|
||
| E | UDP new informationmessage |
Port | Port 52311 is configurable by the BigFix administrator at installation time. |
| Origination | The UDP messages are sent from the BigFix clients'
immediate parent, which can be either a BigFix relay or server. |
||
| Network controls: |
|
||
| F | Relay selection | Port | The ICMP protocol does not use a port. |
| Origination | Each BigFix client sends
progressive roundsof ICMP packets to each relay with increasing TTLs until a BigFix relay responds. For example, in a network of 2 relays, one 1 hop away and one 2 hops away, the BigFix client sends an ICMP message to both with TTL 1 and receives 2 time exceededmessages from the local router. The BigFix client then sends an ICMP message to both relays with TTL 2 and receives one time exceededmessage and one reply message. The BigFix client then chooses the relay that is one hop away. |
||
| Network controls |
|
||
| G | New data download from external BigFix fixlet servers | Port | 80 (typically); possibly 21, 443 |
| Origination | The BigFix server connects to the BigFix fixlet servers | ||
| Network controls | There is a configurable interval that the BigFix server checks for new fixlet messages. |
The following database protocols are used:
- ODBC
- JDBC