Monitoring the shadow job status changes after the bind is established
As soon as the bind is established, the remote engine sends back an HTTP notification containing the status of the bind and, if the bind was successful, the information to identify the remote job instance bound. This information is saved in the shadow job instance details.
- Shadow job data:
-
- Application name
- Input arrival
- Operation
- Job name
- Complete if bind fails
- It determines if the operation must be forced to COMPLETE status when the bind process fails.
- Bind status
- It can be one of the following values:
- Sending bind request
- Waiting for bind result
- The bind was established
- The bind failed
- The remote engine type is z/OS
-
- Application ID
- Input arrival
- Operation number
- Workstation
- Job name
- The remote engine type is distributed
-
- Job stream name
- Input arrival
- Job stream workstation
- Job name
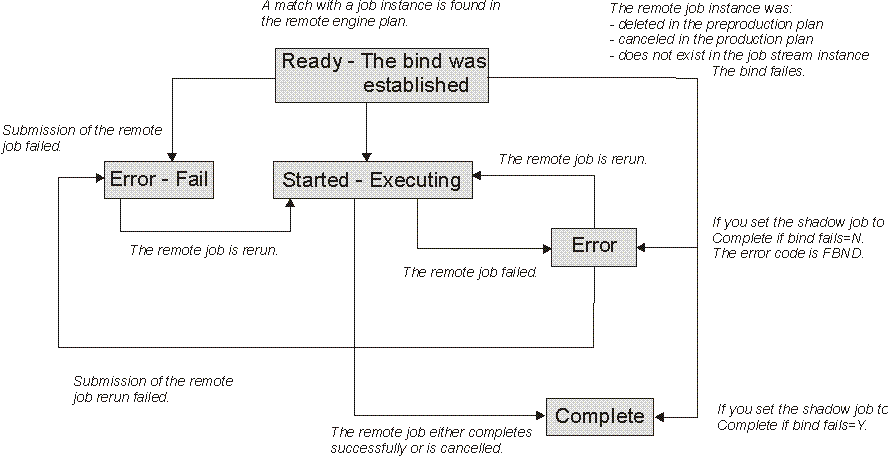
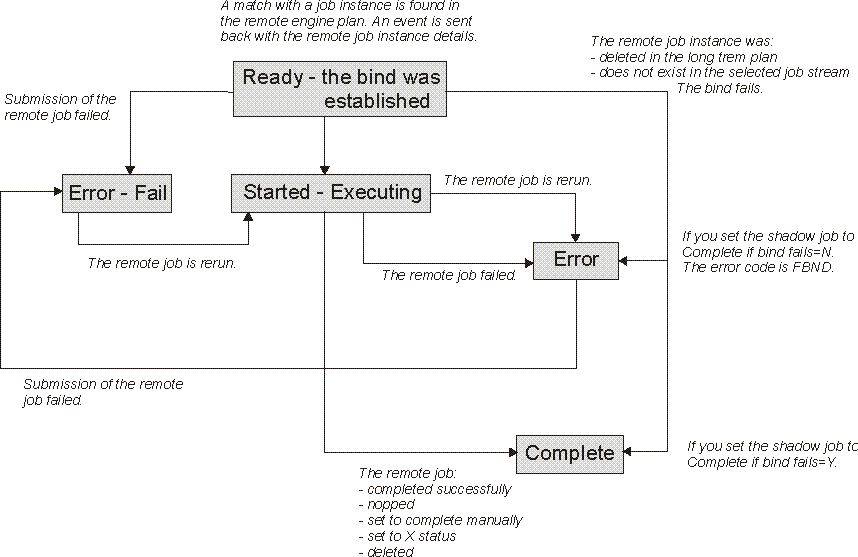
If the remote job instance has already completed successfully when the match is done, the shadow job status becomes C immediately.
If the shadow job ends in ERROR, an error code explains why the job failed. For example, if the job failed because the bind failed then the error code is FBND.
ERROR status is not considered a final status for the shadow job, because the remote job instance bound can be rerun at a later time. Only status C is considered as the final status for a shadow job.
As soon as the shadow job status satisfies the dependency rule, the dependency of the local job from the shadow job is resolved, and the cross dependency for the local job on the remote job is also resolved.