Specifying workstation parallel servers
When you create an operation, you specify how many parallel servers it requires (see Using parallel servers). The workstation that the operation is using must have that number of parallel servers available before the operation can run.
The number of parallel servers a workstation owns limits the number of operations that can be in started status at any time. You set this value when you create the workstation (see EQQWMATL - All open time intervals), but you can change it using the MODIFY CURRENT PLAN (MCP) panel.
You can specify, by setting server usage = P (planning only), that the number of parallel servers should not be considered when HCL Workload Automation for Z is deciding when to start an operation. If you do this, the number of parallel servers will be used only for planning purposes, and the plans that HCL Workload Automation for Z produces cannot accurately predict the behavior of real work in your system, because HCL Workload Automation for Z will submit as many jobs as are ready, regardless of its count of the number of servers in use. It is better to specify server usage = B (both planning and control), so that HCL Workload Automation for Z submits jobs only up to the limit of the number of servers specified.
Operations defined to a computer workstation must allocate at least one parallel server.
If you specify a server usage of B (both) or C (control only), the number of parallel servers required by the operation must also be available on the workstation for the operation to be started. So the number of computer workstations and their availability are important factors when you specify your system to HCL Workload Automation for Z.
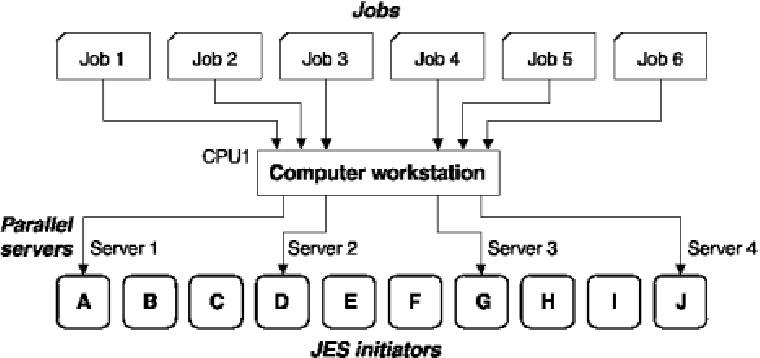
In Computer workstation with server usage set to B or C, controlling job submission, jobs 1 through 6 were defined on an HCL Workload Automation for Z (tracker) computer workstation, CPU1, which has four parallel servers. Server usage B was specified for this workstation. This means that CPU1 can start only four of the six waiting jobs, even though there are several JES initiators free to run the jobs that are waiting. It selects the jobs using the algorithm described in How work is selected for automatic submission.