UDS pipelines process data across various layers applying various data integration
procedures to standardize the source data from Canonical schema, to ultimately create the
360 views for customer consumption.
About this task
These pipelines are executed via DAGs (Directed Acyclic Graphs) scheduled in an
orchestration tool like Airflow. This Airflow setup is a prerequisite for this
installation as mentioned above.
Procedure
-
Extract the
ZIP file provided in the UDS installation package
(HCL_Unica_CDM_<25.1.1>.zip) and navigate to the
dags folder.
-
Copy contents of this folder to the Airflow installation's DAG folder.
Example: /opt/airflow-data/dags
-
ONE-TIME STEPS FOR DAG SETUP
-
Replace the Kubernetes namespace in the Python DAG.
-
Obtain the correct Kubernetes cluster namespace from the Unica DevOps
team and update it in the DAG files located in the DAGs folder.
Example: In the following commands, replace the namespace value
from
unica-dev to
default:
sed -i "s/namespace='unica-dev'/namespace='default'/g" *.py
sed -i 's/NAMESPACE = "unica-dev"/NAMESPACE = "default"/g' *.py
sed -i "s/image_pull_secrets=\[k8s\.V1LocalObjectReference('hclsw-unica-repo')\]/image_pull_secrets=[k8 s.V1LocalObjectReference('hcl')]/g" *.py
-
Replace the image pull secret reference. Obtain the correct secret name
from the Unica DevOps team, navigate to the DAGs folder where the DAGs
are uploaded, and update the reference accordingly.
Example: In the following commands, replace value of
image_pull_secrets from
hclsw-unica-repo to
hcl:
sed -i "s/image_pull_secrets=\[k8s\.V1LocalObjectReference('hclsw-unica-repo')\]/image_pull_secrets=[k8s.V1LocalObjectReference('hcl')]/g" *.py
-
DAG execution order
-
Click download the DAG Execution
Document.
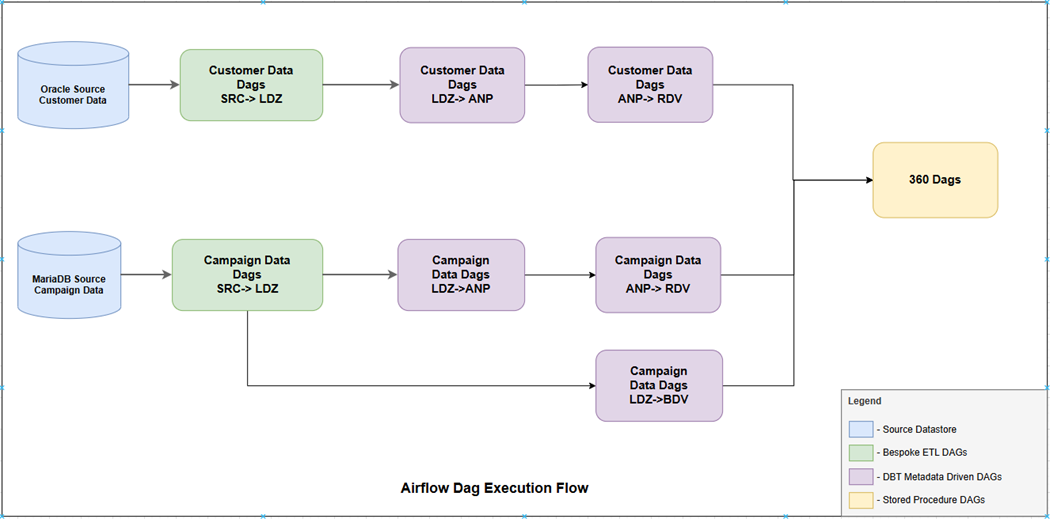
The document summarizes the DAGs that need to be executed and the
order in which they should be executed. The document also contains
additional information regarding sources and targets of DAGs, their
inter dependencies and operational information like date control entries
to manage the business dates for various data groups.
The below
diagram depicts the flow of execution for dags:
-
Importing variables into Airflow
-
Within the UDS Installation package (HCL_Unica_CDM_<25.1.1>.zip),
navigate to the 'configs' folder and import variables from JSON files
using below steps:
- Login to Airflow URL
- Navigate to Admin → Variables
- Click Import Variables
- Upload the JSON file. The JSON files to be imported for first
installation are: bespoke_campaign_config.json,
bespoke_config.json,
c360_variables_config.json, and
variables_dbt.json.
- Verify variables are created
-
Additionally, two connection IDs need to be created using below
steps:
- Navigate to Admin → Connections.
- Click Add Connection.
- Create Connection ID as mentioned in the below
document.
The description of variables in above configs, their
expected values and Connection ID details are present in below
document: DAG Variable
Description.
-
Once variables are imported, set up corresponding environment values as
per installation. For example, below Docker image specific variables
will have to be updated with image values deployed in the Kubernetes
cluster:
Key point:
- Initial Execution (Bespoke, DBT and 360 Docker Images):
The container image is pulled from the registry, cached on the
Kubernetes node, and subsequently utilized for pod
creation.
- Subsequent Executions: The cached image is utilized
directly from the node's local storage, eliminating the need for
registry access.
Once DAG specific variables are imported, the next step is to
import Schedule variables using the same steps mentioned above. The
schedule specific JSON files to be imported are
bespoke_schedule_config.json, dbt_schedule.json,
and schedule_360.json.
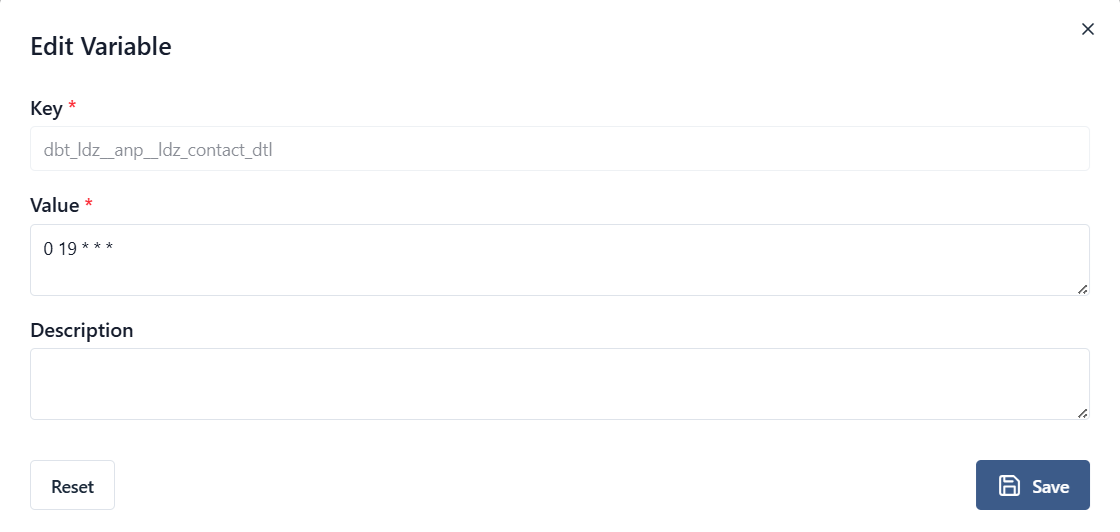
A sample schedule that should run everyday at 7:00PM will have its
schedule variable value set as:
| Field |
Value |
Meaning |
| Minute |
00 |
Run at minute 00 |
| Hour |
19 |
Run at 19:00 (7:00 PM) |
| Day of Month |
* |
Every day |
| Month |
* |
Every month |
| Day of Week |
* |
Every day |