sqlhosts connectivity information
Fields in the sqlhosts file or SQLHOSTS registry key describe connectivity information.
Syntax
| Element | Purpose | Restrictions |
|---|---|---|
| dbservername | Names the database server for which the connectivity information is being specified. If specified with the group keyword instead of the connection type, names a group to treat multiple, related database server entries as one logical entry. You can use groups to establish or change client/server connections, or to simplify the redirection of connections to database servers. |
The name must begin with a lowercase letter, and can contain lowercase letters, numbers, and underscore (_) symbols. The field length is limited to 128 bytes. The database server must exist. Its name must be specified by the DBSERVERNAME or DBSERVERALIASES configuration parameter in the onconfig file. A database server group cannot be nested inside another database server group. Database servers can be members of one group. |
| connection_type | Describes the type of connection that is made between the database server and the client application or another database server. |
|
| hostname | Specifies the computer where the database server is located. |
The field length is limited to 256 bytes. If the group keyword is specified, must be null (-). |
| servicename | Specifies the alias for the port number. The interpretation of the service name field depends on the type of connection in the connection-type field. |
The field length is limited to 128 bytes. If the group keyword is specified, must be null (-). |
dbservername field
Each database server across all of your associated networks must have a unique database server name.
If an sqlhosts file has multiple entries with the same dbservername, only the first one is used.
Connection-type field
The
connection-type field is called nettype in the sqlhosts file
and PROTOCOL in the SQLHOSTS registry key.
| Values for UNIX™ | Values for Windows™ | Description | Connection type |
|---|---|---|---|
| drsoctcp | drsoctcp | Distributed Relational Database Architecture™ (DRDA®) - connection for .NET Core Provider Client. You must configure a new server alias in the sqlhosts file or SQLHOSTS registry that uses drsoctcp connection protocol. |
Network |
| drtlitcp | drtlitcp | Distributed Relational Database Architecture (DRDA) - connection for .NET Core Provider Client. You must configure a new server alias in the sqlhosts file or SQLHOSTS registry that uses drtlitcp connection protocol. |
Network |
| onipcshm | Shared-memory communication. Requires the cfd option in the sqlhosts file if used for a non-root installation where the server and client are in different locations. | IPC | |
| onipcstr | Stream-pipe communication. Requires the cfd option in the sqlhosts file if used for a non-root installation where the server and client are in different locations. | IPC | |
| onipcnmp | Named-pipe communication | IPC | |
| ontlitcp | TLI with TCP/IP protocol | Network | |
| onsoctcp | onsoctcp | Sockets with TCP/IP protocol | Network |
| onsqlmux | onsqlmux | Multiplexed connection | Network |
Host name field
The
host name is entered in the hostname field in the sqlhosts file,
and in the HOST registry key.
If the
connection type is onsqlmux, the hostname field
must not be empty, but any specific value entered in it is ignored.
Following is an explanation of how client applications derive the values that are used in the host name field.
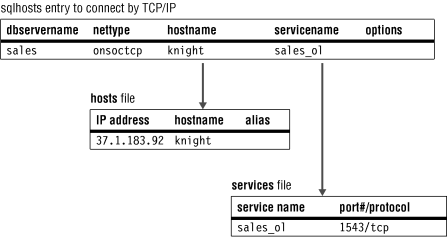
- Network communication with TCP/IP
- When you use the TCP/IP connection protocol, the
host namefield is a key to the hosts file, which provides the network address of the computer. The name that you use in thehostnamefield must correspond to the name in the hosts file. In most cases, the host name in the hosts file is the same as the name of the computer. - UNIX: Shared-memory and stream-pipe communication
- When you use shared memory or stream pipes for client/server communications,
the
hostnamefield must contain the actual host name of the computer on which the database server is located. - Multiplexed connections
- When you use
onsqlmuxas the connection type, thehostnamefield must have an entry, but the entry is ignored. Dashes (-) can be used as entries.
Service name field
- Network communication with TCP/IP
- The service name field is called
servicenameon the UNIX operating system and SERVICE on the Windows operating system. When you use the TCP/IP connection protocol, the service name entry must correspond with the name in the services file. The port number in the services file tells the network software how to find the database server on the specified host. - Windows: Named-pipe communication
- For a named-pipe connection (
onipcnmp), the SERVICE entry can be any short group of letters that is unique in the environment of the host computer where the database server is located. - UNIX: Shared-memory and stream-pipe communication
- For a shared-memory connection (
onipcshm) or a stream-pipe connection (onipcstr), the database server uses the value in the servicename entry internally to create a file that supports the connection. For bothonipcshmandonipcstrconnections, the servicename can be any short group of letters that is unique in the environment of the host computer where the database server is located.Tip: Use the dbservername as the servicename for stream-pipe connections. - Multiplexed connections
- For multiplexed connections (
onsqlmux), thehostnamefield must have an entry, but the entry is ignored. Dashes (-) can be used as entries.