MIB types and objects
This section describes the types of MIBs and the types of MIB objects that the HCL Informix® database server uses.
- Application MIB
- Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) MIB
- HCL Informix® Private MIB
- Online MIB in the HCL Informix® Private MIB
Application MIB
The Application MIB is a public MIB, which means that the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) specifies the structure of the MIB and the MIB tables. A public MIB is the same for all managed components on an SNMP network, not just for HCL® Informix® products.
OnSNMP uses only applTable, which is the portion of the Application MIB that the RDBMS MIB requires.MIB hierarchy shows the position of the Application MIB in the MIB hierarchy.
iso.org.dod.internet.mgmt.mib-2.application1.3.6.1.2.1.27RDBMS MIB
The Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) MIB is a public MIB, which means that the IETF specifies the structure of the MIB and the MIB tables.
A public MIB is the same for all managed database components. However, some of the definitions in the RDBMS MIB are purposely vague to let each vendor tailor the entries to a specific database server. For example, rdbmsSrvLimitedResourceTable contains information about the resources that a database server uses. Each database server vendor can decide which resources to include in this table. MIB hierarchy shows the position of the RDBMS MIB in the MIB hierarchy.
iso.org.dod.internet.mgmt.mib-2.rdbmsMIB1.3.6.1.2.1.39Informix® Private MIB
The Informix® Private MIB is a private MIB, which means that a private enterprise defines and uses it.
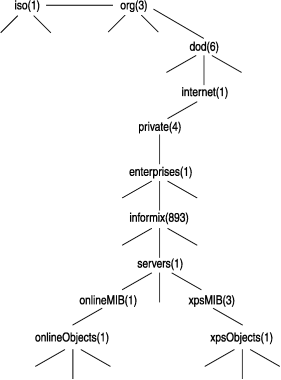
iso.org.dod.internet.private.enterprises.informix1.3.6.1.4.1.893Online MIB
The Online MIB is in the Informix® Private MIB. The Online MIB contains information for all Informix® database servers.
servers.onlineMIB.onlineObjects1.3.6.1.4.1.893.1.1.1MIB objects
An MIB object is similar to a column in a table.
- Traps are defined as MIB objects, but they cannot be retrieved. Instead, when a certain condition is detected, OnSNMP issues an event that includes the object ID that the trap defines.
- Catalog-based MIB objects exist only if the refresh control value
(described in Refresh control value)
is
onceorall. - objects are tables that exist only if a database server is configured to participate in .