Configure Ingress For DX Deployment
With HAProxy replacing Ambassador in our DX deployment, it is much easier to run Ingress in front of DX to handle advance requirements to routing, proxying and other similar use cases. This document explains how to leverage external Ingress alongside with HAProxy as the internal service and load balancer.
Note
- HCL DX intentionally does not ship any Ingress to reduce DX's deployment footprint in any Kubernetes cluster.
- This document shows an example configuration for some Ingress controllers and briefly describes minimally necessary steps to implement it inside a Kubernetes environment. This configuration is neither a proposal nor does HCL provide official support for it.
- Implementing an Ingress for use with a HCL DX deployment in Kubernetes is an optional effort base on the Kubernetes cluster’s requirements and customer’s discretion.
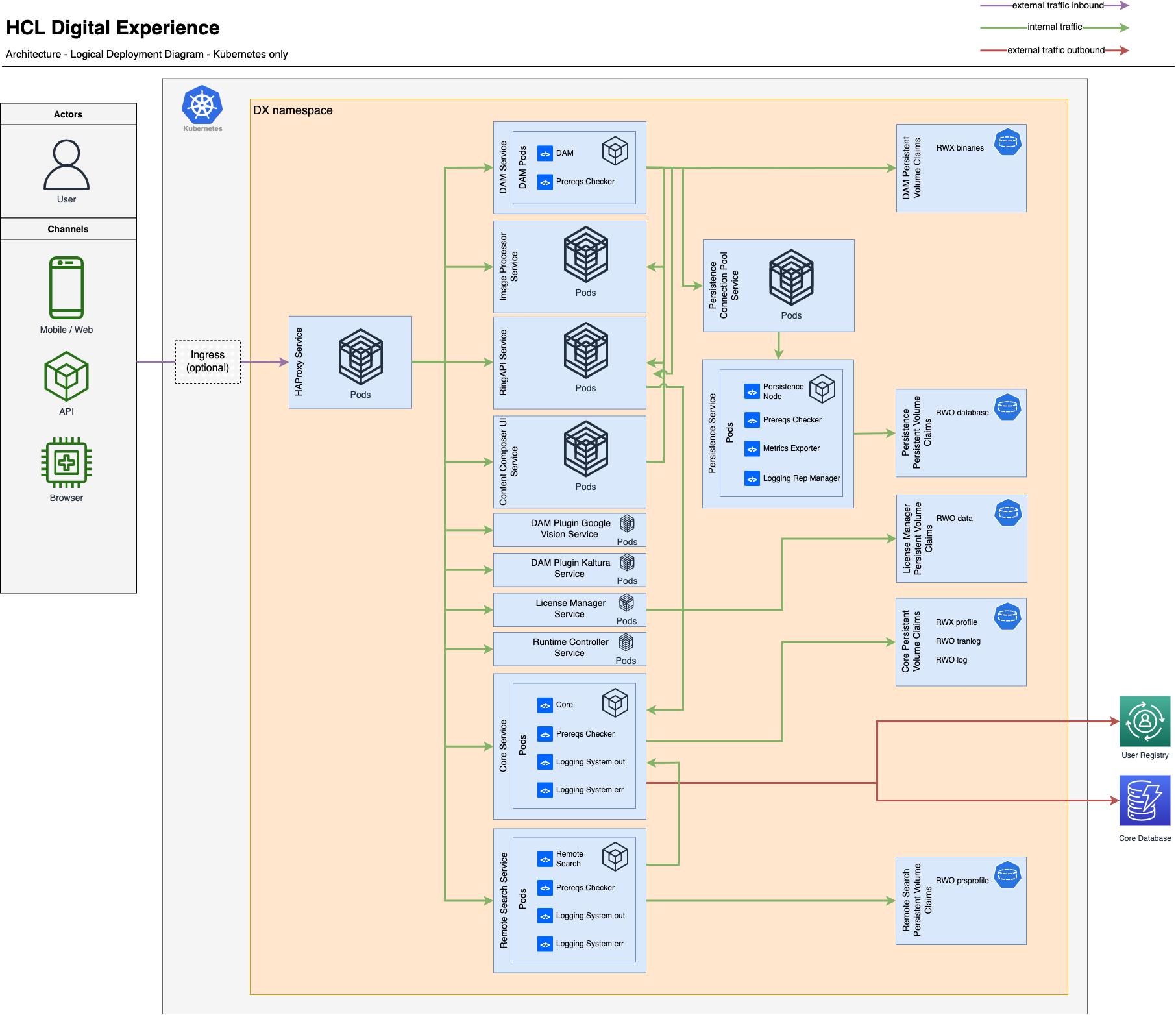
Ingress Implementation
Here’s a basic guide on implementing a generic Ingress on your Kubernetes cluster for use with HCL DX
- In the
custom-values.yamlby default HAProxyserviceTypeis set toloadBalancer. To test the external Ingress you want to deploy you must set the serviceType applicable for your use case, for this exampleClusterIPis used, with that HAProxy service will not have any External IP.
haproxy:
serviceType: ClusterIP
- Install an Ingress controller of your choice, this will serve as the entry point to the cluster. The Ingress controller evaluates the rules that you will set on your Ingress instance and it also handles redirection. Ingress controller can be deployed on any namespace and does not have to be in the same namespace as DX. The controller can be used to route multiple applications in multiple namespaces. NGINX Ingress Controller is used here as an example. To install a NGINX Ingress on your cluster, please issue the following command:
$ helm upgrade --install ingress-nginx ingress-nginx \
--repo https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx \
--namespace <namespace>
- Check if the Ingress controller pod and service is deployed
$ Kubectl get pod -n <namespace>
$ Kubectl get service -n <namespace>
- Define an Ingress instance that will be used to configure the routing rules that point to the existing deployment of HAProxy as the internal service. Here we must configure a host and all of the request received by the host will be handle by
<helm release name>-haproxy.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
rules:
- host: your-kube-deployment.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: dx-deployment-haproxy
port:
number: 80
- Configure your Ingress based on your preference whether you want to access your host via
httporhttps. To handlehttpsrequest a certificate must be declared on your Ingress yaml file. This certificate will be used for the Ingress client to Ingress instance connection.
ingressClassName: nginx
tls:
- secretName: dx-tls-cert
- Configure your Ingress to HAProxy connection based on your preference. To handle
httpsrequest a certificate must also be declared on yourcustom-values.yamlalong with the SSL offloading configuration. set SSL totrueto access your host viahttps.
haproxy:
ssl: true
tlsCertSecret: "dx-tls-cert"
Last update:
December 22, 2022