Management of Dev Containers
With DevOps Code (Code), you can set up the initial process and experience the faster loading of preconfigured containers on subsequent logins. When you terminate a dev container, all files and unsaved work are deleted. Therefore, you must push changes to remote source control before termination.
When you access Code for the first time from the landing page of HCL DevOps Automation (Automation), it takes some time to launch the dev container.
During the initial setup, necessary dependencies, extensions, and libraries are installed and configured to create a standard environment (Java and C++). On subsequent logins, Code loads your pre-configured dev container and workspace much faster.
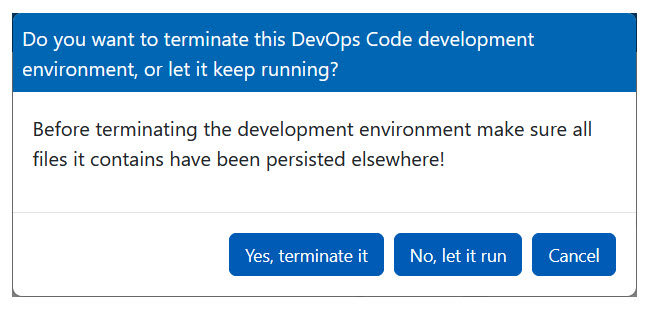
Terminating a dev container
Code manages dev containers by preserving your working environment. The browser IDE settings are saved within the dev container file system. For more information on user and workspace settings, refer to settings.
If you prefer to continue your work, you can let the dev container keep running when you logout. You can then return to your dev container later and find it in the exact same state as when you logged out. However, if you do not plan to use it soon, you should terminate the container to free up resources.