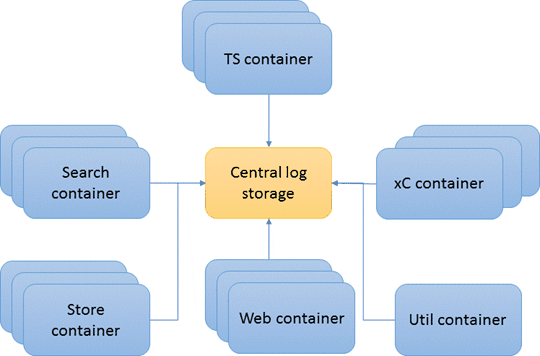
Persist logs to a central storage location
By persisting log files to a central location outside of the Docker containers, you can perform diagnostics and troubleshoot issues even if the container is not accessible or is destroyed.
Starting with HCL Commerce Version 9.0.0.3, inside each Docker container, log files are
collected to a unique folder name that is derived from the
containerType and the containerId. For example,
assuming you have two Search server Docker containers, the log files are in the
following directories.- Search container 1: /opt/WebSphere/Liberty/usr/servers/default/logs/container/search_<containerId1>
- Search container 2: /opt/WebSphere/Liberty/usr/servers/default/logs/container/search_<containerId2>
Note: If you want to set the log folder to a different directory inside
the container, use the following Run Engine
command.
You can persist all
container log files by creating a volume mount point to the Docker host machine or a
central log server. Since every container has a unique log folder
(run set-trace-log-directory <new_log_path>containerType_containerId), mount all container
log directories (*/logs/) to the same path on the host
machine.
About this task
Procedure
-
Create a folder on the Docker host machine to store the log files.
For example, create a
/logsdirectory to store files from the Transaction, Store, Search, xC, and Web servers.The Utility server container does not follow the naming convention
containerType_containerId. Create a separate directory with a name such as/logs/utils. -
Configure the Docker containers to start with a volume mount to the
corresponding directory on the Docker host machine.
If you are using Docker Compose, edit the Compose file to add the volumes flag.
The following examples provide the paths to where the logs are generated in each container.volumes: -"<log_folder_on_machine>":"<log_folder_in_container>"- For Transaction server Docker container,
volumes: -"/logs:/opt/WebSphere/AppServer/profiles/default/logs/container" - For Web server Docker container,
volumes: - "/logs:/opt/WebSphere/HTTPServer/logs" - For Search server Docker container,
The /opt/WebSphere/Liberty/usr/servers/default/logs/container directory also links to the /profile/logs directory in the container.volumes: -"/logs:/opt/WebSphere/Liberty/usr/servers/default/logs/container" - For Store server Docker container,
The /opt/WebSphere/Liberty/usr/servers/default/logs/container directory also links to the /profile/logs directory in the container.volumes: -"/logs:/opt/WebSphere/Liberty/usr/servers/default/logs/container" - For Customization server (xC) Docker container,
volumes: -"/logs:/opt/WebSphere/Liberty/usr/servers/default/logs/container" - For Utility server Docker container
volumes: -"/logs/utils:/opt/WebSphere/CommerceServer90/logs" -"/logs/utils:/opt/WebSphere/CommerceServer90/instances/demo/logs"
- For Transaction server Docker container,
- Deploy containers by using the updated Docker Compose file.
Results
- /logs/search_<containerId>
- /logs/store_<containerId>
- /logs/ts_<containerId>
- /logs/web_<containerId>
- /logs/xc_<containerId>
- /logs/utils