Examples of dimensions
Segmented reporting example
Dimensions and their containing report groups provide a flexible means to report on events and event values. After you defined these data objects and associated them with an event, dimension data is collected and available for reporting when the event fires.
For example, if an event is tracking the shopping cart
value, when a figure of 1000 is detected in the shopping
cart, the following dimensions and values may be detected in the session
and then recorded:
- Dimension Name
- Dimension Value
- Credit Card
Visa- Membership Type
Gold- State
CA
Dimensions can be used to store the recorded values for an event and as the condition inputs for events.
To understand dimensions, the following diagram provides a conceptual view of what Dimension data is and how it is used.
Suppose you created an
event that is called Abandoned Cart. This event is
configured to fire at Session End if both of the following conditions
occur:
- Another event collecting Cart values from Shopping Cart pages was fired
- Another event detecting a successful checkout has not.
The value of the
Abandon Cartevent is taken from the last instance of the event collecting cart values, so it has the last shopping cart amount.
For reporting purposes, suppose you are interested in the following contextual information that is captured when the cart is abandoned.
- State: What state was the user in? This data could come from login or other means.
- Error Message: What was the last error message the visitor saw, if any? This message could come from the value of another event that is designed to detect the occurrence of an error message.
- Referrer: What was the external Referrer for the session? Assume that another event detected this value on the first hit, so only the first value was recorded.
- Browser: What browser was used? This information might have been obtained from a session attribute.
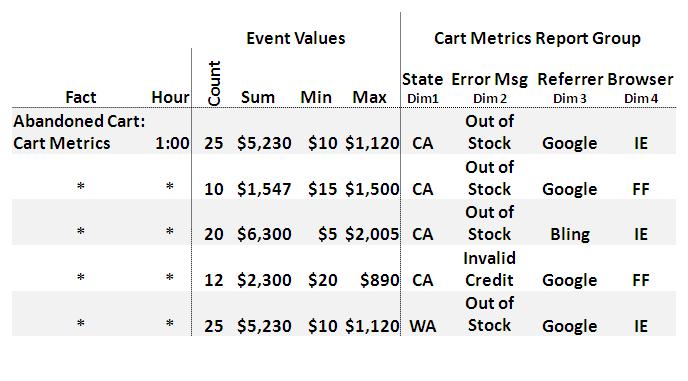
In the above diagram, the Abandoned
Cart event for visitors from California who received the
"Out of Stock" error message and referred by Google while using Internet
Explorer occurred 25 times during the 1:00 hour. The sum of the Abandoned
Carts was $5,230.
If you wanted to know the total amount of dollars that are abandoned by users from California during the 1pm hour, the Report Builder could sum the totals for those rows ($15,377). Or, you could sum the 1:00, California, Firefox users ($3,847).
Example - Top N reporting
You can report on the values of each dimension. For example, you can configure a report to show the top N error messages associated with the Abandonment event.
When an event fires, the event value and dimensions are written to the request buffer of the hit; for session end events, they are written to the request buffer of the last hit of the session. Below, you can see the structure of this data record in the request for the data in the preceding example.
[TLFID_277]
Searchable=True
TLFID=277
TLFactValue= 55.20
TLDimHash1=513982?
TLDimHash2=795479?
TLDimHash4=795479?
TLDimHash4=7954797?
TLDim1=CA
TLDim2=Out of Stock
TLDim3=Google
TLDim4=IE
In the above sample, the event was marked as searchable
(Searchable=True). Using search, Discover users can search for all sessions
where the abandonment event occurred for the state of California using
the dimension values of the human-readable versions (TLDim1, TLDim2, TLDim3,
and TLDim4). The hashed versions (TLDimHash1, TLDimHash2, TLDimHash3,
and TLDimHash4) of the text provide unique values
for searching.
Top N reporting is managed by adding a dimension to the report and then filtering the dimension to display only selected values, to exclude selected values, or to display the topmost values.
Example - Creating a dimension to track whether a login occurred
Discover provides the Login
ID hit attribute and event, which can be configured to identify
and track the login identifiers for each session on your web application.
Login ID hit attribute and event require additional configuration. If you
did not do so already, you should configure these items to capture the login identifiers for
your web application. See "E2E Scenario - Configure Login ID to be Searchable" in the
Unica Discover Manuals.These event objects track and record the login identifiers. However, they are not suitable for detecting whether an identifier occurred or not.
- While it may be useful to create a dimension to capture the login
identifier values, the number of dimension values may be too great
to provide meaningful information in reporting and may be expensive
to capture and store in the database. In general, Discover recommends avoiding the creation
of dimension with a high-number of values.
- See Data Management for Dimensions.
- An exception to this general rule is the URL dimension. See Managing URL and Other High-Volume Dimensions.
In this example, you can create a dimension to track whether the visitor who created the session was logged in or not. For reporting purposes, this dimension is very useful for segmenting whether known customers are performing specific actions, which are tracked by other events, in your application. For example, you may find it useful to track whether a visitor was logged in when your Completed Order event is triggered.
Create the dimension:
You can specify:.
- The dimension is
Populated Withthe count of theLogin ID Sampleevent. - The
Values to Recordis configured to be based on a numeric group list, which is specified later.
The count of the event is always
measured as a non-negative integer (for example, 0, 1, 2, 3, etc.).
In this example, depending on the count, the recorded value needs
to be either Yes or No. For this
dimension, then, the outputted values must be referenced based on
specified numeric lists.
- You could create the dimension to simply capture the number of times that the referenced event occurred. For some applications, it may be useful. For example, you may wish to create a dimension to count the number of times that an order was placed (your Completed Order event) on your web application.
To configure the numeric group list, click Edit Group List....
For this example, the relevant information is whether the visitor was logged in, and not how many times. In the above configuration, two buckets have been created:
| Bucket | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|
No |
Count of Login ID Sample = 0 |
Visitor did not login. |
Yes |
Count of Login ID Sample > 0 |
Visitor logged in at least once during the session. |
For the Bucket value, you might consider substituting True and False for
the above values. However, since the recorded value is a string, as
opposed to T/F Booleans, it is appropriate to leave the value as specified.
In the table below, you can see how the event and dimension are populated based on an example session:
| Page | Event | Count of Login Event | Dimension Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Start of Session | 0 | No |
| 2 | Login | 1 | Yes |
| 3 | View Product | 1 | Yes |
| 4 | Shopping Cart | 1 | Yes |
| 5 | Checkout | 1 | Yes |
| 6 | Order | 1 | Yes |
| 7 | End of Session | 1 | Yes |
For any hit after hit 2, the count of the Login event is
greater than 0, so any event that uses the Logged In? dimension
records the value Yes for the dimension.
- If the dimension is associated with the
Orderevent, since theOrderevent occurs on hit 6, it records aYesvalue.
Suppose the following session occurs, in which the Login
ID Sample event never occurs. The count of the Login
ID Sample event is 0 when the Order event
fires.
| Hit | Event | Count of Login Event | Dimension Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Start of Session | 0 | No |
| 2 | View Product | 0 | No |
| 3 | Shopping Cart | 0 | No |
| 4 | Checkout | 0 | No |
| 5 | Order | 0 | No |
| 6 | End of Session | 0 | No |
If the dimension is associated with the Order event,
since the Order event occurs on hit 6, it records
a No value.
To apply this dimension to your environment, save your group list and the dimension in draft form. Then, click Save Changes.