Planning your HCL Workload Automation environment
HCL Workload Automation orchestrates unattended, scheduled, and event-driven tasks for business and IT processes across on-premises and cloud environments organized in a network. A network consists of a set of linked workstations on which you perform job scheduling and processing to automate and manage your workflows. An HCL Workload Automation network is composed of a master domain manager, one or more Dynamic Workload Console servers, dynamic domain managers, and dynamic agents. You might also have fault-tolerant agents, extended agents, standard agents connected to the master domain manager or to domain managers.
About this task
Graphical overview of a typical HCL Workload Automation environment gives a graphical overview of a typical HCL Workload Automation environment:
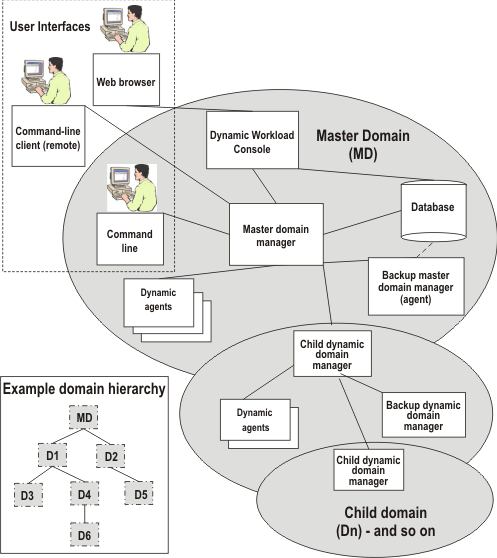
In Graphical overview of a typical HCL Workload Automation environment the master domain is shown with the main components to run your workload, and two levels of subdomain. The available user interfaces are also indicated. An example is provided of the basic domain hierarchical structure, where each domain is named "D1", "D2, and so on. All of these concepts are explained in the following section.
- Master domain manager
- The master domain manager is the highest level workstation of an HCL Workload Automation network. It contains or connects to the relational database that stores scheduling object definitions. It creates or updates a production plan when the plan is created or extended and then distributes the plan to the network. It performs all logging and reporting for the network. It can perform the role of event processing server for the event-driven workload automation feature.
- Backup master domain manager
- Define a backup master domain manager at installation to point to either the database being used by the master domain manager or to a mirror of that database. In this way the backup master domain manager has the latest data available to it at all times and can take over the role of master domain manager seamlessly, in case the master becomes unavailable.
- Dynamic domain manager
- Install this component if you need a multi-domain network . All domains below the master domain have dynamic domain managers to manage the workstations in their domains. Each dynamic domain manager is an agent in the domain of the next higher level. All communications to and from the dynamic agents in the domain are routed through the dynamic domain manager. To define a dynamic domain manager, install a dynamic domain manager and then perform the Configuring a dynamic domain manager procedure.
- Backup dynamic domain manager
- Install this component if you want a backup to your dynamic domain manager. The backup points to either the database being used by the dynamic domain manager or to a mirror of that database. If your dynamic domain manager experiences problems, you can switch to it with a simple procedure.
- Agent
- An agent is a workstation in the network that runs the jobs which are controlled by
the HCL Workload Automation
master domain manager. Several types of
agents are available, as follows:
- Dynamic agent
- An agent that has the following capabilities:
- Run workload dynamically
- It communicates with the server the status of its resources. In this way
the product is able to dynamically run your workload to the best available
resources by:
- Automatically discovering scheduling environment resources.
- Automatically following resource changes
- Requesting additional resources when needed
- Matching job requirements to available resources
- Controlling and optimizing use of resources
The characteristics listed above provide high availability and load balancing potentialities to your environment and well suit virtualized environments.
When a job is submitted, either as part of a job stream in the plan or through ad hoc submission, HCL Workload Automation checks the job requirements, the available resources and the related characteristics and submits the job to the resource that best meets the requirements to run it.
- Manage dynamic workload broker logical resource
- It can remotely run, from the agent, the dynamic workload broker resource command on the server. To manage the resource command you must also install the Java™ run time.
- Extended agent
- Extended agents are logical definitions (hosted by a physical workstation) used to extend job processing to selected applications (SAP R/3, PeopleSoft, and z/OS®). For information about installing an extended agent, see Installing agents .
- Fault-tolerant agent
- A fault-tolerant agent can resolve local dependencies and launch jobs in the absence of a domain manager. It has a copy of the production control file. This allows fault-tolerant agents to continue processing even if the dynamic domain manager or the network connection is down. With a simple reconfiguration, they can serve as subordinate domain managers. To define a fault-tolerant agent, install a fault-tolerant agent on your workstation and then define it as fault-tolerant in the workstation definition.
- Standard agent
- An agent that launches jobs only under the direction of its domain manager. It is not fault-tolerant. To define a standard agent, install a fault-tolerant agent on your workstation and then define it as a standard agent in the workstation definition.