Firewall ports
Your organization's firewall must be configured to allow connections from external clients and devices to the SafeLinx Server. If a second firewall stands between the SafeLinx Server and resources on the internal network, you must also establish rules that enable communications between them.
In a typical SafeLinx Server deployment, the SafeLinx Server is placed in a DMZ between an Internet-facing firewall and an enterprise-facing firewall. The two firewalls block unwanted connections from the external and internal networks. Open firewall ports to and from the SafeLinx Server for known connections only.
Your enterprise might deploy a firewall between the carrier network and the SafeLinx Server. In this case, you must open a mobile network connection (MNC) port on the external firewall.
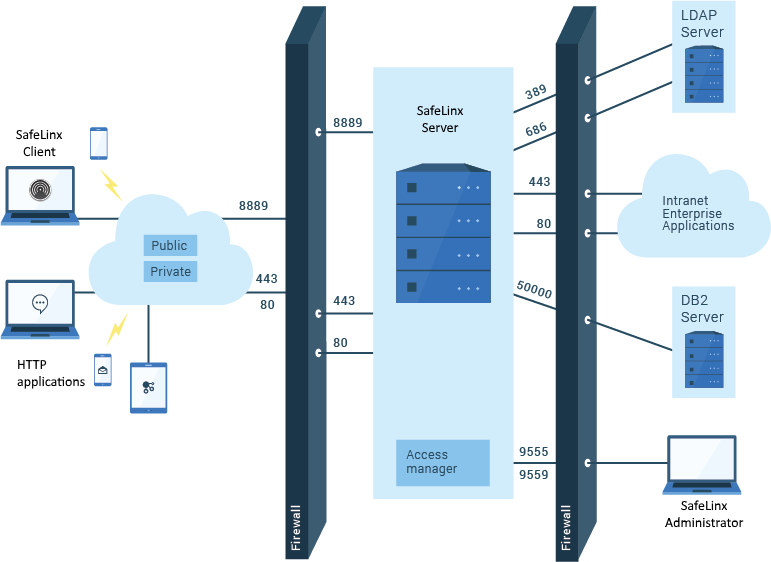
The preceding figure shows how an enterprise might deploy firewalls that use a single User Datagram Protocol (UDP) MNC. For example, you might deploy a firewall between the SafeLinx Server and internal application servers. If traffic connects to the application servers on ports 80 or 443, you must open those firewall ports on both the internal and external firewalls. To enable SafeLinx Clients to access the SafeLinx Server, you must open port 8889 for the MNC on the external firewall. If firewall software is installed on the remote computer that hosts the SafeLinx Client, the firewall software must also allow the SafeLinx Client to access to the Internet.
If your network uses a dynamic host configuration protocol (DHCP) server, make sure it located inside the DMZ between the firewalls.
The IP addressing scheme that you use in the DMZ between firewalls depends on your network topology. You can have private, non-routable IP addresses, in which the firewall provides network address translation (NAT) to substitute the IP address of the SafeLinx Server. In this case, devices on either side of the DMZ, such as SafeLinx Clients or enterprise applications, would use the IP address of the firewall. To route traffic to the SafeLinx Server, the firewall would, in turn, substitute the SafeLinx Server's private, non-routable IP address. Your enterprise might or might not use a backend firewall between the SafeLinx Server and the internal network.
As you plan your network topology, it's important to understand routing issues and the effect of firewalls and NAT. If you use remote servers for persistent data storage, then where you place them also plays a part in your network topology. If you locate your directory service server (DSS) or relational database (RDB) servers outside the DMZ, then they too might use substituted NAT addresses to connect to the SafeLinx Server.
| Port number | Component that uses the port |
|---|---|
| 53 | DNS servers |
| 80 | HTTP access to application servers |
| 389 | Non-secure LDAP server |
| 443 | Secure HTTP service |
| 686 | Secure LDAP server |
| 1433 | Microsoft SQL Server (default instance) Note: Named instances use static
ports. |
| 1812 | RADIUS authentication Note: Older RADIUS servers might use port 1645. |
| 1813 | RADIUS accounting |
| 9610 | Authentication server |
| 50000 | IBM DB2 |
| Port number | Component that uses the port |
|---|---|
| 443 | Secure HTTP service |
| 1812 | RADIUS authentication |
| 1813 | RADIUS accounting |
| 9555/9559 | Remote non-secure/secure SafeLinx Administrator |
| Port number | Component that uses the port |
|---|---|
| 53 | DNS servers |
| 80 | HTTP access to application servers |
| 389 | Non-secure LDAP server |
| 443 | Secure HTTP access to application servers |
| 686 | Secure LDAP server |
| 1433 | Microsoft SQL Server |
| 1812 | RADIUS authentication |
| 1813 | RADIUS accounting |
| 50000 | IBM DB2 |
| Port number | Component that uses the port |
|---|---|
| 80 | TCP-based Mobile Network Connections (MNCs) |
| 443 | TCP-based Mobile Network Connections (MNCs) |
| 1812 | RADIUS authentication |
| 9555/9559 | Remote non-secure/secure SafeLinx Administrator |
To restrict connections from external networks, you can either configure appropriate rules on your external firewall, or specify static routing paths for the appropriate subnets. In this configuration, set the default route of the virtual machine to something other than the Internet-facing adapter.