Configuring HTTP access: Single URL
HTTP Access Services provide load balancing and failover for multiple application servers, and different applications over the same service definition (or TCP listen port).
In a single URL configuration, external users can access an application that is hosted on multiple application servers from one common URL. The HTTP access service distributes server requests to the application servers without the need for an administrator to specify a unique port mapping for each application server.
- Basic server URLs
- The HTTP access service routes traffic to several servers that run the same application, such as
Notes Traveler. The SafeLinx Server balances the load (or provides failover) across the application
servers. The SafeLinx Server assigns users to one of the servers according to the load balancing
configuration.Note: The SafeLinx Server persists the assignment in the user record for iNotes and IBM Notes Traveler, always directing traffic for these user sessions to the same application server URL.You specify application server URLs in a comma-separated list, in the following format:
[ <KEYWORD> | <Map> ] URL,[ <KEYWORD> | <Map> ] URL …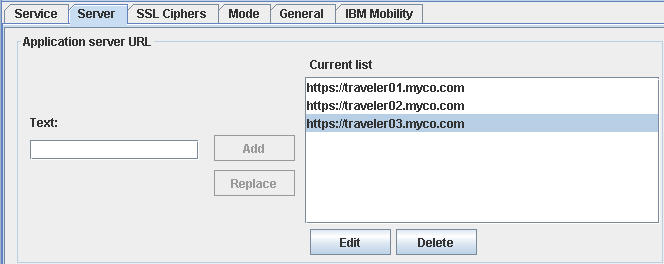
- URLs with keyword designations
- The HTTP access service routes traffic to multiple application servers that are running
different applications. You can pair certain keywords with a URL to specify the application server
to which the HTTP access service routes traffic. You can use the following keywords:
- INOTES
- iNotes® application handler
- TRAVELER
- Notes® Traveler application handler
- SAMETIME
- Sametime® mobile chat application handler
- CONNECTIONS
- Connections mobile application handler
- MEETINGS
- Sametime® meetings application handler
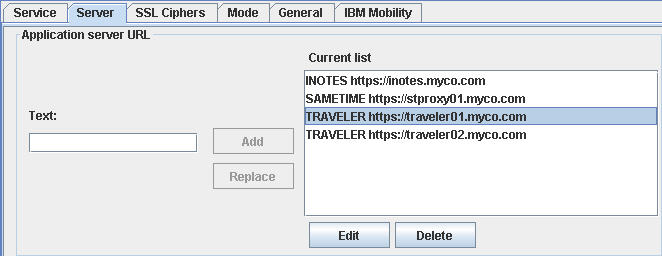
This following image shows how to configure one service to support a single iNotes® server, two IBM® Notes® Traveler instances, and a Sametime® proxy instance.
- Affinity identifiers or URI paths to map requests to specific servers
You can use affinity identifiers or URI paths to route requests to specific servers. Specify combinations of affinity identifiers and server URLs to route traffic that is sent to URLs that contain the identifier string to the specified server. Specify a URI path that extends beyond the root path to restrict clients to connecting to URLs that have that path prefix.
For example, suppose that the Application server URL field includes the following entry:
If the HTTP access services receives a request for https://safelinx.renovations.com/apps/index.htm, the SafeLinx Server detects the affinity identifier/apps/ https://appserver01.myco.com/apps/in the URL string. As a result, the request is routed to the specified internal server at https://appserver01.myco.com/index.htm.If you add the entry https://media.myco.com/mediafiles/, the HTTP access service does not accept requests sent to https://media.myco.com/documents/
Include a default URL in the list to handle requests that don't match an affinity ID. Request that don't include strings that match an affinity identifier are specified
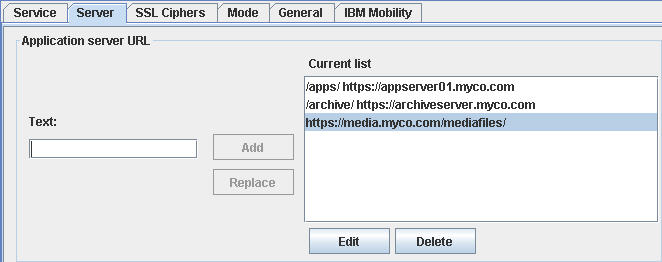
Note: The SafeLinx Server will strip the affinity ID from the target request. In the example, for the first definition, the SafeLinx Server would leave the request unchanged because the affinity ID and the URL have the same string /apps/. In the second definition, the string /archive/ would be removed from the target URL before the request is sent to the archiveserver.myco.com instance.All requests not matching an affinity identifier would result in a 404 Not Found response unless the list includes a default URL (one without an affinity ID or the affinity ID set to '/').- Application server pool
- An application server pool is made up of one or more Traveler high-availability clusters, each
containing one or more server nodes. Server pools support IBM®
Notes® Traveler only. For information about adding
application server pools, see Adding an application server pool.
After a user is assigned to a pool, the SafeLinx Server persists both the pool and node assignments in the user's SafeLinx record. Subsequent connections are always directed to the same application server, unless you modify the assignment in the SafeLinx Administrator.
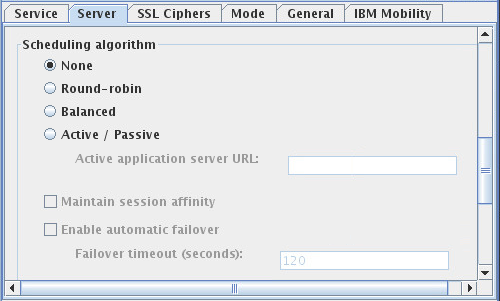
- Round-robin
- The SafeLinx Server assigns incoming requests to the list of application servers sequentially.
- Balanced
- The SafeLinx Server assigns incoming request to the application server that has the lowest
number of current user assignments or current connections. For Traveler, incoming requests are
assigned to the Traveler server or pool that has the least number of assigned users. Note: If the HTTP access service distributes traffic to multiple standalone Traveler servers or to a Traveler pool, you must choose the balanced scheduling algorithm.
- Active / Passive
- Designed to be a fail over, the Active / Passive option uses one server or the other.