cdr delete server
The cdr delete server disables a database server from participating in Enterprise Replication.
Syntax
- 1 See Connect Option.
| Element | Purpose | Restrictions | Syntax |
|---|---|---|---|
| server_group | A database server's group entry
in its ONEDB_ SQLHOSTS file and the global catalog. |
Long Identifiers |
The following table describes the option to the cdr delete server command.
| Long Form | Short Form | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| --force | -f | Remove an inactive Enterprise Replication server from the global catalog. You must use this option for standard servers that were converted from high-availability cluster servers. |
Usage
The cdr delete server command disables a database server from to participating in Enterprise Replication. Use the --force option to disable an inactive replication server or to remove Enterprise Replication from a standard server that has been converted from a high-availability cluster server by the oninit -d standard command. You cannot delete a server that has non-root or leaf children under it. You must delete the children of a server before deleting the parent server.
The cdr delete server command generates event alarms with class IDs of 67 and 71, if the alarms are enabled.
You can run this command from within an SQL statement by using the SQL administration API.
- Run the command on the database server being removed, to disable it. This command does not propagate to other database servers in the domain.
- Run the same command on a different server within the Enterprise Replication domain. This removes the disabled database server from the domain.
- Drops the Enterprise Replication connection to other hosts in the domain. A 25582 error and an operating system error might be printed to the online log.
- Removes Enterprise Replication information, including delete tables and shadow columns.
- Shuts down Enterprise Replication, if it is running.
- Drops the local copy of the global catalog.
- Deletes the command-specified database server from the global catalogs of all other servers in the domain.
- Removes the command-specified database server from all participating replicates.
- Purges all replication data destined for the command-specified database server from the send queues of all other servers in the domain.
Example 1: Removing a single database server from the domain
cdr delete server -c italy g_italy
cdr delete server -c usa g_italy
The first command connects to database server g_italy and disables Enterprise Replication by removing the syscdr database and removing or stopping other Enterprise Replication components.
- Removes g_italy from the g_usa global catalog
- Drops the connection between g_usa andg_italy
- Removes g_italy from all participating replicates
- Purges the replication data destined for g_italy from send queues
- Broadcasts the delete command to all the other database servers in the Enterprise Replication domain so that the other servers can perform the same actions
Example 2: Removing the whole domain
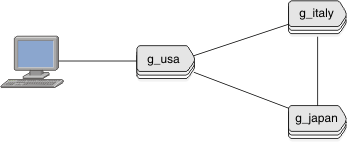
cdr delete server -c italy g_italy
cdr delete server -c japan g_japan
cdr delete server g_usaExample 3: Removing Enterprise Replication from a high-availability server
cdr delete server -c usa_s -f g_usa