Trigger execution
A trigger is a database object that automatically executes one or more SQL statements (the triggered action) when a specified data manipulation language operation (the triggering event) occurs. You can define one or more triggers on a table to execute after a SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE triggering event.
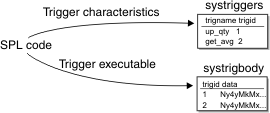
- Stores information about the trigger in the systriggers system catalog table.
- Stores the text of the statements that the trigger executes in the systrigbody system catalog table.
The sysprocedures system catalog table identifies trigger routines that can be invoked only as triggered actions.
Memory-resident tables of the sysmaster database indicate whether the table or view has triggers on it.
Whenever a SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement is issued, the database server checks to see if the statement is a triggering event that activates a trigger for the table and columns (or for the view) on which the DML statement operates. If the statement requires activating triggers, the database server retrieves the statement text of the triggered actions from the systrigbody table and runs the triggered DML statements or SPL routine before, during, or after the triggering events. For INSTEAD OF triggers on a view, the database server performs the triggered actions instead of the triggering events.