onbar -RESTART syntax: Restarting a failed restore
If a failure occurs with the database server, media, storage manager, or ON-Bar during a restore, you can restart the restore from the place that it failed. To restart a failed restore, the RESTARTABLE_RESTORE configuration parameter must be set to ON in the onconfig file when the restore fails.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -RESTART | Restarts a restore after a database
server, storage manager, or ON-Bar failure. The RESTARTABLE_RESTORE configuration parameter must be set to ON when the restore failure occurs. You can restart
the following types of restores:
Do not use the -RESTART option if a failure occurs during a warm logical restore. |
Usage
When you enable restartable restore, the logical restore is slower if many logical logs are restored. However, you save time if the restore fails and you restart the restore. Whether a restore is restartable does not affect the speed of the physical restore.
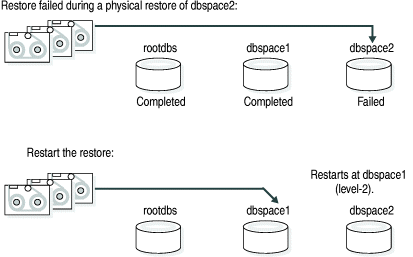
The physical restore restarts at the storage space and level where the failure occurred. If the restore failed while some, but not all, chunks of a storage space were restored, all chunks of that storage space are restored. If storage spaces and incremental backups are restored successfully before the failure, they are not restored again.
If the BAR_RETRY configuration parameter is set to 2, ON-Bar automatically tries to restore any failed storage spaces and logical logs again. If the restore is successful, you do not need to restart the restore.
If the BAR_RETRY configuration parameter is set to 0 or 1, ON-Bar does not try to restore any failed storage spaces and logical logs again. If the database server is still running, ON-Bar skips the failed storage space and attempts to restore the remaining storage spaces. To complete the restore, run the onbar -RESTART command.
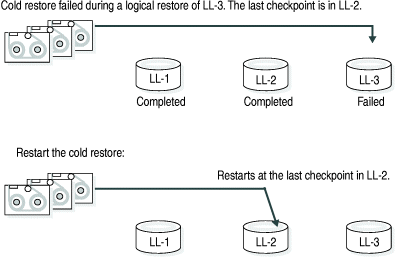
If a restore fails during the logical phase and you restart the restore, ON-Bar verifies that the storage spaces are restored, skips the physical restore, and restarts the logical restore. The following figure shows a cold restore that failed while restoring logical log LL-3. When you restart the cold logical restore, log replay starts from the last restored checkpoint. In this example, the last checkpoint is in logical log LL-2.