Creation of branch nodes
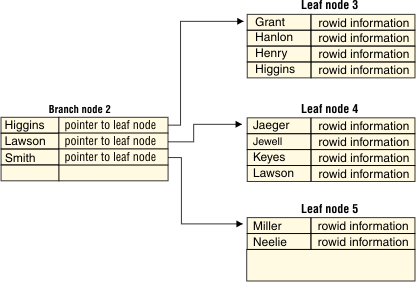
Eventually, as you add rows to the table, the database server fills the root node with node pointers to all the existing leaf nodes. When the database server splits yet another leaf node, and the root node has no room for an additional node pointer, the following process occurs.
The database server splits the root node and divides its contents among two newly created branch nodes. As index items are added, more and more leaf nodes are split, causing the database server to add more branch nodes. Eventually, the root node fills with pointers to these branch nodes. When this situation occurs, the database server splits the root node again. The database server then creates yet another branch level between the root node and the lower branch level. This process results in a four-level tree, with one root node, two branch levels, and one leaf level. The B-tree structure can continue to grow in this way to a maximum of 20 levels.