How Enterprise Replication Replicates Data
Before you can replicate data, you must declare a database server for replication and define the replicates (the data to replicate and the database servers that participate in replication). To declare a database server for replication, see Defining Replication Servers. To define replicates, see Define a replicate. Replication Examples, has simple examples of declaring replication servers and defining replicates.
After you define the servers and replicates, Enterprise Replication replicates data in three phases:
The following diagram shows these three phases of replication and the Enterprise Replication components that perform each task.
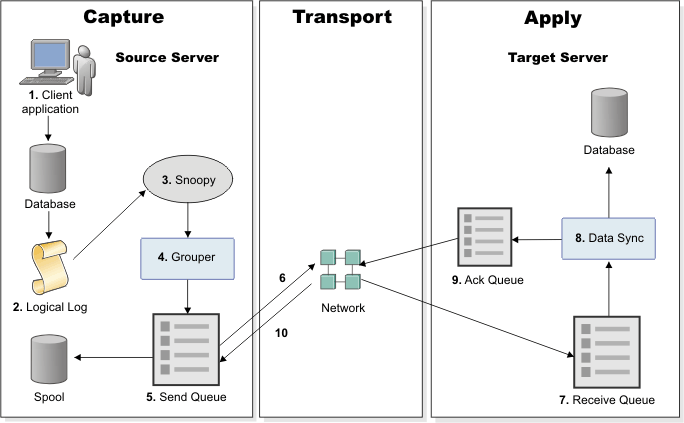
As shown in the diagram, the following process describes how Enterprise Replication replicates a transaction:
- A client application performs a transaction in a database that is defined as a replicate.
- The transaction is put into the logical log.
- The log capture component, also known as the snoopy component, reads the logical log and passes the log records onto the grouper component.
- The grouper component evaluates the log records for replication and groups them into a message that describe the operations that were in the original transaction.
- The grouper component places the message in the send queue. Under certain situations, the send queue spools messages to disk for temporary storage.
- The send queue transports the replication message across the Enterprise Replication network to the target server.
- The replication message is placed in the receive queue at the target server.
- The data sync component applies the transaction in the target database. If necessary, the data sync component performs conflict resolution.
- An acknowledgment that the message was successfully applied is placed in the acknowledgment queue.
- The acknowledgment message is sent back to the source server.