Creating a smart large object
About this task
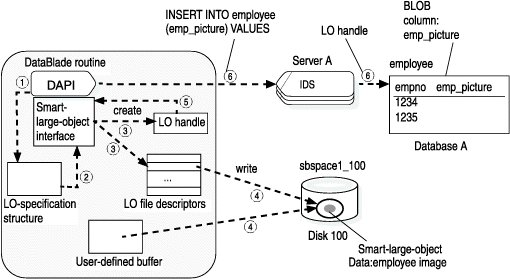
To create a smart large object and save its LO handle in the database, you need to take the following steps.
| Step | Task | Smart-large-object function | More information |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Obtain an LO-specification structure to hold the storage characteristics for the new smart large object. | mi_lo_spec_init(), mi_lo_stat_cspec() | Obtain the LO-specification structure |
| 2. | Ensure that the LO-specification structure contains the desired storage characteristics for the new smart large object. | System-specified storage characteristics: mi_lo_spec_init() Column-level storage characteristics: mi_lo_colinfo_by_name(), mi_lo_colinfo_by_ids() User-specified storage characteristics: Disk-storage information in the LO-specification structure, Access attributes |
Choosing storage characteristics |
| 3. | Create an LO handle for the new smart large object and open the smart large object. | mi_lo_create(), mi_lo_expand(), mi_lo_copy(), mi_lo_from_file() | Initialize an LO handle and an LO file descriptor |
| 4. | Write a specified number of bytes from a user-defined buffer to the open smart large object. | mi_lo_write(), mi_lo_writewithseek() | Write data to a smart large object |
| 5. | Pass the LO handle as the column value for an INSERT or UPDATE statement. | C Casting | Storing an LO handle |
| 6. | Execute an INSERT or UPDATE statement to save the LO handle of the smart large object in a database column. | mi_exec(), mi_exec_prepared_statement(), mi_value() | Storing an LO handle |
| 7. | Close the smart large object. | mi_lo_close() | Free a smart large object |
| 8. | Free resources. | mi_lo_spec_free(), mi_lo_release() | Free resources |
The following figure shows the first six of these steps
that a DataBlade®
API module
uses to insert the smart-large-object data into the emp_picture column
of the employee table (A smart large object in
a database column).Figure 1. Inserting into a BLOB column