Sbspace Structure
An sbspace is similar to a blobspace except that it holds smart large objects.
- Sbspace chunk descriptors
- Chunk free-page list
- An sbspace metadata area (up to one for each chunk)
- Reserved data areas (up to two for each chunk)
- User-data areas (up to two for each chunk)
For best performance, it is recommended that the metadata area be located in the middle of the sbspace. The database server automatically places the metadata area in the correct location. However, to specify the location of the metadata area, specify the -Mo flag in the onspaces command.
If you do not specify the size of the metadata area in the -Ms flag of the onspaces command, the database server uses the value of AVG_LO_SIZE (defaults to 8 kilobytes) to calculate the size of the metadata area. For more information, see Creating an Sbspace with the -Df option.
Normally, you can let the system calculate the metadata size for you. If you want to estimate the size of the metadata area, see the chapter on table performance considerations in the Informix® Performance Guide.
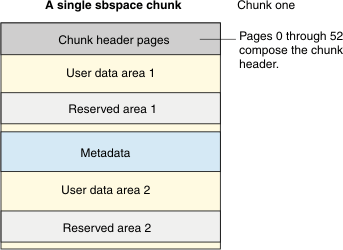
Because the chunk in A Single Sbspace Chunk is the first in the sbspace, it contains an sbspace descriptor. The chunk descriptor tblspace in chunk one contains information about chunk one and all chunks added to the sbspace thereafter.