Editing datasets
You can add, modify, remove, import, or export data from a dataset by using the CSV Editor. The working principle of the CSV Editor is similar to that of a spreadsheet.
Before you begin
About this task
In Test Performance 9.5.0 or later, you can use the CSV Editor to view and edit data in the dataset. You can also view the datasets in other editors by right-clicking the dataset and selecting the Open With option.
You can perform basic tasks in the CSV Editor by right-clicking any row, column, or cell of the dataset to organize your data in a better way. For example, updating the data in a cell, inserting or deleting rows and columns, or renaming column names.
-
Tab - To move the cursor control to the next available option.
-
Shift-Tab – To move the cursor control to the previous option.
-
Shift+F10 – To open the context menu from the dataset cell.
- Comma
- Semicolon
- Space
- Tab
- Other
Consider that you have the data in the CSV file in the following format:
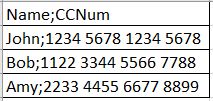
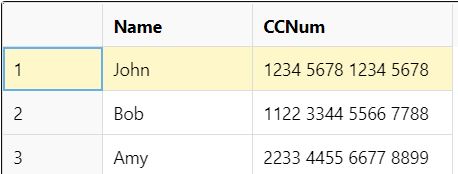
When you import the CSV file in the dataset, and then select the separator value as Semicolon, the data in the dataset is displayed as follows:
Procedure
-
Double-click the dataset that you want to edit in the Test
Navigator.
The dataset opens in the CSV Editor in a browser.
-
Perform the following actions to use the options available in the CSV Editor:
Options Actions Find and Replace 
To find: - Click the Find and Replace icon
 .
. - Enter the content that you want to search in the Find field.
- Select any or all the following options to find the search content more
effectively:
- Select the Case sensitive check box to search the content that is the exact letter case of the content entered in the Find field.
- Select the Match entire cell contents check box to search for cells that contain only the characters that you have entered in the Find field.
- Select the Search using regular expression
check box to search the pattern that matches strings.For example, to search a cell that contains any number between 0 to 9, do the following:
- Enter \d in the Find field.
- Select the Search using regular expression check box.
- Click Find.
- Click Find. If the text is found, the cell containing that text is selected.
- Click Find again to find further instances of the search text.
To find and replace:
- Click the Find and Replace icon
 .
. - Enter the content that you want to search in the Find field.
- Enter the content that you want to replace in the Replace field.
- Select any or all the following options to find and replace the content
more effectively:
- Select the Case sensitive check box to find the content that is the exact letter case of the content entered in the Find field.
- Select the Match entire cell contents check box to find and replace for cells that contain only the characters that you have entered in the Find and Replace fields.
- Select the Search using regular expression check box to find and replace the pattern that matches strings.
- Click Replace to replace the individual instances.
- Click Replace All to replace every instance of the content throughout the dataset.
Undo 
- Click the Undo icon
 .
. - Select the recent changes from the list that you want to undo, and then click the list.
The Undo option undoes anything you do in the dataset. The CSV Editor saves the unlimited undo-able action. You can perform the undo action even after you save your changes made to the dataset.
Redo 
- Click the Redo icon
 .
. - Select the recent changes from the list that you want to redo, and then click the list.
The CSV Editor saves the unlimited redo action.
Import 
- Click the Import icon
 .
. - Click Choose File and select the CSV file that you
want to import in the Import File dialog.Note: If the CSV file contains test data with Unicode characters in it, you must save the CSV file in UTF-8 format. You can then choose the CSV file and import the test data from the CSV file into the dataset.
- Optional. Click Overwrite to add the rows and columns from the selected CSV file from the beginning of the dataset.
- Optional. Click Append to add rows and columns from the selected CSV file to the end of the dataset.
- Optional. Select the First row contains headers check box if your CSV file contains the header.
Export 
Click the Export icon  to download the dataset as a CSV file.
to download the dataset as a CSV file. Set as current row Right-click any cell in a row and select Set as current row. When rows are deleted:
If you delete any row between row 1 to current row, the current row data is taken from the next row.
For example, when you set the current row as 6, and then you delete any row between row 1 to row 6, the current row remains at row 6, but the content of row 7 is moved to row 6.
When rows are inserted:
If you insert any new row between row 1 to the current row, the current row data is taken from the previous row.
For example, when you set the current row as 6, and then you insert any row between row 1 to row 6, the current row remains at row 6, but the content of row 5 is moved to row 6.
Dataset configuration settings 
In the Configure Dataset window, you can set the separator value, change the row and column settings, and configure the string values in the dataset. -
Click the Menu icon
 , and then select the Configure option.
, and then select the Configure option. -
Select any of the separator values that you used in the CSV file.
The available options are Comma, Semicolon, Space, Tab, and Other. In the CSV file, if you have any other separator characters other than the available options, then you can select the Other option, and then can specify a value.
For example, if the data in the CSV file is separated by a character #, then select the Other option and enter # in the field.
-
Configure the following options to change the row and column settings:
-
Column header - Use an up-down control button to increment or decrement the value of the column header.
-
Data start point - Use an up-down control button to increment or decrement the value of the data starting pointer.
-
Current row - Use an up-down control button to increment or decrement the value of the current row.
-
-
Configure the following options to change the string values in the dataset:
-
Treat as null - Enter a string value that is to be treated as null when running the test.
-
Treat as empty - Enter a string value that is to be treated as empty when running the test.
For example, when you run the test and the data 123 in the dataset to be treated as empty, then you can specify 123 in the Treat as empty field.
-
Treat empty text as null - Select this field when you want the dataset that contains any blank cells, and the value of those blank cells to be interpreted as null.
-
-
Click Update to apply the changes.
Discard 
Click the Menu icon  , and then select Discard to discard the changes
made to the dataset.
, and then select Discard to discard the changes
made to the dataset. - Click the Find and Replace icon
-
Click the Save icon
 to save the changes made to the dataset.
to save the changes made to the dataset.