IBM Processor value unit (PVU)
A processor value unit (PVU) is a unit of measurement that is used to determine the licensing cost of BigFix middleware products. It is based on the type of processor that is deployed on the server where the software is installed. For each product, you must acquire the appropriate number of PVUs that is defined for the specific processor on which the software is installed.
The number of required PVUs is based on the processor technology and the number of processors that are available to the software product. For PVU-based licensing, IBM defines a processor as a processor core on a chip. For example, a dual-core processor chip has two processor cores. PVUs are assigned per core, not per processor. The number of PVUs that are assigned to a processor core is defined in the PVU table format. For more information, refer to Processor Value Unit [PVU] licensing for Distributed Software.
Processor value unit license types
PVU licensing can be full capacity or subcapacity. Full capacity licensing is based on the overall number of processor cores on the physical server on which the product is installed. Subcapacity licensing is available only in virtualized environments. It is counted as the highest number of PVUs that are available for the VM on which the product is installed, not the total PVU count on the physical server. You acquire licenses for the lower value: subcapacity or full capacity.
Subcapacity licensing can significantly reduce the licensing cost, especially with a move to a newer processor core technology. However, virtual machines or partitions that restrict the available processor capacity must be created by using eligible virtualization technologies. For more information about subcapacity licensing requirements, see: Passport Advantage® Virtualization Capacity (Subcapacity) Licensing.
For information about rules of subcapacity counting on each virtualization type, see: IBM Virtualization Capacity License Counting Rules.
Scenarios
- Scenario 1: Full capacity on a physical server
- IBM MQ software is installed on a server that has two Intel Xeon 3400 processors, each processor
with eight cores (16 cores in total).
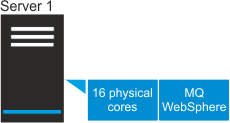
Because the environment is not virtualized, subcapacity license does not apply. Full capacity license is counted as the highest number of PVUs on the server where the software is installed. According to the PVU table, when the server has two sockets, this processor model is assigned 70 PVUs per core. The following table shows how the cost of full capacity license is calculated for IBM MQ software that is installed on this server.
Table 1. Cost of full capacity license for IBM MQ software The table consists of two columns and five rows.
Description Full capacity Cores to license 16 PVU per core 70 Software cost per PVU $50 License cost 16 * 70 * $50 = $56,000
- Scenario 2: Subcapacity on two virtual machines
- Two virtual machines are deployed on a server that has two Intel Xeon 3400 processors, each
processor with eight cores (16 cores in total). Each VM is assigned eight virtual cores. WebSphere
software is installed only on the first virtual machine and has access to eight cores. IBM MQ
software is installed on both virtual machines and thus has access to 16 cores.
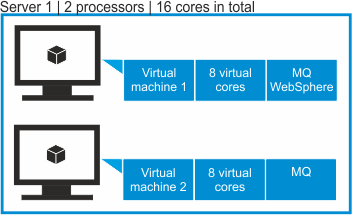
According to the PVU table, when the server has two sockets, this processor model is assigned 70 PVUs per core. The following table shows how the cost of full capacity license and subcapacity license is calculated for IBM MQ software and WebSphere software that is installed on this server.
Table 2. Cost of full capacity and subcapacity license for IBM MQ software and WebSphere software The table consists of two columns and five rows.
Description Full capacity for IBM MQ and WebSphere software Subcapacity for IBM MQ software Subcapacity for WebSphere software Cores to license 16 16 8 PVU per core 70 70 70 Software cost per PVU $50 $50 $50 License cost 16 * 70 * $50 = $56,000 16 * 70* $50 = $56,000 8 * 70 * $50 = $28,000
- Scenario 3: Capacity in a virtual environment where connection to the VM manager is not configured
- Important: In this scenario, default PVU counting is applied due to the lack of connection to the VM manager. IBM accepts audit reports that contain PVU values calculated based on the default PVU counting instead of considering the client to be ineligible for subcapacity or liable for full capacity. For more information, see: Default PVU counting on x86 processors and Managing VM managers.Two virtual machines are deployed on a server that has two Intel Xeon 3400 processors, each with eight cores (16 cores in total). The first VM is assigned 12 virtual cores. The second VM is assigned 10 virtual cores. IBM MQ software is installed on both VMs.
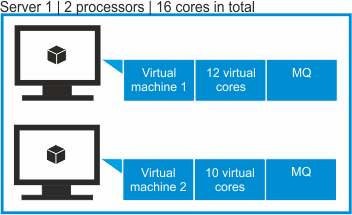
If a virtual machine manager is not defined, BigFix Inventory does not have access to information about the number of sockets and physical cores on the server on which the VMs are deployed. It has access only to information about the processor model and the number of virtual cores that each virtual machine is assigned. The sum of virtual cores to which IBM MQ software has access is greater than the number of physical cores that are available on the server.Tip: If the hypervisor data is missing from a virtual machine and default PVU counting is applied, ID of the server on which the machine runs begins withTLM_VM.The number of PVUs per core that is assigned to a processor depends on the number of sockets on the host. Because BigFix Inventory does not have access to this information, it assigns the highest PVU per core value that is defined for the particular processor in the PVU table. According to the PVU table, when the server has two sockets, this processor model is assigned 70 PVUs per core. However, due to the lack of information about the number of sockets, software is charged 120 PVUs per core. It is the highest number of PVUs that is defined in the PVU table for this type of processor.
The following table shows the cost of license for the IBM MQ software depending on whether the VM manager is defined.Table 3. Cost of license for IBM MQ software depending on whether the VM manager is defined The table consists of two columns and five rows.
Description Capacity for IBM MQ software when the VM manager is defined Capacity for IBM MQ software when VM manager is not defined Full capacity Subcapacity Cores to license 16 22 capped to 16 22 PVU per core 70 70 120 Software cost per PVU $50 $50 $50 License cost 16 * 70 * $50 = $56,000 16 * 70 * $50 = $56,000 22 * 120 * $50 = $132,000