Fix groups
Fix groups currently apply only to issues found in static analysis scans.
Fix groups are a new approach to managing, triaging and solving issues found during static analysis scan. Once you have run a static scan, AppScan 360° organizes the issues found into fix groups based on vulnerability type and the required remediation task. In every new static scan, new issues are added to these groups, and new groups are created as needed.
- Common Fix Point
- Contains issues that share the same vulnerability. The entire group can be remedied by a single fix (one code point).
- Common API
- Contains issues that are related to the same API call. A common API group puts findings with the same root cause together if they cannot fit into a common fix point group. This lessens the context switching when reviewing results and applying the fix. In general, the fix is similar for each of the affected findings; the same fix can be applied to all issues in the group.
- Common Open Source
- Contains issues identified in third-party code, based on the library in which they were found. For each vulnerable library identified in the application, a fix group is created. Each fix group can have one or multiple vulnerabilities depending on how many vulnerabilities were found in the specific library. The same fix can be applied to all issues in the group.
Issues in any group always share the same vulnerability type.
Fix Group Severity
Fix Group Severity is determined by the highest severity of all the issues it contains.
Fix Group Status
Fix Group Status is assigned only when all issues in the group have the same status.
When changing the status of all issues in a group, you can select whether or not to apply the status to issues added to group from future scans. If the status is not applied to future issues, the group's status will change to Mixed when new issues are added.
Tutorial
Examples
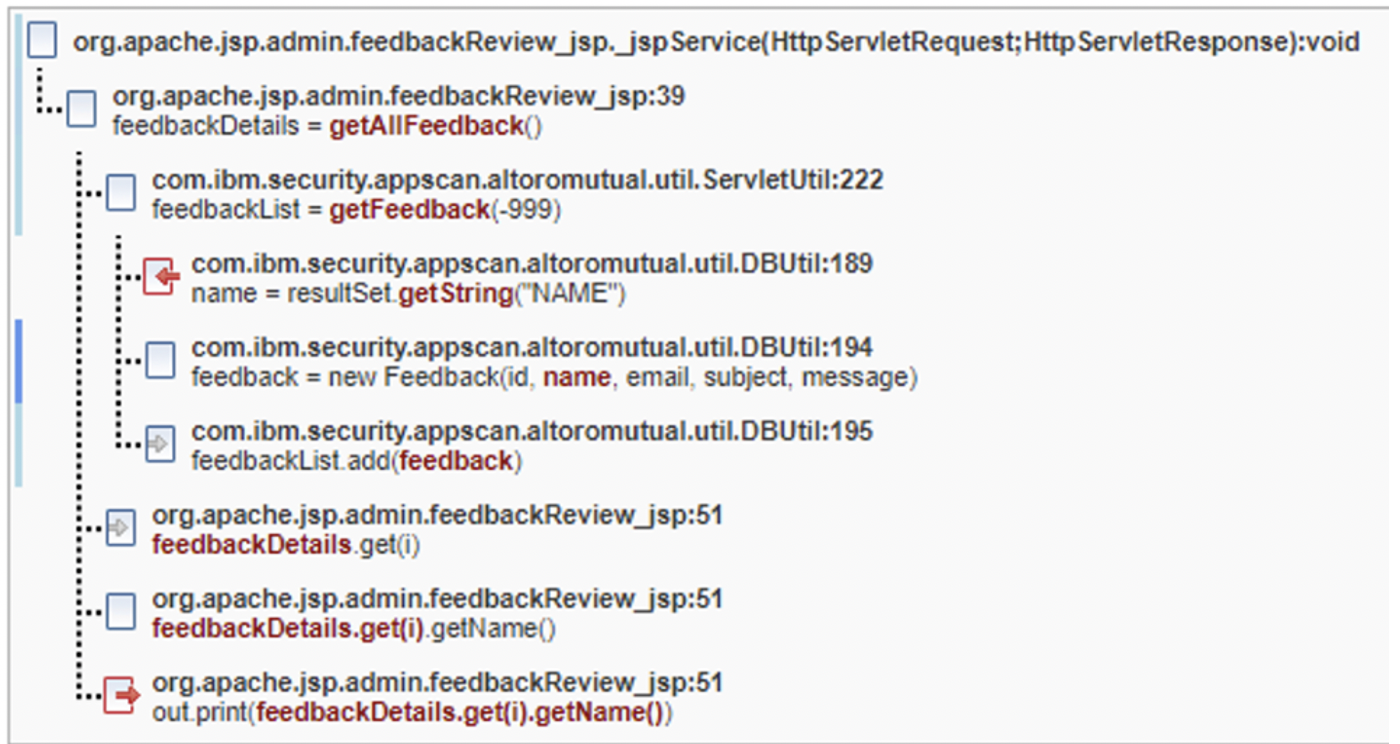
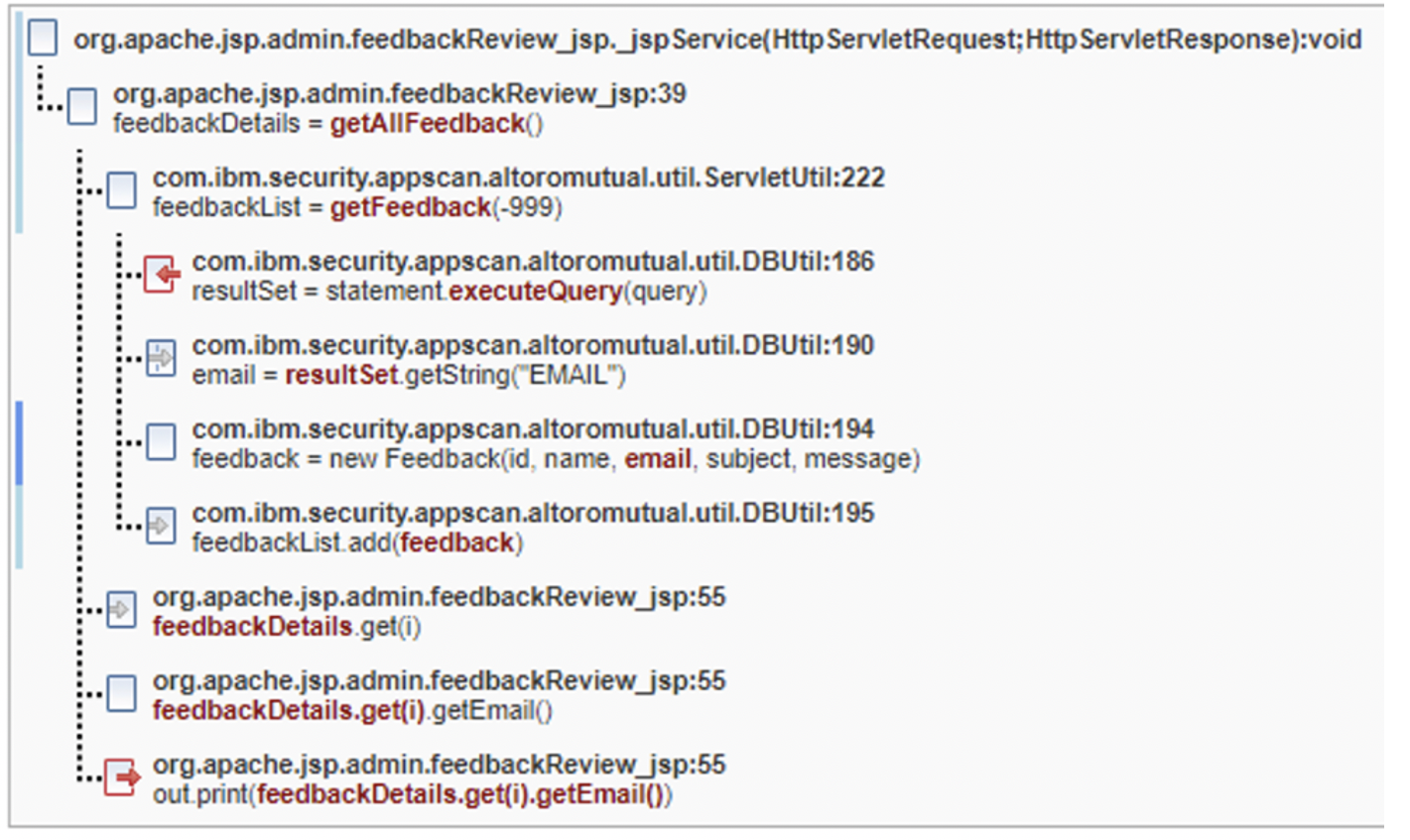
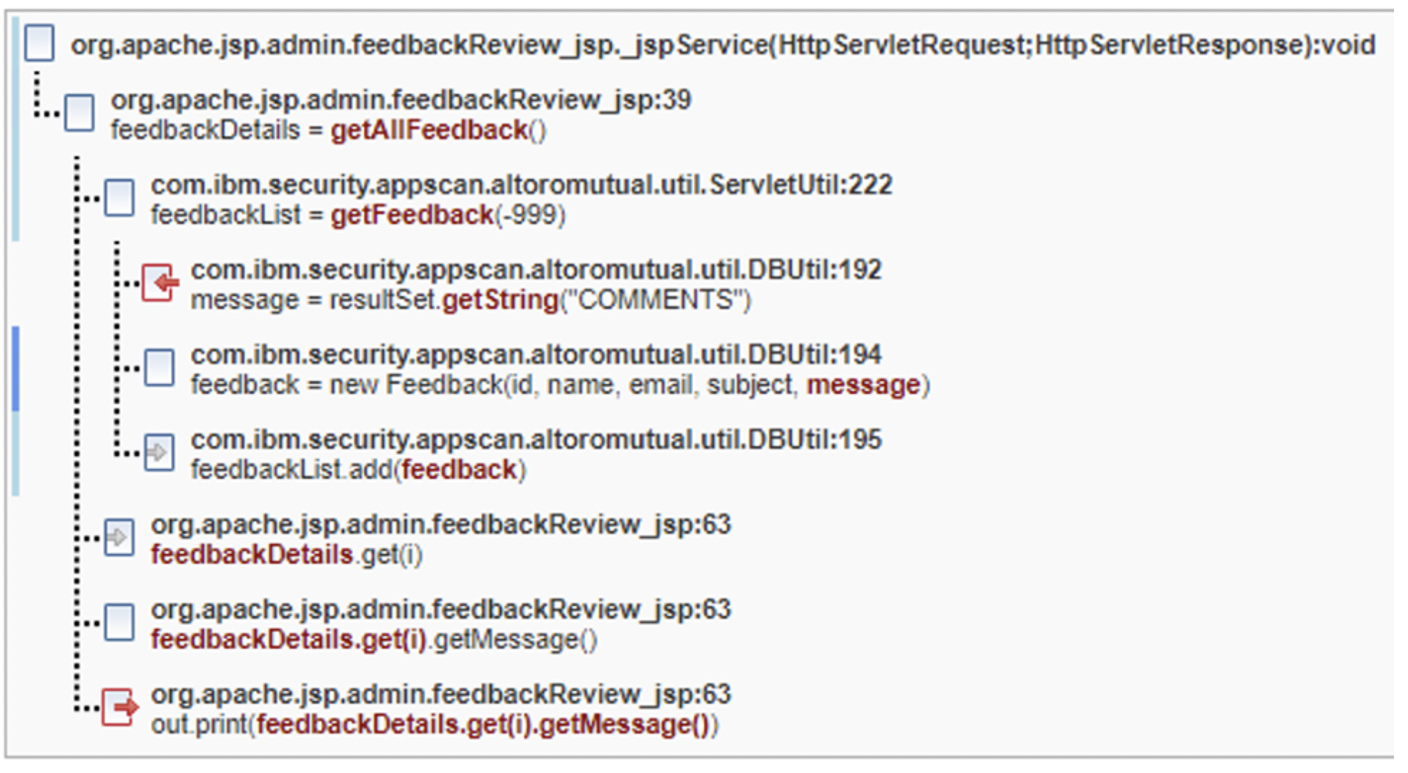
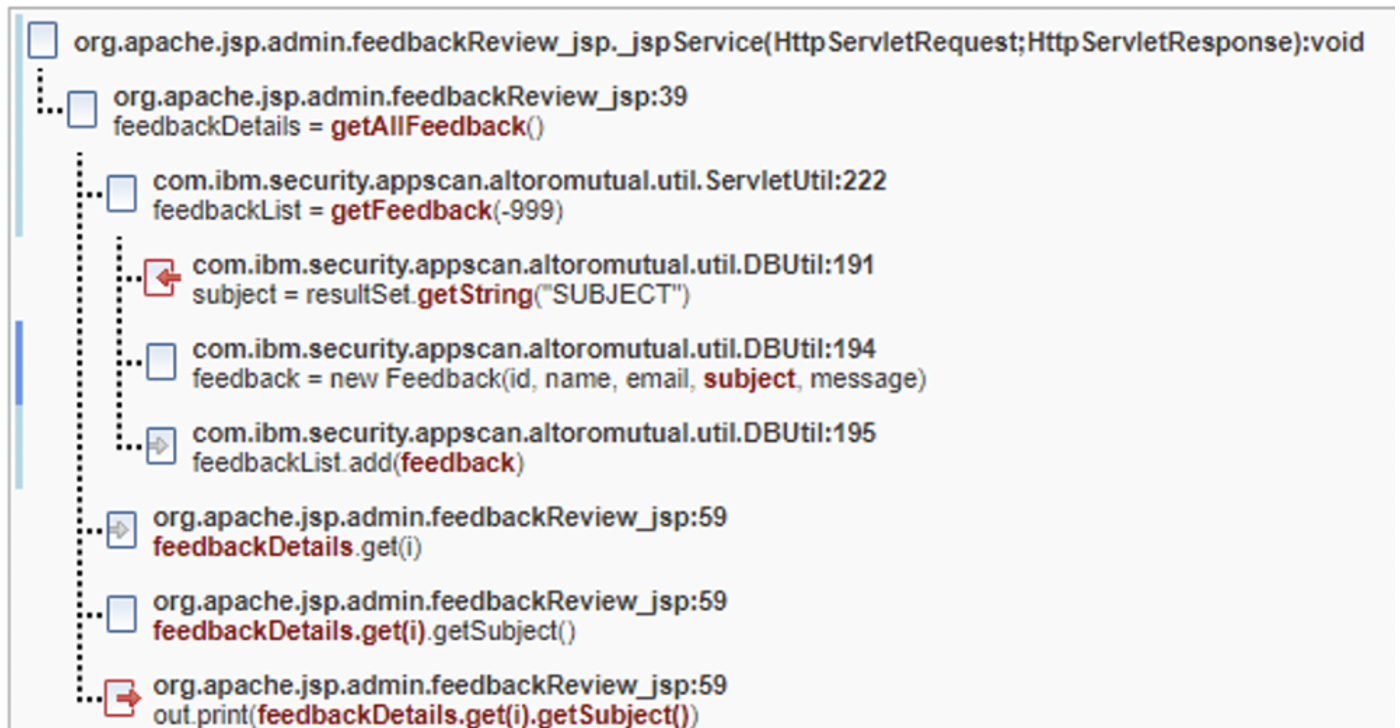
Common Fix Point fix group
In the following images, there are five parameters (id,
name, email, subject,
message) that eventually make it into a fix point new
Feedback in DBUtil.java on line 194. While
id is an int and not an attackable vector for
cross-site scripting, the other four are attackable and must be remediated.
The Trace tells us that five different symptoms are present
and make it onto the browser page as a result of the out.print
calls that appear on different lines. If the new Feedback call did
allowlisting of allowable characters or some kind of sanitation/validation of the
data for those five entities inside the constructor, then all findings in the fix
group would then be resolved. If the fix group fix point is ignored, then four
different encoding calls need to be added for each of these findings.
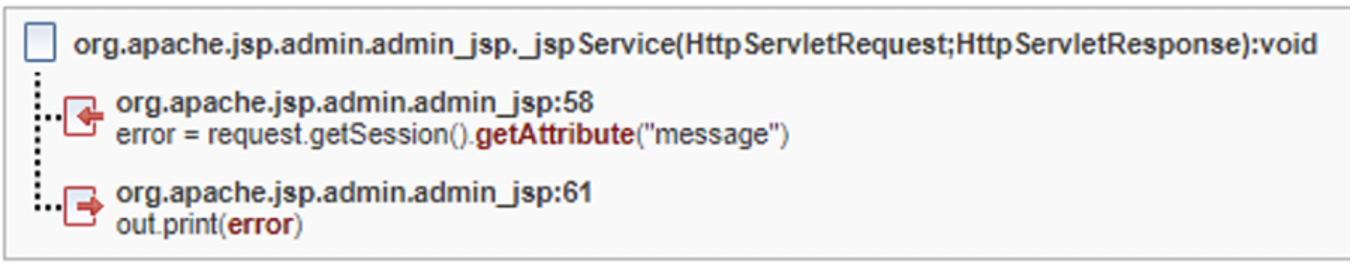
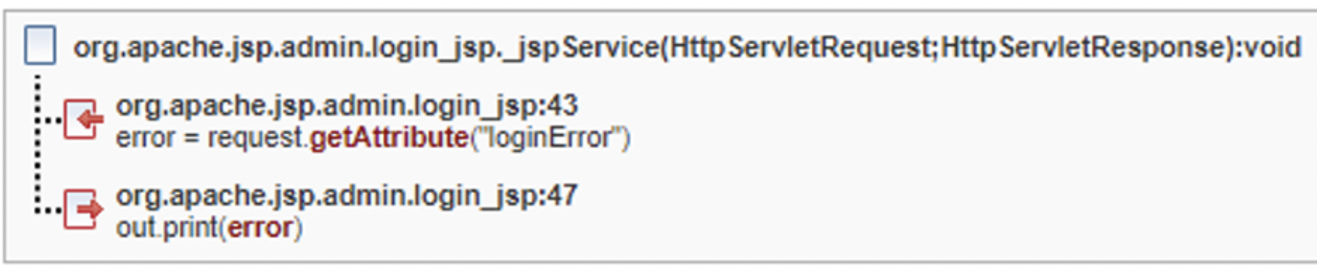
Common API fix group
In this example there have two findings with the same root cause (no escaping for input string). They each need to be resolved separately, however the fix is similar, or in this case, identical for both instances.
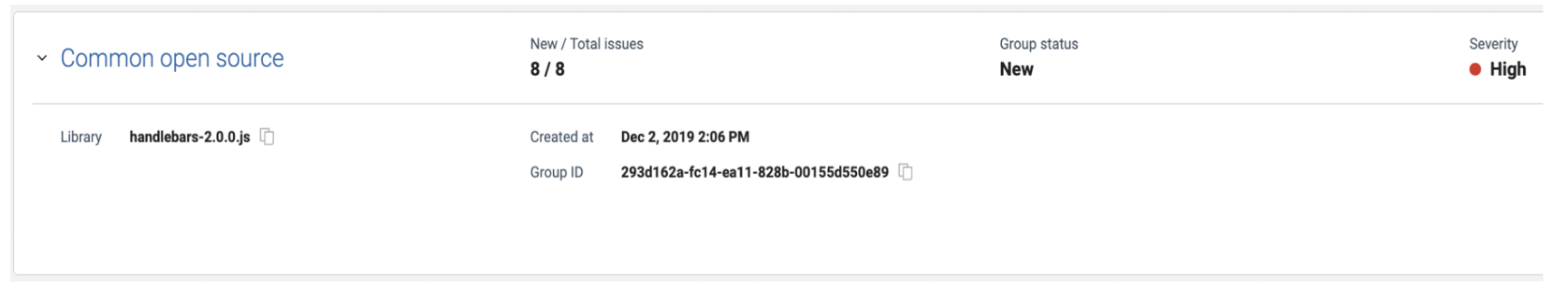
Common Open Source fix group
In this example, the library was found to have eight different vulnerabilities. As such, a fix group was created to show all the vulnerabilities for this library and thus speed up the process of reviewing each vulnerability associated with the library.