WebSphere Commerce AJAX framework
The WebSphere Commerce AJAX framework is an extension of the Dojo AJAX and events API. It provides an easy to use framework that meets most AJAX requirements for storefront development, and hides some of the complexity and repetitive code that a storefront developer often encounters.
There are four common scenarios involved with the WebSphere Commerce AJAX framework:
- An AJAX call is made to the WebSphere Commerce server to update a business object. Sections of the page are refreshed with new content if the update is successful. The new content is retrieved using subsequent AJAX calls to the WebSphere Commerce server.
- An AJAX call is made to refresh a section of the page because of certain customer interactions.
- An AJAX call is made to the WebSphere Commerce server to update a business object. Sections of
the page should refresh with new content if the update is successful. The new content is retrieved
using subsequent AJAX calls to the WebSphere Commerce server. This is a repeat of the first
scenario, however, instead of making the code modular, a less traffic intensive approach to the
server is wanted.
In this scenario, an AJAX call is made to the WebSphere Commerce server to update a business object. Sections of the page are refreshed with new content if the update is successful. All the relevant information to refresh the contents of the page are returned as a JSON object. The client then has the contents of the JSON object and uses the DOM manipulation API to modify all the areas of the page that should change as a result of the successful update.
- An AJAX call is made to the WebSphere Commerce server requesting JSON data. Sections of the page are then updated using JavaScript and the DOM manipulation API.
The WebSphere Commerce AJAX framework is not required for the third and fourth scenarios, as these scenarios can be performed directly using the Dojo AJAX API.
You can make concurrent Ajax calls for views.
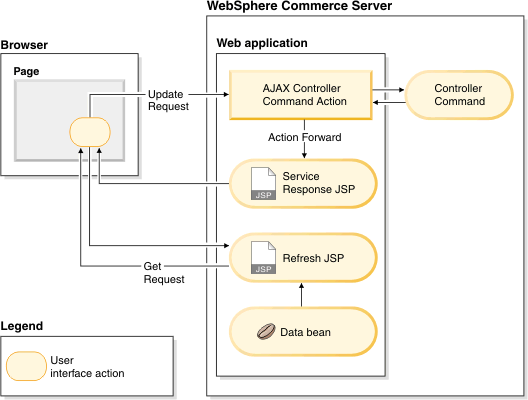
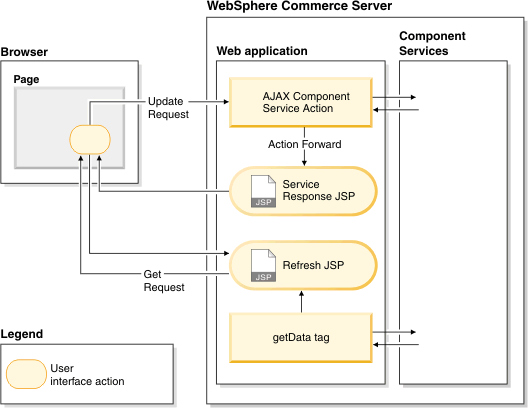
Scenario 1: Updating a business object in WebSphere Commerce using AJAX, then refreshing multiple areas using subsequent AJAX requests to get the refresh contents
- An AJAX call is made to a WebSphere Commerce controller command or WebSphere Commerce service to update a business object (or multiple business objects).
- Subsequent AJAX get requests are made to WebSphere Commerce views to retrieve the new HTML contents for each area if the update is successful.
Interaction diagram when calling WebSphere Commerce controller commands:
Interaction diagram when calling WebSphere Commerce services:
1. Making an AJAX call to a WebSphere Commerce controller command or service
Before the client is able to call a WebSphere Commerce controller command or service using AJAX, the WebSphere Commerce server must define that the controller command or service can be called using AJAX (rather than the traditional programming model where the request is made and a new redirect is implied by the WebSphere Commerce runtime).
To define a controller command or service to be available for AJAX type requests, simply define a new struts-action entry in the struts-config XML file that identifies the controller command or service as an AJAX type of action. For example, to create a new struts-action for the InterestItemAdd controller command that can be called using AJAX, it must be defined it in the struts configuration XML file:
<action
parameter="com.ibm.commerce.interestitems.commands.InterestItemAddCmd"
path="/AjaxInterestItemAdd"
type="com.ibm.commerce.struts.AjaxAction">
<set-property property="authenticate" value="0:0"/>
<set-property property="https" value="0:1"/>
</action>
<action
parameter="order.addOrderItem"
path="/AjaxOrderChangeServiceItemAdd" type="com.ibm.commerce.struts.AjaxComponentServiceAction">
<set-property property="authenticate" value="0:0"/>
<set-property property="https" value="0:1"/>
</action>
- WC_eardir/Stores.war/AjaxActionResponse.jsp (success case)
- WC_eardir/Stores.war/AjaxActionErrorResponse.jsp (failure case)
 WCDE_installdir/workspace/Stores/WebContent/AjaxActionResponse.jsp
WCDE_installdir/workspace/Stores/WebContent/AjaxActionResponse.jsp WCDE_installdir/workspace/Stores/WebContent/AjaxActionErrorResponse.jsp
WCDE_installdir/workspace/Stores/WebContent/AjaxActionErrorResponse.jsp
wc.service.declare({
id: "AjaxInterestItemAdd",
actionId: " AjaxInterestItemAdd",
url: " AjaxInterestItemAdd",
formId: "",
successHandler: function(serviceResponse) {
alert("success");
},
failureHandler: function(serviceResponse) {
if (serviceResponse.errorMessage) {
alert(serviceResponse.errorMessage);
}
}
});
wc.service.invoke("AjaxInterestItemAdd");
2. Making AJAX calls to WebSphere Commerce views to get refresh contents
<div dojoType="wc.widget.RefreshArea"
id="MiniShoppingCart"
widgetId="MiniShoppingCart"
controllerId="MiniShoppingCartController">
</div>
wc.render.declareRefreshController({
id: "MiniShoppingCartController",
renderContext: wc.render.getContextById("MiniShoppingCartContext"),
url: "MiniShoppingCartView",
formId: "",
modelChangedHandler: function(message, widget) {
if(message.actionId in order_updated){
widget.refresh();
}
},
renderContextChangedHandler: function(message, widget) {
},
postRefreshHandler: function(widget) {
}
});
Scenario 2: Refreshing an area of the page using an AJAX request to get the refresh contents
Areas of the page should refresh with new content when users interact with the user interface. This scenario uses the render context, refresh area and refresh controllers API from the WebSphere Commerce AJAX framework.
A render context object keeps track of context information of the client and it can trigger renderContextChanged events whenever updates occur to any of the properties in the render context object. The refresh controllers are automatically registered to listen to all the renderContextChanged events. The refresh controller logic determines if the context change should trigger an update of a refresh area widget. Therefore, in the refresh controller's renderContextChangedHandler, the API is used to compare the context properties testForChangedRC to determine if the context property has changed and then trigger the refresh of the refresh area.
<div dojoType="wc.widget.RefreshArea"
widgetId="OrderItemPagingDisplay"
id="OrderItemPagingDisplay"
controllerId="OrderItemPaginationDisplayController"
role="wairole:region" waistate:live="polite" waistate:atomic="false" waistate:relevant="all">
<%out.flush();%>
<c:import url="${jspStoreDir}ShoppingArea/CheckoutSection/SingleShipment/OrderItemDetailSummary.jsp">
<c:param name="catalogId" value="${WCParam.catalogId}" />
<c:param name="langId" value="${WCParam.langId}" />
<c:param name="storeId" value="${WCParam.storeId}" />
<c:param name="orderPage" value="summary" />
</c:import>
<%out.flush();%>
</div>Scenario 3: Updating a business object in WebSphere Commerce using AJAX and returning all relevant update information using JSON
var parameters = {};
parameters.storeId = storeId;
parameters.langId=langId;
parameters.catalogId=catalogId;
parameters.catentryId=productId;
parameters.URL="MiniCartContentsJSON";
parameters.errorViewName="MiniCartContentsJSON";
dojo.xhrPost({
url: "OrderChangeServiceItemAdd",
handleAs: "json-comment-filtered",
content: parameters,
service: this,
load: refreshMiniCart,
error: function(errObj,ioArgs) {
alert("error");
}
});
The load function uses the JSON object and DOM manipulation API to replace all the elements in the page that should be updated with new data that resulted from the server update. URLs do not need to be registered as AjaxAction, as this scenario does not make use of any of the new WebSphere Commerce AJAX framework.
Scenario 4: Calling WebSphere Commerce server using AJAX to gather new data as a JSON object and refreshing the page contents
This scenario can be achieved using the Dojo API directly. Therefore, there is no need to use the WebSphere Commerce AJAX framework if this scenario is of relevant interest. The dojo.xhrPost API is used in conjunction with the traditional WebSphere Commerce runtime programming model, where a request is made to a view that maps to a JSP file that creates a JSON object. On the load function of the xhrPost API, the DOM manipulation API is used to put the JSON contents in the web page elements.